Volume 18 Issue 3
Latest articles
- Researchpp 5813-5837Wang, Y., Zhang, P., Guo, J., Zhong, Z., Li, W., and Liu, X. (2023). “Aligned cellulose nanocrystal composite filament with high tensile strength enhanced by cationic polyacrylamide via flow focusing approach,” BioResources 18(3), 5813-5837.AbstractArticlePDF
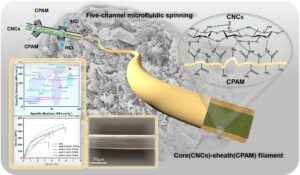
Unsatisfactory macroscopic strength is one of the important reasons that limit the application of cellulose composites. However, the mechanical properties of cellulose composites could be improved by the directional orientation of cellulose nanofibers. In this paper, a five-channel microfluidic chip was designed to fabricate core-sheath cellulose nanocrystal/ cationic polyacrylamide (CNC/CPAM) composite filament. The core spinning solution with high flow velocity promoted the extended arrangement of CPAM in sheath flow. CPAM with long chain structure could not only reduce the electrostatic repulsion between CNCs, but also ensures the fiber orientation by inhibiting the disorderly diffusion of CNCs, thus improving the toughness of the composite filament. The orientation of the composite fiber was studied by wide-angle X-ray scattering, showing an orientation index of 0.725. The mechanical properties of the composite fiber were tested by a universal material testing machine. The tensile strength was 510 ± 20 MPa, which was about 117% higher than that of pure CNC spun fiber, and the elongation at break was also increased by about 70%. The improvement in mechanical properties was attributed to the increase in the content of intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen bonds. In addition, the demonstrated spinning technology provided a new way for preparing high-performance composite fibers.
- Researchpp 5838-5858Gaudelas, A., Blanchet, P., Gosselin, L., and Cabral, M. R. (2023). “Physical characterization of biobased corrugated panels, an innovative material,” BioResources 18(3), 5838-5858.AbstractArticlePDF

Corrugated panels possess excellent thermomechanical properties, but, with presently no hygrothermal applications for building envelopes, their full potential still needs to be explored. This study characterized the physical properties of three biobased corrugated compositions to identify potential building applications. Flat samples of the same compositions were analyzed for certain properties to aid in understanding. As this characterization is groundbreaking, the testing was based on or inspired by established standards. Results suggest that the panels with two wood veneer cores and two kraft paper surfaces coated with polymers are the most promising, as such structures are less sensitive to water and possess a good moisture buffer value that should be advantageous for building construction. Corrugated panels are particularly interesting because their inner materials have properties comparable to those of conventional wood-based panels such as plywood. However, the apparent properties of corrugated panels become one to ten times smaller or larger, which opens up new design possibilities for building envelope applications.
- Researchpp 5859-5872Lee, M., Kang, E.-C., and Lee, S.-M. (2023). “Effects of different flame-retardant treatments on the sound absorption properties of low-density fiberboard,” BioResources 18(3), 5859-5872.AbstractArticlePDF
Internal finishing materials for large auditoriums or public facilities are regulated in South Korea to ensure their flame-retardant performance. Flame-retardant treatment of low-density fiberboard (LDF), an eco-friendly material, was performed to expand its use as a sound absorber by improving its fire safety. In this study, an LDF with a target density of 0.15 g/cm3 was prepared from radiata pine wood fibers and melamine–urea–formaldehyde resin, and recommended amounts of commercially available flame retardants (liquid type) were applied immediately after hot pressing. A powder-type flame retardant was blended with the resin used in LDF manufacture. The surface color and material changed partially depending on the flame-retardant type. The external application method slightly increased the moisture content and density, but it did not affect the physical properties of the LDF. The flame-retardant treatment reduced the emission of formaldehyde, as a scavenger. After treatment, the char area and char length of the LDFs decreased significantly to 9.42–23.64%, and 6.11–11.91%, respectively. The sound absorption performance of the flame-retardant-treated LDFs improved 4.08–9.11%, while their thermal-insulation performance remained unaffected. The flame-retardant-treated LDFs satisfy the regulation of flame retardancy, while maintaining sound absorption and thermal insulation functions.
- Researchpp 5873-5886Alipraja, I., Hernández, R. E., and Koubaa, A. (2023). “Effects of wood species on the energy requirements and size distribution of strands produced by a strander-canter,” BioResources 18(3), 5873-5886.AbstractArticlePDF
The effects of wood species on the performance of the strander-canting process were studied. Logs of balsam fir (Abies balsamea (L.) Mill.), black spruce (Picea mariana (Mill.) B.S.P.), and jack pine (Pinus banksiana Lamb) were processed under two temperature conditions (-13.3 °C and 22.3 °C). The cutting and feed speeds, rake angle, cutting width, and strand thickness were kept constant. The strander-canting process was evaluated by the strand dimensions and yield, as well as by the energy requirements. The results showed that wood species significantly affected the proportions of strands and fines, maximum power, mean energy consumption, and specific cutting energy when processing the logs under frozen conditions. In unfrozen conditions, wood species only affected the strand width and the maximum power. Unfrozen logs produced higher proportions of strands and a lower volume of pin chips and fines than frozen logs. The maximum power, mean energy consumption, and specific cutting energy were, on average, 2 to 4 times higher for the processing frozen logs than for unfrozen logs.
- Researchpp 5887-5907Mendez, O. E., Astete, C. E., Hermanová, S., Boldor, D., Orts, W., and Sabliov, C. M. (2023). “Biobased films from amphiphilic lignin-graft-PLGA copolymer,” BioResources 18(3), 5887-5907.AbstractArticlePDF

Amphiphilic copolymers were synthesized by grafting poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid with two lignin types: alkaline lignin and lignosulfonate. An interphase formation technique was used to produce films based on the copolymers. Films presented one side as being more hydrophobic (O-side) and smoother, and the second side more polar and with an uneven surface (W-side). Contact angle of water on the W-side was lower than the O-side corresponding to a higher lignin content and influenced by the lignin type (alkaline < lignosulfonate) and lignin: PLGA ratio. X-ray photoelectric spectroscopy analysis showed higher percentages of sulfur on the W-side, which supports a preferential partitioning of the lignin. Tensile testing demonstrated the significant impact of lignin type on the mechanical properties of the films. Alkaline films showed a higher maximum strength, a higher stiffness, and a higher tensile strength at the elastic limit compared to lignosulfonate films. However, for lignosulfonate films, ductility at break point was 4-fold higher than that of alkaline films.
- Researchpp 5908-5923Al-Rajhi, A. M. H., Moawad, H., Alawlaqi, M. M., Felemban, H. R., and Abdel Ghany, T. M. (2023). “Bread spoilage fungi as creators of α amylase using two types of wheat flour,” BioResources 18(3), 5908-5923.AbstractArticlePDF
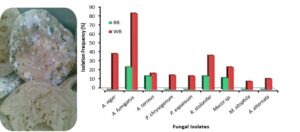
Fungal spoilage of bread can be a great problem; however, it can be explored as a producer of enzymes. The fungi were isolated from breads, and their activity for α-amylase production was planned. The results identified nine fungi on spoiled breads. Aspergillus fumigatus occurred with 85% frequency, followed by other isolates. Starch yeast (SY), white flour (WF), and black flour (BF) were applied as substrates for α-amylase activity using fungal isolates. The SY was the best, followed by WF and BF for α-amylase activity. Using SY, A. niger showed the greatest potency for α-amylase (7.67 U/mL) unlike Monilia sitophila, which reflected low α-amylase activity (2.69 U/mL). Using WF, A. fumigatus reflected high amylase activity (5.76 U/mL) while A. niger, A. terreus, and Penicillium expansum showed less activity (5.12 U/mL, 4.41 U/mL, and 3.56 U/mL, respectively). The temperature 30 °C and pH 6 were the optimum for α-amylase activity by A. niger, A. fumigatus, and P. chrysogenum, using the three media, but α-amylase activity of A. fumigatus at 40 °C was higher than at 20 °C. At the ninth day of incubation, the maximum α-amylase activity was reported using SY, while at the twelfth day, maximum activity was reported using WF and BF.
- Researchpp 5924-5950Tai, R., Li, B., Sun, Z., Li, Q., Liang, R., and Zhong, B. (2023). “Design reuse method of corn picking device based on case-based reasoning,” BioResources 18(3), 5924-5950.AbstractArticlePDF
In order to shorten the design cycle of corn snapping mechanism, a case reuse design method of snapping devices based on user requirements was proposed. A matter-element model is used to build a case matter-element database and parametric model library together to form a case database; the case attributes are divided, the retrieval scope is narrowed through the matching of core parameters, and the similarity of matching parameters and performance evaluation parameters is calculated by using analytic hierarchy process and deviation maximization method to realize the retrieval of similar cases. The transformation relationship between the design requirements and the main driving parameters of the parametric model is established by using the rule association method to realize the case’s modification. The engineering discrete element method is used to simulate the reuse case, and an improved method is proposed according to the simulation results. The improved device is verified by simulation and field experiments. The results show that the operating performance of the improved snapping device is improved, and the feasibility and effectiveness of the design reuse method are verified, which can provide technical reference for the intelligent design of agricultural machinery and equipment.
- Researchpp 5951-5966Matygulina, V., Chistova, N., and Vititnev, A. (2023). “Assessment of the morphological properties of secondary semi-finished wood-fibre products obtained from production waste,” BioResources 18(3), 5951-5966.AbstractArticlePDF
This paper presents the results of an assessment of the morphological characteristics of semi-finished wood-fibre products obtained from waste fibreboard using a rotary cutting machine by dry grinding. The work has established the influence of machine design parameters, such as the gap between the rotor and stator cutters and the angle of the stator cutter contact with the raw materials, on the mass fraction of small fibres and fines in wood-fibre pulp. These parameters determine the main structural characteristics of boards and ensure fibre bonding. The paper describes the collision of single secondary wood fibres that leads to the development of primary cracks, contributing to external and internal fibrillation in the absence of high temperatures and pressure without using chemical additives or water and steam.
- Researchpp 5967-5992Rahman, M. R., James, A. A., Othman, A. Bin Bakri, M. K., Uddin, J., Sueraya, A. Z., Matin, M. M., Alfaifi, S. Y., Madkhali, O., Aljabri, M. D., and Rahman, M. M. (2023). “Extraction and characterization of modified algae derivative cellulose and its mixtures for dye removal,” BioResources 18(3), 5967-5992.AbstractArticlePDF
A new bio-sorbent derived from green algae biomass, Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina), was found to be economically practical for water decontamination. This biosorbent comprised of microalgae cellulose, poly(lactic acid) (PLA), Dabai activated carbon (AC), and montmorillonite (MMT), each plays a distinctive role in removing methylene blue (MB) dye. The presence of hydroxyl and carbonyl functional groups in algae cellulose, confirmed by the FTIR analysis, offered binding sites for dye removal. Scanning electron microscopy demonstrated the morphological structure of the biosorbent, highlighting the combined effect of microalgae cellulose, PLA, Dabai AC, and MMT mixtures. The inclusion of Dabai AC and MMT improved micropores and mesopores, enhancing adsorption reactions. The Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) analysis confirmed that the sample containing microalgae cellulose, Dabai AC, and MMT clay in PLA had a specific surface area of 0.784 m2/g, three times higher than the PLA + cellulose sample. Additionally, adding 1% MMT to the sample improved the particle dispersion on the surface of the hydrophobic PLA, thereby improving its thermal properties. Remarkably, the biosorbent effectively eliminated 86.8% of MB dye from an initial concentration of 50 mg/L after 60 min of Vis-light irradiation using Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy.
- Researchpp 5993-6012Tozluoğlu, A., and Fidan, H. (2023). “Effect of size press coating of cationic starch/ nanofibrillated cellulose on physical and mechanical properties of recycled papersheets,” BioResources 18(3), 5993-6012.AbstractArticlePDF
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of size press coating on two types of recycled papers using different types of nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) and cationic starch (CS) on physical and mechanical properties. Wheat straw was used as a cellulose source, and NFC was obtained through oxidative and enzymatic pretreatments. Recycled fluting and coreboard papers were coated with cationic starch/NFC blends at various concentrations of NFC (0.5%, 1%, 2%, 3%, and 4%) using a three-time repetitive size press application, followed by one-time drying section, and compared to uncoated papers. The application of a coating suspension containing 4% periodate-oxidized NFC on both paper surfaces resulted in a significant improvement in the tensile index, burst index, and internal bond strength of the papersheets, with increases of up to 60.6%, 96.3%, and 119.9%, respectively. Furthermore, significant decreases in air permeability were also observed with reductions of 75% and 81.6% for coreboard and fluting papers, respectively. Compared to other pretreatment methods, periodate oxidation resulted in higher viscosity values in NFC samples. Therefore, the application of periodate-oxidized NFC with a size press resulted in a significant improvement in the mechanical and barrier properties of papers made from recycled pulps.
