Volume 17 Issue 3
Latest articles
- Researchpp 5038-5048Özel, H. B., Şevik, H., Onat, S. M., and Yigit, N. (2022). "The effect of geographic location and seed storage time on the content of fatty acids in stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) seeds," BioResources 17(3), 5038-5048.AbstractArticlePDF
The fatty acids content in pine seeds is important because it affects germination success and commercial value. In this study, the amount of fatty acids in the seeds of stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) was determined in seeds collected from different geographical locations and after two-year storage. The pine seeds were collected from different locations where peanut pine is densely located in the Western Black Sea Region of northern Turkey in 2019. The results showed that the content of some fatty acids (C18:1n-9, ƩMUFA, C18:2n-6, and ƩPUFA) in the seeds collected from different geographical locations did not differ significantly, but the content of others (C16:0, C18:0, C20:0, ƩSFA, and C18:3n-3) was dependent on the locations. The difference among locations was up to 40% (p < 0.05). In general, the lowest values were obtained from the seeds of Bartın Karaçaydere, and the highest values were obtained from the seeds of Bartın Çakraz and Bartın Avara locations. After two years of storage, the content of all the fatty acids in the seeds decreased based on the location, and a decrease of more than 25% in the content of some fatty acids was observed.
- Researchpp 5049-5064Han, M., Yang, J., Ma, J., Wang, C., Chen, S., Xu, M., Yang, Q., Bian, L., Yan, X., and An, Q. (2022). "Extracellular laccase activity among Ganoderma and Coriolopsis species grown on lignocellulosic wastes," BioResources 17(3), 5049-5064.AbstractArticlePDF
The extensive application of laccase in various fields depends on the supply of a large amount of laccase with high activity and low cost. Interest on the screening of fungal strains suitable for obtaining massive high-activity laccase in solid-state fermentation with suitable low-cost lignocellulosic wastes has increased. The present work determined the laccase secretion from different species belonging to genera Ganoderma and Coriolopsis fermented on different lignocellulosic wastes. Maximal laccase activity was obtained from Ganoderma lingzhi Han 1345 grown on rice straw for 9 days and indicated the capacity of secreting laccase of G. lingzhi Han 1345 was superior to that of Coriolopsis trogii Han 1211, C. strumosa Han 1356, and G. applanatum Han 1578. The presence of cottonseed hull was more favorable for Coriolopsis species secreting laccase, while Ganoderma species were more preferred to secrete laccase on rice straw. Further, the consistent substrate preference in laccase production of different species in the same genus was first exhibited. The results are useful to screen and obtain new species with superior capacity of secreting laccase and suitable low-cost lignocellulosic wastes as fermentation substrate for further industrial application of laccase.
- Researchpp 5065-5078Liu, W., Zhang, X., Ren, H., Hu, X., Li, J., and Liu, H. (2022). "Spirocyclic alkoxysilane synthesized from rice straw ash for preparation of eco-friendly hydrophobic silicone coatings," BioResources 17(3), 5065-5078.AbstractArticlePDF
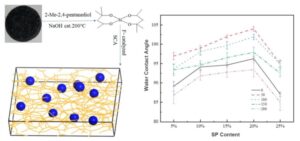
The purpose of this study was to use biomass silicon resources in rice straw to synthesize high value-added organosilicon products to solve the problem of low utilization of rice straw and high pollution and energy consumption in the silicon chemical industry. In this work, spirocyclic alkoxysilane was successfully synthesized by an environmentally friendly method from rice straw ash for the first time. The spirocyclic alkoxysilane yield per gram of rice straw ash can reach up to 1.9 g. Spirocyclic alkoxysilane was used to modify silicone resin coating. This coating can withstand 150 applications of friction and still maintain good hydrophobic effect. The maximum water contact angle after friction can reach 104°. This study broadens the application of rice straw. Furthermore, this research lays the foundation for the improvement of energy-saving and emission reduction process of silicon chemical industry.
- Researchpp 5079-5094He, T., Tong, G., Li, P., Miao, C., Zhang, X., and Xu, X. (2022). "Effect of nano precipitated calcium carbonate on the properties of hydrogels prepared with acrylamide, starch, and TEMPO-oxidized nanocellulose," BioResources 17(3), 5079-5094.AbstractArticlePDF
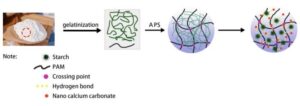
A variety of water-retaining hydrogels possessing macroporous interiors resembling a honeycomb framework were developed by free radical polymerization of acrylamide (AM), starch, and TEMPO-oxidized nanofibrillated cellulose (TONFC) (Poly (AM-co-TONFC/Starch) (PATS) hydrogels). With the help of ultrasound, nano precipitated calcium carbonate (NPCC) was gelatinized in the preformed NPCC suspension in a monomer solution that forms a hydrogel. When NPCC was dispersed in water, its surface was positively charged, and NPCC could be used as a condensation center to form hydrogen bonds with AM, TONFC, and starch, shortening the distance between AM, TONFC, and starch, increasing the pore size, and thinning the pore wall. The uniform dispersion of NPCC in hydrogels could also promote a more uniform degree of cross-linking in hydrogels. When the hydrogels was extruded and deformed by external forces, the stress of hydrogels was more uniform, so that they could withstand more forces without collapsing. When 4% NPCC was added (relative to starch and TONFC), the pore size of PATS2 hydrogel was uniformly distributed in the range of 10 to 20 μm. The maximum tensile strength of PATS2 hydrogel reached 84.8 KPa, and the elongation at break was 399%. The water absorption reached 172.3, and 65% water content was maintained after 720 h.
- Researchpp 5095-5105Li, M. (2022). "Impact of continuous electrochemical degradation of eucalyptus alkaline peroxide mechanical pulping wastewater," BioResources 17(3), 5095-5105.AbstractArticlePDF
Levels of pollutants in pulp and papermaking wastewater are an important issue for environmental protection. High concentrations of contaminants can seriously affect the environment if they are not processed. Therefore, treating paper wastewater is a necessary option for governments to select appropriate treatment methods to remove the multi-component pollutants. In this study, the impact of continuous electro-degradation of eucalyptus alkaline peroxide mechanical pulping wastewater was studied. An electrolytic treatment method performed at a low voltage was used. Through the electrolysis method, the wastewater chemical oxygen demand was decreased by 98%, and color-generating groups were nearly all destroyed. During the electrolysis process, the pH value of wastewater continuously decreased and finally reached 2.5. Lowering the pH of the waste solution will help increase the electrolysis efficiency of the wastewater. A total of 5.8 g of alkali was obtained. The wastewater precipitation before and after electrolysis was analyzed by X-ray photoelectron, Fourier transform infrared, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopies.
- Researchpp 5106-5115Chen, H., Yang, T., Wang, J., Song, J., Wo, Q., Zheng, B., and Jiang, L. (2022). "Study on the application of Zizania latifolia straw in papermaking," BioResources 17(3), 5106-5115.AbstractArticlePDF
Zizania latifolia is a vegetable that is native to China. Z. latifolia has a long history and a huge yield. Usually, the biological mass of leaves and sheaths of Z. latifolia account for 50% to 70% of the total mass of the plants, so there is a lot of residual Z. latifolia straw after cultivation. This causes pollution to the local environment and rivers. At the same time, non-wood fiber materials have always been one of the raw materials used in the paper industry. The purpose of this study was to turn the large-scale abandoned Z. latifolia straw into a valuable resource and bring a new treatment idea of Z. latifolia straw papermaking. By comparing the Z. latifolia paper with conventional old corrugated container paper, this study introduced a new idea for solving the treatment of Z. latifolia straw abandoned in Jinyun, China.
- Researchpp 5116-5128Liu, H., Xie, J., and Zhang, J. (2022). "Moisture transfer and drying stress of eucalyptus wood during supercritical CO2 (ScCO2) dewatering and ScCO2 combined oven drying," BioResources 17(3), 5116-5128.AbstractArticlePDF
Supercritical CO2 (ScCO2) dewatering is a lumen water expulsion process, in which CO2 is cycled between atmospheric pressure and supercritical phase and results in a fast expulsion of free water. In this study, specimens of 100 mm length Eucalyptus exserta F.V. Muell. wood were dewatered using ScCO2, then the dewatered and un-dewatered wood were dried in oven at 100 °C to investigate moisture transfer and drying stress. The ScCO2 dewatering was very fast. When the moisture content (MC) was over 40%, the MC distribution and gradient after dewatering and oven drying were different. The oven drying MC showed a ring contour distribution, but the ScCO2 showed a higher MC in one side and a lower MC in the opposite; the oven drying MC gradient was great in the middle and small in the end part of wood, but the ScCO2 MC gradient was small and roughly consistent. The oven drying moisture migration rates along the fiber and transverse directions were similar; however, the ScCO2 migration rate was faster in the transverse directions. The MC distributions of the dewatered and un-dewatered wood after oven drying were similar at 30% MC. The ScCO2 dewatering reduced wood residual stress, and it affected the stress development in the subsequent oven drying.
- Researchpp 5129-5145Baharuddin, N., Lee, S., Anwar Uyup, M., and Md Tahir, P. (2022). "Effect of preservative treatment on physical and mechanical properties of bamboo (Gigantochloa scortechinii) strips," BioResources 17(3), 5129-5145.AbstractArticlePDF
Using a vacuum pressure cylinder, Gigantochloa scortechinii was treated with boron and copper chrome boron (CCB) preservative at different concentrations of 2% and 3%. The treatability of untreated and treated bamboo, as well as its physical and mechanical properties, were investigated. Both preservatives showed a high level of penetration into the bamboo strips. Weight percent gain (WPG) and extent of retention of CCB-treated bamboo strips were higher than those of the boron-treated samples. Swelling and shrinkage were proportionately reduced with treatment, with a significant difference between radial and tangential dimensions. When compared to untreated bamboo, treated bamboo showed a greater reduction in radial swelling but a lower reduction in shrinkage. The mechanical properties of untreated and treated samples differed in modulus of elasticity (MOE) and compression. Untreated samples had the highest MOE of 26,100 N.mm-2, while boron and CCB had MOE values of 22,800 and 22,900 N.mm-2, respectively. Copper chrome boron samples had the highest compression value of 86.3 N.mm-2, while the boron and untreated samples had values of 84.0 and 78.3 N.mm-2, respectively.
- Researchpp 5146-5163Hao, Y., Wang, J., Qi, L., Qiu, Y., Liu, H., Zhang, Y., and Wang, X. (2022). "A comparative study of apricot kernel oil yield using different extraction methods," BioResources 17(3), 5146-5163.AbstractArticlePDF
Apricot kernel was used as a raw material to compare and analyze the yield of apricot kernel oil using a pressing method, an ultrasonic-assisted extraction method, and a Soxhlet extraction method. The optimum extraction conditions were further verified through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The fatty acid composition of the apricot kernel oil consisted of palmitic acid and stearic acid, and the total content of cis-oleic acid and cis-linolenic acid reached 93%. The apricot kernel oil obtained by Soxhlet extraction had the highest yield. However, the Soxhlet method has some limitations, such as high consumption of energy, long extraction time, and low efficiency. Ultrasound-assisted extraction has been developed by the industry to minimize these disadvantages. Finally, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis was carried out on the ultrasonic-assisted extraction method, and it was again shown that the apricot kernel oil contained many unsaturated fatty acids.
- Researchpp 5164-5177Im, W., Park, S., Lee, J., Yook, S., Lee, H., and Youn, H. (2022). "Wet strength improvement of nanofibrillated cellulose film using polyamideamine-epichlorohydrin (PAE) resin: The role of carboxyl contents," BioResources 17(3), 5164-5177.AbstractArticlePDF
An approach to improve water resistance and wet strength of films from nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) was investigated using polyamideamine-epichlorohydrin (PAE) as a cross-linker. To increase the cross-linking reaction, carboxymethylation of pulp fiber was conducted as a chemical pretreatment. NFC was prepared by grinding, and the pass number required in the grinding process differed depending on the carboxyl contents introduced by the carboxymethylation process. First, PAE was added to the NFC suspension, and then NFC films were prepared by casting the suspension followed by heat treatment. The covalent bond formation between the azetidium groups of PAE and carboxyl groups of NFC was confirmed by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy analysis. The water contact angle indicated that hydrophobicity of PAE/NFC films remarkably increased by the carboxyl content of NFC indicating that the carboxyl groups interacted with the cationic PAE to give higher water contact angles. While the dry tensile strength of NFC films was not influenced by PAE, wet tensile strength was clearly improved with PAE.
