Volume 18 Issue 3
Latest articles
- Researchpp 5466-5475Ulay, G. (2023). “Effects of artificial weathering on some surface properties of Anatolian chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) wood applied with yacht varnish,” BioResources 18(3), 5466-5475.AbstractArticlePDF
Anatolian chestnut wood is an industrial material used in various indoor and outdoor applications in Turkey. This study investigated the effects of artificial weathering (times: 144, 288, 432, and 576 h) conditions on color parameters (L*, ∆L*, a*, ∆a*, b*, ∆b*, ∆E*, ho, ∆H*, C*, and ∆C*), glossiness values at 60° in different directions (║ and ⊥), pendulum hardness (König method) values, and surface adhesion strength (pull-off method, MPa) on the layers of yacht varnishes applied to Anatolian chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) wood. The results showed that the univariate analysis of variance was significant by obtaining the weathering factor for all tests. While the brightness values perpendicular (⊥) and parallel (║) to the fibers increased at 144 and 288 h, they decreased at 432 and 576 h. Adhesion strength to the surface decreased 4.35% at the 576th h of weathering. At the end of weathering, a*, C*, b*, and pendulum hardness values increased, while ho and L* values decreased compared to un-weathered samples. The ∆a* and ∆E* values increased with increased weathering time.
- Researchpp 5476-5493Kocaman, A., Savaş, B. F., and İşler Ceyhan, D. (2023). “Removal efficacy of toxic metals in leachate through micro-organisms isolated from the natural environment,” BioResources 18(3), 5476-5493.AbstractArticlePDF
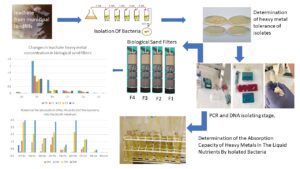
Landfill leachate is a serious contaminant for groundwater and surface water because of its potentially toxic metal content. In many countries, leachate is discharged into the natural environment without treatment because of the high disposal cost. However, this environmental problem can be solved by microorganisms, as they can adsorb the contaminants or convert them into end products, and this is cost-effective. This study focused on determining bacteria capable of efficiently removing toxic metals from leachates. Therefore, bacteria were isolated from nature that have a high adsorption and resistance capacity to a number of toxic metals. This potential was achieved by Enterobacter hormaechei, Priestia aryabhattai, and Mycobacterium sacrum, among others. Their efficiency in removing toxic metals compared to raw leachate was Cd (78%, 67%, 78%), Ni (64%, 57%, 56%), Pb (99%, 75%, 76%), Cr (41%, 46%,19%), Co (45%, 60%, 40%), and Cu (80%, 80%, 60%), respectively. According to the results, these bacterial strains proved to be very effective in the treatment of toxic metals from leachate. Therefore, they are good candidates for the treatment of wastewater by bioremedial methods.
- Researchpp 5494-5511Ushakov, A., Alashkevich, Y., Kozhukhov, V., and Marchenko, R. (2023). “Role of external fibrillation in high-consistency pulp refining,” BioResources 18(3), 5494-5511.AbstractArticlePDF
The mechanical and hydrodynamic phenomena occurring in the refining zones of disc refiners cause fibres to undergo fibrillation. This paper presents a study of the changes occurring during fibre fibrillation as expressed in terms of the fibrillation index when refining pulp with a 10%, 15%, and 20% consistency. The influences of the tangential force of a circular bar and a straight bar on fibre fibrillation were compared. The changes in the tangential force are shown to depend on the angle between the tangent to the cutting edge and the radius from the centre of the disk to the tangency point. Increasing the angle between the tangent to the cutting edge and the radius from the centre of the disk to the tangency point gives higher fibrillation index values. The study revealed a relationship between fibre fibrillation and the strength characteristics of handsheets.
- Researchpp 5512-5530Ashraf, S. R., Afroz, A., and Anwar, Z. (2023). “Physicochemical parameters optimization and peroxidase characterization from Aspergillus niger native strain by solid-state fermentation for improved dye decolorization,” BioResources 18(3), 5512-5530.AbstractArticlePDF
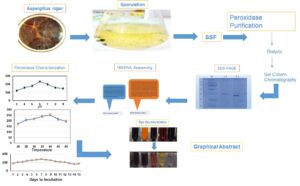
The hyper yield of peroxidase (POX) was investigated for a novel native Aspergillus niger strain identified by 18S RNA analysis. A. niger strains sequences were submitted to GenBank; IDs allotted were MN611114.1 (BMB 17) and MN559756.1 (BMB-18). The identified Aspergillus strains in combination showed enhanced (POX) activity (601.5 U/mL) by solid-state fermentation in comparison to their individual activities. POX was purified by ammonium sulfate, and size exclusion gel chromatography exhibited a 7.83-fold increase in POX concentration (13.3 U/mg) in comparison to BMB17 and BMB 18 (11.8 & 7.6 U/mg respectively). The best POX activity was obtained with pH 6.5, 37 °C, and 5 days of incubation. Using guaiacol as substrate, POX showed maximum activity (Vmax) of 537 U/mL with a corresponding Michaelis constant (Km) value of 126 µM. Calcium chloride worked as a POX activator at 300 & 400 mM. Zinc sulfate (500 mM), EDTA (5 mM); ethanol, propanol, and acetonitrile (50%) inhibited (18-30%) POX. Urea (1M), and copper sulfate (500 mM) strongly inhibited POX up to 40%. Polysorbate-80 (1%) slightly reduced the POX by 10% to 15%. BMB17+18-induced promising dye decolorization (88-98%) against all vat dyes, methylene blue, and phenol red.
- Researchpp 5531-5548Wang, J., Lyu, J., Li, X., Jiang, Y., and Chen, M. (2023). “Optimization of parameters for vacuum heat modification of Cupressus funebris wood,” BioResources 18(3), 5531-5548.AbstractArticlePDF
A full factorial experiment was conducted to analyze the main and interaction effects on the physical and mechanical properties of Cupressus funebris Endl. wood subjected to vacuum heat modification. The response variables evaluated were mass loss rate (ML, %), moisture resistance (MR, %), and modulus of rupture in bending (MOR, MPa). The results reveal significant variations in the effects of modification time, holding temperature, and vacuum pressure as independent factors, along with varying degrees of interaction effects among them. Simplifying the analysis model, a regression equation was derived to describe the relationship between the response variable (mass loss rate) and the factors: The model achieved an R-squared value of 96.0% and an R-squared (predicted) value of 73.7%, indicating good overall predictive performance. Optimal process parameters for mid-temperature vacuum heat modification of cypress were determined based on the mass loss rate and modulus of rupture (MOR), resulting in a modification temperature of 120 °C, holding time of 5 h, and a pressure intensity of 0.1. The reliability of the full factorial experiment was further confirmed through orthogonal testing.
- Researchpp 5548-5573Rahman, M. R., James, A. A., Marwani, H. M., Hamdan, S. Said, K. A. M., Bakri, M. K., Uddin, J., Matin, M. M., Madkhali, O., Aljabri, M. D., and Rahman, M. M. (2023). “Synthesis and characterization of ground biochar (GB) reinforced composites for removal of heavy metal from palm oil mill effluent (POME),” BioResources 18(3), 5548-5573.AbstractArticlePDF
Heavy metal contamination ruins the ecosystem and water quality. The adsorption method for heavy metal remediation is preferred because of its low cost and high efficiency. This work created eco-friendly ground biochar (GB) biomass-based derivatives reinforced polylactic acid (PLA) with titanium dioxide (TiO2). The composites improved palm oil mill effluent (POME) conditions, and H2SO4 activation increased pores by 80%. PLA and TiO2 altered GB characteristics, according to FTIR analysis. A significant adhesion interaction showed that GB, PLA, and TiO2 particles were compatible. Ball milling’s shear force increased surface area, according to Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) research. Particle size reduction increased GB porosity. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to study the porous structure of GB and the synergistic effect of PLA and TiO2 on POME during treatment. The SEM showed several components on the composite surface, demonstrating its efficacy. Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) showed that sample C’s composite, which had the most GB, decreased POME heavy metals by 94.4% manganese (Mn), 88.4% cadmium (Cd), and 94.4% zinc (Zn). The resulting POME met the Malaysian Department of Environment’s POME discharge limit by reducing chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS), turbidity, and pH.
- Researchpp 5574-5584Yang, G., Wang, X., and Zhong, D. (2023). “Properties of engineered wood flooring with cold-pressing and emulsion polymer isocyanate adhesive,” BioResources 18(3), 5574-5584.AbstractArticlePDF
For the sake of improving the product quality and economy, a series of cold-pressing experiments were carried out to investigate the material properties of engineered wood flooring with emulsion polymer isocyanate adhesive. Effect of pressing time, pressure, and adhesive spreading rate on modulus of elasticity (MOE) and modulus of rupture (MOR) was analyzed based on orthogonal experimental design. According to the results, both the MOE and MOR were positively correlated with pressing pressure and adhesive spreading rate. The MOE first increased and then decreased with the increase of pressing time, and MOR showed an increasing trend with the pressing time. Meanwhile, pressing time had the greatest effect on the MOE, followed by adhesive spreading rate, and pressing pressure. However, adhesive spreading rate had the greatest influence on the MOE, followed by pressing time and pressure. Furthermore, pressing time had a significant contribution to both MOE and MOR, and adhesive spread rate had a significant effect on only the MOR. Finally, the optimal cold-pressing condition was determined as 18 s pressing time, 1.25 MPa pressure, and 200 g/m3 adhesive spreading rate, and it is proposed for application in the industrial cold pressing of engineered wood flooring for the highest MOE, MOR, and production benefit.
- Researchpp 5585-5598Limhengha, S., Chueangchayaphan, N., Karrila, S., Madmaeroh, N., and Yangthong, H. (2023). “Properties and cost of natural rubber latex foam using biomass ash filler from agarwood pellets,” BioResources 18(3), 5585-5598.AbstractArticlePDF

The purpose of this work was to add value to biomass ash, which is a waste product from combustion of agarwood pellets as fuel. Ash was used as filler in accordance with the Bio-Circular-Green economy model to reduce the cost of manufacture of natural rubber latex foam (NRLF) produced with the Dunlop technique. The agarwood pellet biomass fuel was heated in an incinerator at 700 to 750 °C for 6 h to start the process. The mixture was then passed through a 120-mesh sieve after ball milling for 72 h. The next step involved dispersing 10% agarwood pellet biomass ash (APBA) at 0, 1.5, 2.5, 3.5, or 4.5 phr loadings in latex. This was followed by other actions such as visual inspection of the foaming and gelling stages. The influence of APBA loading on density, hardness, compression set and morphological properties of NRLF were investigated, and also the cost of production was estimated. The findings revealed that NRLF with 1.5 phr of APBA exhibited good physical properties, having a smooth surface and small foam cells. Moreover, the compression set properties of NRLF with 1.5 phr APBA comply with the Thai Industrial Product Standard (TIS 173-2529) for NRLF (Industrial Product Standard Act, 1986). Regarding the production costs, they were below those of filler- free NRLF by 0.03 USD/kg.
- Researchpp 5599-5622Kanking, S., Pulngern, T., Rosarpitak, V., and Sombatsompop, N. (2023). “Mechanical performance and anti-fungal and anti-algal properties for teakwood/parawood/PVC composites in UV-weathering and seawater immersion conditions,” BioResources 18(3), 5599-5622.AbstractArticlePDF
This work examined teakwood and parawood in wood/poly(vinyl chloride) composite (WPVC) materials under UV-weathering and seawater immersion. The mechanical properties as well as anti-fungal and anti-algal performance were considered. Teakwood and parawood (a rubberwood product) in WPVC materials at ratios of 0:100, 20:80, 40:60, 50:50, 60:40, 80:20, and 100:0 were investigated. UV-weathering ageing periods of 0 to 32 days and seawater immersion periods of 0 to 90 were studied. Aspergillus niger TISTR 3012 and Chlorella vulgaris TISTR 8580 were used as marine fungi and marine algae, respectively. Higher parawood content (in formulations of 0:100, 20:80 and 40:60) in WPVC composite materials enabled better mechanical properties than those of higher teakwood content (in formulations of 60:40, 80:20 and 100:0). Seawater immersion caused more deterioration of WPVC composite materials than UV-weathering ageing. Both anti-microbial agents and wood particles are potentially used in WPVC composite materials for anti-microbial properties, including the percentage reduction of fungal and algal growth. Increasing UV-weathering ageing and seawater immersion periods decreased the percentage reduction of fungal growth, but increased the percentage reduction of algal growth in WPVC composite materials. The results suggested higher parawood content (in a formulation of 20:80) for WPVC composite materials for coastal environment applications.
- Researchpp 5623-5634Foti, D., Amiandamhen, S. O., Fernando, D., Letoffe, A., and Adamopoulos, S. (2023). “Heat treatment’s effect on properties of polystyrene from building demolitions,” BioResources 18(3), 5623-5634.AbstractArticlePDF
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer widely used as a packaging material and in thermal insulation of buildings. At end-of-life, there are not many recycling management options of PS because of the reduced incentive and high cost. PS is non-biodegradable, and consequently, the disposal of this product causes serious health and environmental concerns. This study discusses the application of thermal treatment to modify the properties of PS waste foams. Both expanded and extended polystyrene were collected from building demolitions and subjected to different temperature treatments and duration. The effect of the treatment was investigated on the density, structure, glass transition temperature, mechanical properties (hardness, compression strength), thermal conductivity, and sound absorption of treated PS. The results showed that density increased with treatment temperature, which had a corresponding effect on the evaluated properties. The study concluded that thermal treatment is a beneficial way to improve the mechanical properties of PS waste from buildings. However, a trade-off between application and relevance still needs to be ascertained, as the thermal and acoustic insulation properties of PS decreased with the treatment.
