Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 5908-5923Al-Rajhi, A. M. H., Moawad, H., Alawlaqi, M. M., Felemban, H. R., and Abdel Ghany, T. M. (2023). “Bread spoilage fungi as creators of α amylase using two types of wheat flour,” BioResources 18(3), 5908-5923.AbstractArticlePDF
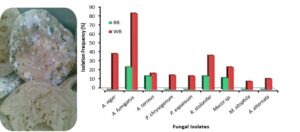
Fungal spoilage of bread can be a great problem; however, it can be explored as a producer of enzymes. The fungi were isolated from breads, and their activity for α-amylase production was planned. The results identified nine fungi on spoiled breads. Aspergillus fumigatus occurred with 85% frequency, followed by other isolates. Starch yeast (SY), white flour (WF), and black flour (BF) were applied as substrates for α-amylase activity using fungal isolates. The SY was the best, followed by WF and BF for α-amylase activity. Using SY, A. niger showed the greatest potency for α-amylase (7.67 U/mL) unlike Monilia sitophila, which reflected low α-amylase activity (2.69 U/mL). Using WF, A. fumigatus reflected high amylase activity (5.76 U/mL) while A. niger, A. terreus, and Penicillium expansum showed less activity (5.12 U/mL, 4.41 U/mL, and 3.56 U/mL, respectively). The temperature 30 °C and pH 6 were the optimum for α-amylase activity by A. niger, A. fumigatus, and P. chrysogenum, using the three media, but α-amylase activity of A. fumigatus at 40 °C was higher than at 20 °C. At the ninth day of incubation, the maximum α-amylase activity was reported using SY, while at the twelfth day, maximum activity was reported using WF and BF.
- Researchpp 5924-5950Tai, R., Li, B., Sun, Z., Li, Q., Liang, R., and Zhong, B. (2023). “Design reuse method of corn picking device based on case-based reasoning,” BioResources 18(3), 5924-5950.AbstractArticlePDF
In order to shorten the design cycle of corn snapping mechanism, a case reuse design method of snapping devices based on user requirements was proposed. A matter-element model is used to build a case matter-element database and parametric model library together to form a case database; the case attributes are divided, the retrieval scope is narrowed through the matching of core parameters, and the similarity of matching parameters and performance evaluation parameters is calculated by using analytic hierarchy process and deviation maximization method to realize the retrieval of similar cases. The transformation relationship between the design requirements and the main driving parameters of the parametric model is established by using the rule association method to realize the case’s modification. The engineering discrete element method is used to simulate the reuse case, and an improved method is proposed according to the simulation results. The improved device is verified by simulation and field experiments. The results show that the operating performance of the improved snapping device is improved, and the feasibility and effectiveness of the design reuse method are verified, which can provide technical reference for the intelligent design of agricultural machinery and equipment.
- Researchpp 5951-5966Matygulina, V., Chistova, N., and Vititnev, A. (2023). “Assessment of the morphological properties of secondary semi-finished wood-fibre products obtained from production waste,” BioResources 18(3), 5951-5966.AbstractArticlePDF
This paper presents the results of an assessment of the morphological characteristics of semi-finished wood-fibre products obtained from waste fibreboard using a rotary cutting machine by dry grinding. The work has established the influence of machine design parameters, such as the gap between the rotor and stator cutters and the angle of the stator cutter contact with the raw materials, on the mass fraction of small fibres and fines in wood-fibre pulp. These parameters determine the main structural characteristics of boards and ensure fibre bonding. The paper describes the collision of single secondary wood fibres that leads to the development of primary cracks, contributing to external and internal fibrillation in the absence of high temperatures and pressure without using chemical additives or water and steam.
- Researchpp 5967-5992Rahman, M. R., James, A. A., Othman, A. Bin Bakri, M. K., Uddin, J., Sueraya, A. Z., Matin, M. M., Alfaifi, S. Y., Madkhali, O., Aljabri, M. D., and Rahman, M. M. (2023). “Extraction and characterization of modified algae derivative cellulose and its mixtures for dye removal,” BioResources 18(3), 5967-5992.AbstractArticlePDF
A new bio-sorbent derived from green algae biomass, Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina), was found to be economically practical for water decontamination. This biosorbent comprised of microalgae cellulose, poly(lactic acid) (PLA), Dabai activated carbon (AC), and montmorillonite (MMT), each plays a distinctive role in removing methylene blue (MB) dye. The presence of hydroxyl and carbonyl functional groups in algae cellulose, confirmed by the FTIR analysis, offered binding sites for dye removal. Scanning electron microscopy demonstrated the morphological structure of the biosorbent, highlighting the combined effect of microalgae cellulose, PLA, Dabai AC, and MMT mixtures. The inclusion of Dabai AC and MMT improved micropores and mesopores, enhancing adsorption reactions. The Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) analysis confirmed that the sample containing microalgae cellulose, Dabai AC, and MMT clay in PLA had a specific surface area of 0.784 m2/g, three times higher than the PLA + cellulose sample. Additionally, adding 1% MMT to the sample improved the particle dispersion on the surface of the hydrophobic PLA, thereby improving its thermal properties. Remarkably, the biosorbent effectively eliminated 86.8% of MB dye from an initial concentration of 50 mg/L after 60 min of Vis-light irradiation using Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy.
- Researchpp 5993-6012Tozluoğlu, A., and Fidan, H. (2023). “Effect of size press coating of cationic starch/ nanofibrillated cellulose on physical and mechanical properties of recycled papersheets,” BioResources 18(3), 5993-6012.AbstractArticlePDF
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of size press coating on two types of recycled papers using different types of nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) and cationic starch (CS) on physical and mechanical properties. Wheat straw was used as a cellulose source, and NFC was obtained through oxidative and enzymatic pretreatments. Recycled fluting and coreboard papers were coated with cationic starch/NFC blends at various concentrations of NFC (0.5%, 1%, 2%, 3%, and 4%) using a three-time repetitive size press application, followed by one-time drying section, and compared to uncoated papers. The application of a coating suspension containing 4% periodate-oxidized NFC on both paper surfaces resulted in a significant improvement in the tensile index, burst index, and internal bond strength of the papersheets, with increases of up to 60.6%, 96.3%, and 119.9%, respectively. Furthermore, significant decreases in air permeability were also observed with reductions of 75% and 81.6% for coreboard and fluting papers, respectively. Compared to other pretreatment methods, periodate oxidation resulted in higher viscosity values in NFC samples. Therefore, the application of periodate-oxidized NFC with a size press resulted in a significant improvement in the mechanical and barrier properties of papers made from recycled pulps.
- Researchpp 6013-6024Yu, L., Dai, F., Zhang, K., Jiang, Z., Tian, G., and Wang, Y. (2023). “Anatomical and microstructural features of rattan (Calamus caesius),” BioResources 18(3), 6013-6024.AbstractArticlePDF
Calamus caesius, one of the most valuable high-quality rattans, has emerged as an economical material for use in commercial products. This study systematically investigated the anatomical and microstructural characteristics of Calamus caesius in terms of the frequency, radial diameter, tangential diameter, and form factor of the vascular bundles in both inner and outer regions, as well as the frequency, proportion, length, diameter, and length-diameter ratio of the vessel elements, and the size, double wall thickness, lumen diameter, and ultrastructure of the fibers. The results revealed that the sizes of both vascular bundles and vessel elements in the inner regions were larger than the outer regions, while the fiber proportions and morphological features remained relatively constant. The fibers have a multi-layered structure, most of which exhibited a four-layered structure in their secondary walls. The properties of various tissue structures reflect rattan’s desirable characteristics for use as high-quality commercial timber.
- Researchpp 6025-6043Kara, F., Turfan, N., and Alay, M. (2023). “Understory junipers, and light environment effects on biomass, chemical composition, and nutrient contents of black pine seedlings,” BioResources 18(3), 6025-6043.AbstractArticlePDF
In forest environments, the establishment, survival, and recruitment of seedlings of desired species can often be influenced by biotic interactions between the competing understory shrubs and the seedlings, as well as by the understory light environment. Previous studies regarding competing effects were mostly focused on the survival and growth of seedlings, but it is still largely unclear how competition with shrubs impacts the biomass of the seedlings and physiological traits connected to photosynthesis and nitrogen metabolism in various forest ecosystems. Moreover, there is limited knowledge on the influence of light conditions on the biomass of understory seedlings is limited for different species. The main objectives of this study were to examine the effects of understory junipers and light conditions on the above and belowground biomass of black pine seedlings (Pinus nigra Arnold). This study also examined the changes in chemical composition and plant nutrient contents in the organs of black pine seedlings (i.e., root, stem, and needle) with the presence of junipers in the understory. Seedling biomass was significantly affected by understory light conditions, while the presence of junipers negatively affected the root-biomass of black pine seedlings. Moreover, understory junipers influenced some photosynthetic pigments in black pine seedlings.
- Researchpp 6044-6056Masis Ulloa, J. A., Horvath, L., and White, M. S. (2023). “Comparison of damage to wood pallets in use with damages occurring using the Virginia Tech FasTrack simulation of pallet use,” BioResources 18(3), 6044-6056.AbstractArticlePDF
The durability of a pallet affects the amount of use a pallet can withstand before functionality is lost. A reliable prediction of durability can be used to determine the effect of pallet performance on supply chain operating costs. The objective of this research was to correlate damage modes, location, severity, and frequency observed for pallet in the field, to damages observed during Virginia Tech’s FasTrack simulation system. Several 1219 mm x 1016 mm (48 x 40 inch) stringer class wooden pallets used in the field were inspected for damages, and the results were compared to historical pallet damage information from FasTrack. The pallet damage behavior did not change for different levels of damage severity, which indicates that pallets fail as the initial damage worsens due to prolonged use. Inspected pallets from the field showed high damage occurrence on the stringer notches and bottom lead deckboards. Pallets tested via FasTrack exhibited significantly more top deck and end board damage and less stringer damage than observed in the field.
- Researchpp 6057-6067Entsminger, E. D., Mohammadabadi, M., and Stokes, C. E. (2023). “Effects of guayule resin on structural performance and durability of wood strand-based composites,” BioResources 18(3), 6057-6067.AbstractArticlePDF
Effects of guayule resin on mechanical, physical, and biological performance of wood strand-based panels were evaluated. Southern yellow pine (Pinus spp. L) wood strands were mixed with phenol formaldehyde (PF) resin to a target resin content of 5% and hot-pressed to manufacture wood strand-based panels. A guayule resin solution was prepared and sprayed on the wood strands immediately after PF resin to different guayule resin contents of 0.5% and 1.0%. Specimens cut from treated panels and control panels were subjected to tensile, internal bond, water absorption and thickness swelling, and fungi soil block tests. Guayule resin had a positive effect on tensile strength, as specimens showed 8.0% and 9.5% increase compared to control specimens. However, the internal bond strength decreased 5.3% and 6.4%, respectively. Water absorption and thickness swelling for the treated specimens with guayule resin decreased as compared to control specimens. The fungal decay resistance test indicated little differences in the average percent mass loss across the untreated and treated wood strand-based composite materials. Regardless of increase or decrease, the effects of guayule resin on mechanical, physical, and biological performances of wood strand-based panels were not statistically significant.
- Researchpp 6068-6085Can, A., Ergun, M. E., and Özlüsoylu, I. (2023). “Properties of oak wood incorporating microencapsulated phase change material,” BioResources 18(3), 6068-6085.AbstractArticlePDF
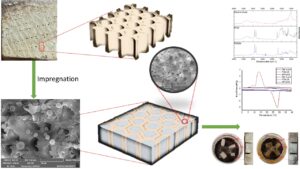
Microencapsulated phase change materials (MPCMs) incorporated into oak wood via vacuum impregnation have shown promise as thermal energy storage (TES) materials. Physical and chemical properties of MPCMs and resulting Phase Change Energy Storage Wood (PCESW) were analyzed. Scanning electron microscopy and particle size analyses revealed similar particle sizes, while X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectra confirmed crystal phase and chemical structure. Thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry determined thermal properties, including phase change temperature, enthalpy, thermal stability, and conductivity. The MPCMs exhibited a phase change enthalpy of 146.0 J/g and temperature of 35.0 °C, with excellent thermal stability. The FTIR, XRD, and TGA analyses showed unchanged chemical structure, crystallinity ratios, and decomposition in two stages, respectively. The PCESW exhibited a latent heat storage of 3.02 J/g at 25.4 °C. Decay tests demonstrated noticeably reduced weight loss (1.22% and 1.55%) for MPCMW samples treated with Trametes versicolor and Coniophora puteana, compared to unleached control samples (19.7% and 20.8%). These findings indicate the high efficiency and potential of PCESW as a thermal energy storage material.
