Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 7684-7701Panchan, N., Wattanapan, P., Sungsinchai, S., Roddecha, S., Dittanet, P., Seubsai, A., Niamnuy, C., and Devahastin, S. (2021). "Optimization of synthesis conditions for carboxymethyl cellulose from pineapple leaf waste using microwave-assisted heating and its application as a food thickener," BioResources 16(4), 7684-7701.AbstractArticlePDF

Pineapple leaf waste, with its high cellulose content, can serve as alternative starting material for the production of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC). In this study, synthesis conditions of CMC from pineapple leaves via the use of microwave heating were optimized. Box-Behnken design and response surface methodology were applied to schedule the experiments and to optimize the synthesis condition, respectively. Preparation of CMC was investigated by varying three factors, namely, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) concentration, monochloroacetic acid (MCA) dose, and etherification time. The process of carboxymethylation was optimized to produce CMC with high degree of substitution (DS). Optimal condition for CMC synthesis was noted to be 50% (w/v) NaOH solution, 8 g of MCA/g cellulose, and etherification time of 16 min; such optimal condition resulted in the maximum DS of 0.78. Synthesized CMC was utilized as a thickener for liquid foods (water, orange juice, milk, and mushroom cream soup) where 2% (w/v) as-synthesized CMC increased the viscosity of the foods and changed their characteristics from thin to nectar-like liquids.
- Researchpp 7702-7715Alishiri, M., Hemmasi, A. H., Khademi Eslam, H. K., Basirjafari, S., and Talaeiypour, M. (2021). "Evaluation and comparison the properties of acoustic boards made of date palm fiber," BioResources 16(4) 7702-7715.AbstractArticlePDF
Applying acoustic panels made of natural fibers, due to their high biodegradable characteristics, light weight, low density, cheap price and non-toxicity, are proper alternatives to acoustic absorbers made of synthetic fibers. Considering their stance and vast applicability in industry, the possibility of producing them of natural palm fibers with sodium silicate adhesive of 10 and 20% in two 16 and 32 mm thicknesses, 350 and 450 kg/m3 densities, 50 and 100 mm particles length (strands), as variable factors in 16 types of matched panels with 3 repetitions is proposed in this article. The palm-trunk discs constituted the control sample. The effect of variables on sound absorption coefficient was assessed. The effect of variable thickness and adhesive percentage on all frequencies was significant and the effect of density variable on all frequencies except 250 and 2000 Hz was also significant. The effect of particle length was significant except at the 500 Hz frequency. The effects of all variables on porosity were significant. The results of this study suggest that by applying date palm-trunk (an agricultural waste) combined with sodium silicate adhesive, industrial environment-friendly panels can be produced with proper sound absorption coefficient in the field of acoustics. This 32-mm-thick panel was composed of 80% date palm-trunk particles of 50 mm length, 450 kg/m3 density, and 20% sodium silicate adhesive.
- Researchpp 7716-7728Lee, M., Kang, D., and Seo, Y. (2021). "Development of post hybrid calcium carbonate for high loaded paper," BioResources 16(4), 7716-7728.AbstractArticlePDF
In papermaking, pre-flocculation of fillers such as ground calcium carbonate (GCC) improves the tensile strength of paper sheets. However, the pre-flocculated fillers mostly suffer from the instability of the floc shape such as the decrease in floc diameter with time elapse after preparation and no improvement of bulk and stiffness. The addition of calcium compounds such as calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide to the pre-flocculated GCC, and injection with carbon dioxide caused pre-flocculated GCC flocs to be covered with newly formed calcium carbonate. This product, called post hybrid calcium carbonate (pHCC), was found to be more stable in size and gave better sheet strength than the pre-flocculated ones. Furthermore, pHCC gave remarkably higher bulk and stiffness than the pre-flocculated flocs did without impairing smoothness that was essential in printing paper. The proper use of pHCC in papermaking could allow the production of high loaded paper with more than 10% higher filler contents, which could reduce paper production cost and save drying energy. The proportion of the newly formed calcium carbonate in pHCC, turbulence intensity at preparation stage, and the effect of storage time were investigated.
- Researchpp 7729-7750Kamaruddin, Z. H., Jumaidin, R., Rushdan, A. I., Selamat, M. Z., and Hanim Alamjuri, R. (2021). "Characterization of natural cellulosic fiber isolated from Malaysian Cymbopogan citratus leaves," BioResources 16(4), 7729-7750.AbstractArticlePDF
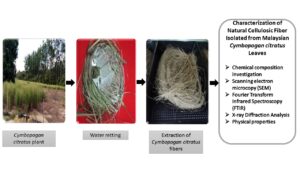
A novel natural fiber derived from the Cymbopogan citratus plant was investigated for the first time. The characterization of the C. citratus fibers was conducted, and the chemical composition and physical, thermal, mechanical, crystallinity, and morphological characteristics were studied. The chemical composition analysis of Cymbopogan citratus fiber revealed that the suggested fiber was rich in cellulose contents (37.6%). The tensile test of C. citratus fiber demonstrated the fiber’s average tensile strength of 43.81 ± 15.27 MPa and modulus of elasticity of 1.046 ± 0.33 GPa. Further analysis with X-ray diffraction (XRD) confirmed that the crystallinity index of Cymbopogan citratus fiber was 35.2%, and the crystalline size was estimated as 4.28 nm. The Cymbopogan citratus fiber’s thermal stability was investigated via thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and observed to be thermally stable (230 °C). A morphological investigation was employed on the fiber via a scanning electron microscope (SEM). The morphological study result exhibited that the fiber had a perforated and rough surface with the lumen in the center. Thus, the findings revealed that the Cymbopogan citratus fiber was a promising potential reinforcement for thermoplastic green composite applications.
- Researchpp 7751-7766Vititnev, A., Chistova, N., Alashkevich, Y., Matygulina, V., and Marchenko, R. (2021). "Optimization of wood fibre refining process in fibreboard production with new refiner disc working surface geometry," BioResources 16(4), 7751-7766.AbstractArticlePDF
Refining of fibrous semi-finished products is an important stage in fibreboard production because the efficiency of this stage affects the resulting fibres’ dimensional and qualitative characteristics. These, in turn, determine the physical and mechanical properties of the finished products, as well as the energy intensity of the process. The efficiency of this process depends on the raw materials used and the geometry of the refiner disc working surface and its operational modes. This article presents the results of the optimisation of wood fibre refining at a low concentration (2 to 4%), using fundamentally new refiner discs in high-density fibreboard production. Based on numerous theoretical and experimental studies, and on the results of processing, the problem of optimising the refining process was solved, taking into account the use of new refiner disc geometry. As a result, the optimal values of refiner process parameters and operation modes making it possible to prepare wood-fibre semi-finished products efficiently while reducing power consumption in refining were established. After optimising the refining process, the new geometry of refiner disc working surfaces provides optimal dimensional and qualitative characteristics of wood fibres, which results in finished products with high physical and mechanical properties in accordance with GOST 4598 (2018) without using bonding resins.
- Researchpp 7767-7783Tawfeek, M. E., Ali, H. M., Akrami, M., and Salem, M. Z. M. (2021). "Potential insecticidal activity of four essential oils against the rice weevil, Sitophilus oryzae (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae)," BioResources 16(4), 7767-7783.AbstractArticlePDF
Oils extracted from Cymbopogon citratus, Lantana camara, Artemisia camphorata, and Imperata cylindrica plants were used as potential insecticides against the rice weevil, Sitophilus oryzae (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). The phytochemical composition of the isolated oils was identified by gas chromatograph-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Oil contact toxicities were evaluated against the adults of S. oryzae. The activities of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and transaminases enzymes (AST) were measured. L. camara oil (LC50 = 9.81 mg/cm2) demonstrated the highest effect, followed by C. citratus oil (LC50 = 10.89 mg/cm2), A. camphorata EO (LC50 = 16.12 mg/cm2), and I. cylindrica oil (LC50= 36.85 mg/cm2) against the adults of S. oryzae. The inhibition percentages of AChE were 38.8, 41.7, 35.0, and 27.2%; ALP were 42.4, 49.3, 28.1, and 18.7%; AST were 33.9, 38.7, 20.8, and 11.8%; and ALT were 22.7, 30.5, 14.6, and 9.6% after treated S. oryzae with oils from C. citratus, L. camara, A. camphorata and I. cylindrica, respectively. The highest abundant compounds in C. citratus were geranial (25.95%), nerylacetal (8.85%), and neral (8.45%), in L. camara were caryophyllene (12.2%), and 3-elemene (8.89%), in A. camphorata were germacrene D-4-ol (20.83%), and borneol (19.47%), and in I. cylindrica were 5-phenylundecane (10.68%), and 6-phenyldodecane (8.70%).
- Researchpp 7784-7798Chen, A., Liang, Y., Jiang, Z., and Sun, J. (2021). "Prediction of elastic modulus and mid-span deflection of bamboo-wood composite laminates," BioResources 16(4), 7784-7798.AbstractArticlePDF

To better guide the manufacturing of bamboo-wood composite laminates, classical theory, first-order shear theory, and finite element method were used to predict the elastic modulus and deflection of bamboo-wood composite laminates. The influence of the adhesive layer on the elastic modulus and deflection of composite materials was considered. The effect of transverse shear on the mechanical properties of materials became smaller and smaller with an increasing span-to-height ratio. The effects of the adhesive layer on the elastic modulus and deflection were ± 0.5% and -0.1% to 0.3%, respectively. The transverse elastic modulus and mid-span deflection predicted by the three methods were quite different from the experimental results. When the span-to-height ratio was equal to 20, the prediction error of longitudinal elastic modulus by the three methods was less than 6%, which can be used to predict the elastic modulus of composite materials. The results provide a novel method to predict the properties of bamboo-wood composite laminates.
- Researchpp 7799-7816Potkany, M., Škultétyová, M., Schmidtová, J., and Hajdúchová, I. (2021). "Customer preferences for wood-based houses in Slovakia," BioResources 16(4), 7799-7816.AbstractArticlePDF

Housing is one of the basic needs of every person. Most people usually encounter the problems of the availability of financial resources and real construction costs. The objective of this paper is to present customer preferences for the construction of family houses in Slovakia with the assessment of possible perception disproportions regarding economic characteristics in the context of interest and reality. A specific part of this paper includes the presentation of interest in the construction of wood-based houses. The questionnaire survey show that, in the target group (respondents aged 26 to 50 years), significant dependencies were found between the monitored traits and the amount of planned investment. For each dependence, possible disproportions were also revealed, which could lead to an overall threat of the plans for the construction of a family house. The disproportions, which were associated with 25 to 30% of respondents, depended on the amount of investment and net household income as well the outlay and usable floor area. This is an original survey in the field, the benefit of which should be its use for a comparison of similar research.
- Researchpp 7817-7829Ashrafi Birgani, S., Talaeipour, M., Hemmasi, A. H., Bazyar, B., and Larijani, K. (2021). "Production of nanocrystalline cellulose from bleached soda bagasse pulp," BioResources 16(4), 7817-7829.AbstractArticlePDF
The cellulose used in this study was prepared from bleached soda bagasse obtained from the Pars paper factory. To prepare nanocellulose, the sample was subjected to alkaline pretreatment and then acid hydrolysis using 54% sulfuric acid at several temperatures (35, 50, 60, and 65 °C) and different times (30, 60, 90, and 120 min). Then, they were prepared using a centrifuge, dialysis bag, ultrasound, and freezer, respectively. The produced nanocellulose was characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). According to the results, temperatures of 50 and 90 °C were selected for the preparation of nanocellulose. The crystallization index of the hydrolyzed pulp and produced nanocellulose was 53 and 61%, respectively. The produced nanocellulose had a fibrillar shape.
- Researchpp 7830-7845Trenčiansky, M., Štěrbová, M., Výbošťok, J., and Lieskovský, M. (2021). "Impacts of forest cover on surface runoff quality in small catchments," BioResources 16(4), 7830-7845.AbstractArticlePDF
Forest cover influences not only the amount of surface runoff, but also its quality. The concentrations of chemicals in surface runoff differ between forest catchments and non-forest catchments (agricultural areas). The authors investigated the chemical compositions of surface runoff in two small neighboring catchments (forest, non-forest), by analyzing and summarizing data over a period of 26 years from 1986 to 2012. During this period, the stock and absorption area of forest stands increased, air quality improved, the agricultural landscape was partly regenerated, and global climate change became apparent. The authors observed differences in surface runoff between forest- and non-forest catchments. However, these differences were not mainly caused by the influence of the forest cover, but by changes in agricultural land management. Since 2006, agricultural land has been managed without the use of artificial fertilizers, which reduced the contents of pollutants in surface runoff from the non-forest catchment. The existence of the forest as such excludes or noticeably eliminates the use of fertilizers and chemical substances that affect water quality.
