Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 1696-1706Chowdhury, G., Sharma, R., and Sarkar, U. (2024). “Cultural studies and yield attributes of pink oyster mushroom (Pleurotus djamor) in West Bengal,” BioResources 19(1), 1696-1706.AbstractArticlePDF
The pink oyster mushroom, scientifically known as Pleurotus djamor, is characterized by its appealing color, positive sensory qualities, substantial nutritional content, and its possession of antioxidant, antimicrobial, and medicinal properties. Mushrooms degrade lignocellulosic substrates through lignocellulosic enzyme production and utilize the degraded products to produce their fruiting bodies, contributing to sustainable agriculture and forestry and a short-term generation of income. The present study was carried out to assess the effect of various cultural parameters viz. temperatures, pH, solid culture media, carbon, and nitrogen sources on mycelial growth of the fungus and to identify the suitable grain for spawn production, optimum dose of spawn and suitable substrate for obtaining the highest yield of the mushroom. All of the experiments were conducted following standard protocols after procuring the pure culture of P. djamor from DMR-Solan. The optimum temperature for mycelial growth of the fungus was 28 °C at pH 7.5, and the best solid culture media was oat meal agar. Starch was the best carbon source and 0.3% L-asparagine served as the best source of nitrogen. Sorghum grains promoted the fastest spawn production. Out of five different doses of spawn and two assessed substrates, 4% spawn on paddy straw promoted the highest yield.
- Researchpp 1707-1727Xue, G., and Chen, J. (2024). “Strategies for applying shape grammar to wooden furniture design: Taking traditional Chinese Ming-style recessed-leg table as an example,” BioResources 19(1), 1707-1727.AbstractArticlePDF
This paper uses shape grammar to conduct strategic research and innovative translation of existing wooden furniture designs. A traditional Chinese Ming-style recessed-leg table was used as an example to demonstrate its feasibility. The paper applies biological DNA genetic information to furniture products, and combines shape grammar to evolve and mutate them, thereby creating new forms of wooden furniture that maintain the original genes. A DNA gene pool of recessed-leg table was constructed, and an architectural queti replacement pool was constructed based on the rules of shape grammar as backup for subsequent experiments to replace part of the designed genes of the recessed-leg table. Shape grammar was used to deduce the recessed-leg table and generate three plans. A consumer questionnaire was established through the semantic differential method. After evaluating these three design plans, an optimal plan that meets market demand was selected, and modeling, rendering, and concept elaboration were performed. Finally, the paper takes Ming-style recessed-leg table as an example to demonstrate that it is effective and feasible to use shape grammar to guide the design and research of domestic wooden furniture.
- Researchpp 1728-1743Law, J. C. H., Wade, K. R., Parker, K. G., Mutukumira, A. N., and Sloane, M. (2024). “Sustainable paper-based packaging from hemp hurd fiber: A potential material for thermoformed molded fiber packaging,” BioResources 19(1), 1728-1743.AbstractArticlePDF
Hemp hurd fiber, a low-value waste stream from the hemp industry, has potential downstream applications as an alternative to non-renewable plastics for single-use food service ware and packaging applications. Packaging paper substrates made from chemically pulped hemp hurd, mixed in varying ratios with bleached thermomechanical radiata pine pulp were developed and tested. Handsheets were characterized using several mechanical property tests including tensile strength, tearing resistance, burst strength, short-span compression, ring crush, together with Gurley air resistance, contact angle, and Cobb60 tests. Generally, addition of hemp hurd fibers significantly improved handsheet mechanical properties. Hot-pressing of the handsheets so as to approximate molded fiber thermoforming further enhanced their performance, with pure hemp hurd handsheets having the highest mechanical properties and barrier performance. A prototype was successfully thermoformed from hemp fiber, demonstrating overall feasibility of this fibre source for molded fibre objects.
- Researchpp 1744-1756Miric-Milosavljevic, M., Svrzic, S., Nikolić, Z., Djurkovic, M., Furtula, M., and Dedic, A. (2024). “Signal processing and machine learning as a tool for identifying idling noises of different circular saw blades,” BioResources 19(1), 1744-1756.AbstractArticlePDF
This study examines the possible utilization of machine learning and decision-making in the woodworking sector. This refers to the recognition of certain sounds produced during tool idling. The physical and geometric properties of the circular saw blade result in different noises being generated during idling. It was assumed that the respective circular saw blades can be recognized by these noises. The noises of three different circular saw blades were examined while idling at the same speed. In order to obtain useful data for the deep learning process, the coarse signals were subjected to frequency analysis. A total of 240 noise samples were taken for each circular saw blade and later subjected to signal processing. Frequency-power spectra were created using a custom program in Matlab Campus Edition software, such as for the spectrograms. A short Fourier transform was used to create the average spectral density plot using self-made software. The input data for the deep learning network was created in Matlab using a custom program. The GoogleNet deep learning network was used as a data classifier. After training the network, an accuracy of 97.5% was achieved in recognizing circular saw blades.
- Researchpp 1757-1776Mirițoiu, C. M., and Rădoi, A. I. (2024). “Mechanical properties for composites with dammar resin reinforced with crushed corn cob,” BioResources 19(1), 1757-1776.AbstractArticlePDF
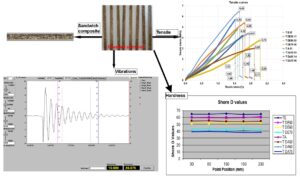
The study focused on the potential use of agricultural waste (corn cob) in the manufacturing of composite materials. In the first stage, composite materials were manufactured and tested using synthetic matrices (epoxy and acrylic) and hybrid matrices based on dammar resin (50% dammar, 60% dammar, and 70% dammar). Since it was observed that the samples had low mechanical properties under tensile and bending loads, the study was expanded to the production of sandwich-type composites with silk fabric facings. It was found that, by utilizing silk fiber, both tensile and bending strength increased from a few hundred percent up to a few thousand percent, compared to the samples that are only reinforced with crushed corn cob.
- Researchpp 1777-1788Fredriksson, M. (2024). “Predicting strength of Norway spruce and Scots pine sawn timber using discrete X-ray log scanning, optical board scanning, traceability, and partial least squares regression,” BioResources 19(1), 1777-1788.AbstractArticlePDF
Recently developed technology in sawmills such as advanced log scanning and traceability concepts enable new ways of grading logs and boards. When it comes to strength grading, this is often done on sawn boards using automatic scanning systems. However, if board scanners were to be augmented with data from log scanners by using traceability, more information on the wood properties is available. In this study, the main objective was to compare the strength prediction capability of board scanning alone, to board scanning augmented with X-ray and 3D data from log scanning, for Norway spruce (Picea abies L. Karst.) and Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.). In that case, data from three different scanning systems was combined, two for logs and one for boards. A further objective was to investigate whether pre-sorting logs for strength grading can be done using either 3D log data alone, or 3D log data augmented with X-ray data. The results show an improved strength prediction when adding log data to board data, and that 3D log data alone is not enough to pre-sort logs for strength, while adding X-ray log data makes it possible. Strength prediction on Scots pine performed somewhat better than prediction on Norway spruce.
- Researchpp 2017-2028Yasar S. S., Komut, O., Yasar, M., and Fidan, M. S. (2024). “Noise as a physical risk factor in furniture industry machines,” BioResources 19(2), 2017-2028.AbstractArticlePDF
This study aimed to determine the risk level of noise, which is an important physical risk, in small and medium-sized furniture industry enterprises. The noise levels of the circular sawing machines, edge banding machines, and mitre cutting machines, which are among the main processing machines of the sector, were measured. The study was carried out in 32 furniture businesses. The possible risks of noise on the operators of the machines in question and other employees were evaluated. Noise level measurements were made with the help of TESTO 815 measuring device. Dunnett’s T3 test was used to detect differences in noise levels for machine operators and other employees. It was determined that the edge banding machine does not pose an occupational health and safety risk in terms of noise risk factors. However, the mitre cutting machine and the circular sawing machine pose a risk for the machine operator in active production by creating noise above the established exposure limit value. The mitre cutting machine carries the same risk for the machine operator when it is in operation but in passive production. The results revealed the need for personal protective equipment for machine operators for mitre cutting and circular sawing machine.
- Researchpp 2029-2044Myeong, S., and Yun, J. (2024). “Culture of Trichoderma sp. with biochar to produce high-activity cellulase in a laboratory,” BioResources 19(2), 2029-2044.AbstractArticlePDF
Biochar (BC) was used in Trichoderma sp. culture to produce high-activity cellulase on a laboratory scale. The biochar was added into the flask before being applied to the fermenter to identify the enhancement effect and to determine the best amount of addition and the most suitable incubation period. Cellulase production was performed with a working volume of 4 L, and enzymatic hydrolysis was conducted to evaluate the saccharification ability of the enzyme. During incubation, the activities of three enzymes (Endoglucanase (EG), β-glucosidase (BGL), and cellobiohydrolase (CBH)) were measured for three days, and the cellulase activity was determined using a filter paper unit (FPU). In flask scale, EG, BGL, and CBH activities were increased by 1.4, 2.1, and 1.8 folds, respectively, and the incubation period was shortened by adding BC. In the fermenter scale, EG, BGL, and CBH activities were noticeably enhanced by 12.1, 5.8, and 7.2 folds, respectively, and FPU was 42.1 (9.8 folds). Additionally, the conversion rates of cellulose and steam exploded softwood and hardwood were 109.4%, 75.4%, and 87.3%, which were similar to a commercial enzyme (Cellic CTecⅡ). This study demonstrated that biochar could be used to produce high-activity cellulase in a shorter period and suggests a novel method for effective cellulase production.
- Researchpp 2045-2066Miao, Y., Yan, S., and Xu, W. (2024). “The study of children’s preferences for the design elements of learning desks based on AHP-QCA,” BioResources 19(2), 2045-2066.AbstractArticlePDF
Children’s study tables are an integral part of a child’s learning life. Consumers are often attracted to their styling when deciding on the use and purchase of a children’s study desk. This study focused on consumption preference for the styling of children’s study desks and delved into the factors that influence these preferences. An important aspect of this research is to understand how different shapes of children’s desks influence consumer preferences through morphological analysis. The study breaks down these desks into six different parts based on morphological analysis: backplane, bookshelves, desktop, cabinet, drawer, and table legs. Through a hierarchical analysis (AHP) and pairwise comparisons, the study created a hierarchy of preferred morphological elements. The hierarchy ranked the importance of each element in influencing consumption preference, revealing the order of preference from backsplash to table legs. In addition, by integrating personal interviews and employing Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA), this study provides insights into the most preferred components – backplane and bookshelves. This integrated approach revealed a preference for desks with curved backsplashes and multi-tiered functional shelves, which was ultimately validated by successfully combining weighted rankings of specific component styles.
- Researchpp 2065-2076Sinin, A. E., Hamdan, S., Mohamad Said, K. A., Abdullah, S., and Musib, A. F. (2024). “Gendang Melayu Sarawak (GMS) – Sarawak Malay Drum, the dying and forgotten tradition,” BioResources 19(2), 2065-2076.AbstractArticlePDF
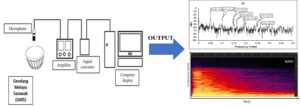
This work was conducted using the Picoscope signal extraction procedure, which revealed significant insights regarding the belian wood and its application in Gendang Melayu Sarawak (GMS) production. The amplitude of belian wood GMS signal remains constant, allowing it to sustain its timbre for a longer duration compared to durian wood GMS using the same procedure. Considering that the dimensions of the big belian (BB) and big durian (BD) GMS are almost the same, both GMS yield almost the same note, i.e. G1# (51.9 Hz). Considering that the dimensions of both the small belian (SB) and small durian (SD) GMS are almost the same, both GMS yield almost similar note, i.e. F3 (174 Hz) and E3 (164 Hz). Although both BB and BD showed consistent harmonics, BD only displays 2 harmonics. The SB and SD both display consistent harmonics. Both BB and BD showed pleasing tonal qualities. These occurred due to the closeness of the principal overtones to the consonant interval.
