Volume 18 Issue 4
Latest articles
- Researchpp 8264-8283Sjöstrand, B., Tremblay, B., and Danielsson, M. (2023). “Enhancing Through Air Drying process efficiency: Investigating laboratory-to-pilot scale correspondence and impact of process variables on tissue paper manufacturing,” BioResources 18(4), 8264-8283.AbstractArticlePDF
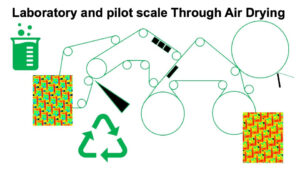
State-of-the-art manufacturing of tissue paper by Through Air Drying provides excellent product performance, although at a high production cost and energy use. In this work, a laboratory scale vacuum suction box was used to mimic the initial dewatering and the Through Air Drying molding, together with a pilot-scale trial. The purpose was to investigate both how the laboratory scale corresponds to pilot scale testing and investigate how fabric design, basis weight, beating, and fibers affect dewatering and sheet caliper. This study reevaluates dewatering mechanisms during molding, challenging the previous hypothesis of pure air displacement dewatering. Results show a parallel mechanism of compression dewatering and air displacement. The influence of rush transfer is examined, impacting the sheets’ visual appearance, thickness, and solids content. Correlations between molding box solids content and headbox freeness emphasize significance of fibers and beating levels. Pilot results confirm the link between former solids and molding box solids. Pilot trials validate the laboratory results, facilitating comprehensive simulation of full-scale manufacturing. This research reveals dewatering mechanisms, highlights operational parameters, and enables effective Through Air Drying process design and refinement.
- Researchpp 8284-8295Yurtayeva, L. V., Alashkevich, Y. D., Kaplyov, E. V., Slizikova, E. A., and Marchenko, R. A. (2023). “Bio-damaged wood processing in microcrystalline cellulose production,” BioResources 18(4), 8284-8295.AbstractArticlePDF
Bio-damaged wood was studied as a potential raw material for the production of hydrolytic degradation cellulose products. Conditions for obtaining fine-dispersed microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) based on hydrolytic treatment of cellulose from bio-damaged wood were determined. A comparative analysis of the quantitative values of the degree of polymerization of default commercial cellulose and cellulose from damaged wood was performed. The objective of the work was to study the possibilities of obtaining MCC from bio-damaged wood possessing quantitative characteristics close to those obtained from the commercial wood, reducing the concentration of inorganic acid during the hydrolytic degradation. The experimental analysis showed that with an increase in the pulp refining degree from 15 °SR to 75 °SR, the time for the hydrolysis process decreased from 150 to 90 min, the temperature of chemical treatment decreased from 100 °C to 80 °C, and acid concentration by 0.5 N. The polymerisation degree of microcrystalline cellulose, regardless of the type of raw material, also decreased with an increase in the refining degree.
- Researchpp 8296-8310Yang, S., Kim, J., and Kang, S. (2023). “Assessment of color and contact angle change of weathered wood in relation to wood species and different coating types,” BioResources 18(4), 8296-8310.AbstractArticlePDF
Color change was compared through artificial and outdoor weathering tests according to wood species and stain type. In the artificial weathering tests, the color change DE was the highest for the initial 200 hour, and teak solvent-based stain was the most effective in preventing color change. Outdoor weathering tests also showed a rapid color change until the initial 60 days, and the uncoated larch specimens exhibited graying after 120 days. Teak solvent-based stain had the highest preventing color effect, whereas water-based white semi-transparent stain had the highest contact angle. It is difficult to check the color change of wood due to the addition of pigment in teak, as its resistance to moisture is rapidly reduced and its surface protection effect is poor. Water-based white semi-transparent stain prevented color change and maintained a contact angle of 57.1° for up to 150 days, confirming the effect of moisture resistance. This study aimed to provide basic data on weather resistance by wood species and to suggest that the development direction of outdoor exposed wood is a water-based semi-transparent stain.
- Researchpp 8311-8322Klement, I., Vilkovský, P., and Vilkovská, T. (2023). “Impact of sawmill processing on the yield and longitudinal warping of beech blanks,” BioResources 18(4), 8311-8322.AbstractArticlePDF
This study focused on the impact of the wood sawing pattern on 50 mm thick beech timber, followed by cross-cutting on the 3 m long, 50 × 50 mm beech blanks. The study analyzed two methods of cutting patterns of beech blanks (parallel to the surface of the timber and parallel to the grain fiber of the timber) regarding yield values and the size of longitudinal warping after air-drying. The yield values were higher (from 65.14 to 72.70 %) when producing long beech blanks using the method of sawing parallel to the timber’s axis (B) compared to parallel to the edge of the blank (from 60.38 to 68.40 %). Results showed that a crucial factor for choosing the cutting method (A or B) is the taper of the logs. For blanks with a taper ≥ 1.3 cm.m-1, it is more advantageous in terms of longitudinal warping and yield to use the method of sawing parallel to the timber’s axis.
- Researchpp 8323-8340Dong, L., Wang, L., Huan, X., Liu, B., Yi, B., Hu, H., and Huang, F. (2023). “Combustion and flue gas evolution characteristics of rice husk in various mixtures and layers with Al2O3 particles and char prepared with different pyrolysis parameters,” BioResources 18(4), 8323-8340.AbstractArticlePDF
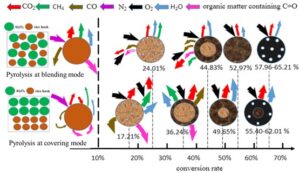
During pyrolysis and combustion experiments, rice husk and Al2O3 were combined in two ways, namely blending (rice husk was blended with Al2O3) and covering (rice husk was covered by Al2O3) modes, respectively. Rice husk biomass (RHB) char was prepared under different pyrolysis conditions. The resulting combustion characteristics and corresponding gaseous evolution of the biochar were compared. The maximum combustion rate decreased as particles accumulated, causing a shift in the thermo-gravimetric curve to higher temperature ranges. The combustion reaction was hindered in the covering mode. The combustion reactivity of the prepared char decreased as the char preparation time increased. During the char oxidation process, the release amounts of H2O and CO2 from char combustion increased first and then decreased, while the release amounts of CO, CH4, and organic components containing C=O gradually decreased with increasing char preparation time. Char prepared with the covering mode exhibited higher burn-out rates and combustion indices but lower activation energies required for combustion reaction. Additionally, the covering mode delayed the timely release of gases from the biomass heating in air, and the quantity of combustion gas released from the char produced at covering mode was greater than that released from the char produced at blending mode. The results obtained can improve the understanding of stacked biomass particles combustion process.
- Researchpp 8341-8361Pranowo, D., Savira, T. D., and Sukardi (2023). “Rice bran stabilization using autoclave and optimization of crude rice bran oil recovery using ultrasound-assisted extraction,” BioResources 18(4), 8341-8361.AbstractArticlePDF
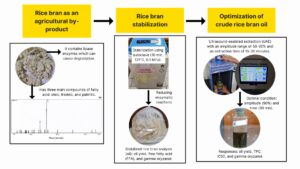
This research aimed to stabilize rice bran to reduce enzymatic reactions and optimize rice bran oil extraction using ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE). The optimization was performed using response surface methodology (RSM). The results showed that rice bran oil has three primary fatty acids (oleic, linoleic, palmitic). Stabilization of rice bran using an autoclave (121 °C) for 10 min was recommended, with oil yield (14.2%), free fatty acid/FFA (0.41%), and gamma oryzanol (16.1 ppm). The storage significantly affected oil yield and gamma oryzanol but not FFA (p>0.05). The untreated and stabilized rice bran FFA during 18-day storage ranged from 1.33 to 5.73% and 0.41 to 1.12%. This confirmed that stabilization could inactivate lipase enzymes by reducing FFA. The optimization showed that the linear model best explained oil yield, total phenol content (TPC), and antioxidant activity (IC50), while the 2FI model was best fitted for gamma oryzanol. The optimal condition was found for UAE extraction at an amplitude of 90% and a time of 30 min. Verifying optimal conditions resulted in oil yield (13.6%), TPC (44.8 mg GAE/g), IC50 (207.2 ppm), and gamma oryzanol (15.8 ppm). Further in-depth studies are required to investigate using green solvents in the UAE and gamma oryzanol purification.
- Researchpp 8362-8373Tichi, A. H., and Razavi, M. (2023). “Construction of cement composite using walnut shell reinforced with bacterial nanocellulose gel,” BioResources 18(4), 8362-8373.AbstractArticlePDF
The effect of nanocellulose on mechanical, physical, and morphological properties of composites made of walnut shell and cement was investigated. The mixing ratio of walnut shell as a lignocellulosic material with cement at three levels (10:90, 20:80, and 30:70) and nanocellulose at three levels (0%, 1%, and 3%, based on dry weight of cement) were considered as the variables. Boards were prepared according to the ISO 11925-2 (2020) specifications for the fire resistance properties and according to the DIN EN 634-1 (1995) specifications for the mechanical and physical properties. Morphological properties of composites and nano distribute were evaluated by scanning electron microscopic (SEM) imaging. The results showed that boards containing nanocellulose increased the mechanical properties compared with cement board without nanoreinforcement. The modulus of rupture, modulus of elasticity, and internal bonding of the boards decreased with increased walnut shell amount, and its maximum value was obtained when using 10% walnut shell. Nanocellulose remarkably reduced the fire resistance of the boards. The results from SEM showed that nanocellulose can fill the pores of the composite and create a uniform structure, and thus improved the strength of the boards.
- Researchpp 8374-8393Li, J., Liu, P., Chen, H., and Cheng, F. (2023). “Improved method to determine standard values of mechanical properties of original bamboo,” BioResources 18(4), 8374-8393.AbstractArticlePDF
The standard values of mechanical properties are important performance indexes of original bamboo as a sustainable building material. Such values should be determined by combining the requirement of confidence level and the number of samples. In this paper, systematic tests of longitudinal compression, bending, longitudinal tensile, longitudinal shear, transverse compression, and transverse tensile of bamboo were performed. Based on parametric and non-parametric methods, the influencing factors of the standard values of mechanical properties of bamboo were analyzed. A calculation method and prediction formulas were proposed and the standard values of mechanical properties of bamboo were determined. The results show that the choice of parametric method to calculate the standard value of bamboo strength in the case of a small number of samples may lead to distortion of the results, and the use of non-parametric analysis can effectively reduce the error.
- Researchpp 8394-8408Wang, F., Zhou, J., Miao, Z., Liu, Y., Feng, H., Lei, Y., Wang, T., and Xiong, C. (2023). “Simulation and experimental analysis of Camellia oleifera fruit shedding based on finite element explicit dynamics,” BioResources 18(4), 8394-8408.AbstractArticlePDF
As an important oil crop in China and the world, the harvesting problem of Camellia oleifera has attracted much attention. Research is needed on mechanical characteristics of harvesting equipment. Explicit dynamics was used to establish a finite element model under a simulated load response to the branch-pedicel-fruit system of C. oleifera to predict the fracture process at the pedicel junction. The separation mechanism of C. oleifera fruit was determined by measuring the constitutive parameters of fruit branches and pedicels and conducting separation experiments and explicit dynamics simulations on different hanging fruits. The maximum stress at the fruit pedicel was 1.14 MPa, and the goodness of fit between the simulation and experiment was approximately 89.5%, indicating that the branch-pedicel-fruit finite element model could accurately reflect the fruit shedding process and that the pedicel diameter was correlated positively with the separation force. This study provides technical parameters for the optimized design of existing C. oleifera harvesting equipment.
- Researchpp 8409-8431Yıldızbaş, N. T., Hernández, H. K., Yıldırım, H., and Güneş, Y. (2023). “Carbon emissions trading potential of Turkiye's forest,” BioResources 18(4), 8409-8431.AbstractArticlePDF
The current study emphasizes the inherent shortcomings of laws and policy approaches that are based on the premise that by increasing wood production, much more emission credits can be achieved by using wood in alternative uses. The article aims to exploit the financing of emission reductions, discuss how carbon sinks held in forest resources can be activated, traded, and financed, and explain how Turkiye’s forest carbon potential can be exploited. To make a comparative analysis of the situation of Turkiye at global level, Russian’s potential for carbon sequestration and its trade have been dealt with as a comparison by following quantitative research methodology. In this research, the calculation method has been used to determine the number of houses that are likely to be built in rural areas using wood materials, e.g., the construction of 100,000 houses with a construction area of 100 m2 per year. Consequently, the forest carbon generated by alternative scenarios contributes positively to the emission balance sheet, as well as climate change mitigation through carbon emission trade despite all legal and technical constraints. Although both countries have similar shortcomings of obtaining carbon credits and its trade, of course Russia has a promising situation in comparison with Turkiye with respect to the amount of carbon sequestered and the likelihood of its trade potential at global level.
