Abstract
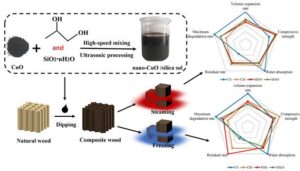
A nano-CuO/silica sol wood preservative was obtained by dispersing CuO nanoparticles in propylene glycol and silica sol. Scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, and compressive tests were conducted to investigate the effects of different post-treatments, i.e., steaming at 100 °C and freezing at -30 °C, on the variations in microstructure, mechanical, physical, and thermal stability properties of the preservative-impregnated wood. The results revealed that the mechanical properties, water resistance, and thermal stability of the impregnated specimens were greatly ameliorated. The steaming treatment resulted in a more uniform and dense distribution of the preservative in the blocks. The steaming treatment performed better in terms of enhancing the compressive strength of the specimens, while the freezing treatment was more effective in improving the thermal stability of the specimens. Both the steaming and freezing treatments can considerably improve the water resistance of the specimens. The different post-treatments retain the basic properties of the wood; however, they differ in the improved wood properties and provide a basis for their selection in the industrial production of nano-preservatives.
Download PDF
Full Article
Combination of Nano-CuO/Silica Sol Preservative with Various Post-treatments to Improve the Compressive Strength, Water Resistance, and Thermal Stability of Wood
Pengwei Zhao,a Hong Yang,b Guoqi Xu,a,* Congxun Huang,a and Yan Zhong a
A nano-CuO/silica sol wood preservative was obtained by dispersing CuO nanoparticles in propylene glycol and silica sol. Scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, and compressive tests were conducted to investigate the effects of different post-treatments, i.e., steaming at 100 °C and freezing at -30 °C, on the variations in microstructure, mechanical, physical, and thermal stability properties of the preservative-impregnated wood. The results revealed that the mechanical properties, water resistance, and thermal stability of the impregnated specimens were greatly ameliorated. The steaming treatment resulted in a more uniform and dense distribution of the preservative in the blocks. The steaming treatment performed better in terms of enhancing the compressive strength of the specimens, while the freezing treatment was more effective in improving the thermal stability of the specimens. Both the steaming and freezing treatments can considerably improve the water resistance of the specimens. The different post-treatments retain the basic properties of the wood; however, they differ in the improved wood properties and provide a basis for their selection in the industrial production of nano-preservatives.
Keywords: Wood preservatives; Steaming; Freezing; Physical and mechanical properties; Wood protection
Contact information: a: College of Engineering and Technology, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin 150040 China P. R.; b: College of Science, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin 150040 China P. R.;
* Corresponding author: xuguoqi_2004@126.com
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT

INTRODUCTION
Wood is an eco-friendly construction material, and soaring prices have made it an invaluable resource for the economic recovery of a country. It consists of three primary polymers, i.e., cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignins, and a small amount of low molecular weight components, called extractives. Wood is susceptible to insect damage, bacteria and fungi, and climate change, rendering its strength and dimensional stability poor, which hinders its wider utilization in numerous sectors, e.g., construction materials, packaging boxes, crates, joinery, wood panels, etc. (Gérardin 2016). Many different techniques have been tried to improve the physical and mechanical properties as well as the weather resistance of wood, e.g., heat treatment, chemical treatment, etc. (Kookandeh et al. 2014; Yang et al. 2021; Yona et al. 2021). Inorganic nanomodification has currently become a widespread study interest. In recent years, nanomaterials have been adopted by the wood protection industry for its great compatibility, large effective surface area, high dispersion stability, and reservoir effect that can provide long-term protection (Mohanraj and Chen 2007; Clausen 2012; Goffredo et al. 2017; Mattos et al. 2017; Teng et al. 2018). The porous nature of wood also provides a channel for the penetration of nanoparticles. After modification treatment, the nanoparticles not only form insoluble substances that fill the pores of the wood, but they also can enhance the strength of the cellulose and hemicellulose material, thus improving the physicochemical properties of the wood and increasing its use value (Huang et al. 2019; Schwarzkopf 2019). Nair et al. (2017, 2018) investigated the decay resistance of ZnO and CuO nanoparticles dispersed in propylene glycol impregnated rubber wood as well as the UV stabilization of the wood by ZnO, CeO2, and TiO2. In addition, Xu et al. (2020) prepared wood-silica composites via in-situ polymerization, which considerably improved the microstructure, thermal and mechanical properties, and hydrophobicity of the wood. Li et al. (2021) constructed nano-ZnO-coated veneers using common structural features of wood and nano-ZnO particles. As a result, the microstructure of the wood surface was changed, and the elastic modulus and hardness of the wood were enhanced, providing greater resistance to elastic deformation.
Although the above studies have made great progress, there remain some deficiencies. Given the poor water solubility of the copper nanoparticles (0.1 g per 100 mL of water) and their fixation method primarily occurring via deposition on the grain orifice and the third cell wall, the preservative becomes unevenly distributed and is easily dislodged in the treated material. Thus, this greatly limits the effectiveness of nanoparticle preservatives and poses an environmental hazard (Matsunaga et al. 2009; Stirling and James 2009). Improving the performance and practical application of nano-sized wood preservatives without sacrificing the physical or strength properties of the wood is of great importance in terms of wood protection. Research has shown that steaming treatments and freezing treatments can play a considerable role in improving wood permeability. A steaming treatment can cause a portion of the internal grain pore film to hydrolyze or peel off at the edge of the grain pore or cause physico-chemical changes in the wood. This increases the radius and number of effective capillaries, thus improved the permeability of the wood preservative in the wood. Additionally, under high temperature and high humidity conditions, the preservative reacts with the wood during a short period of time, thus improving the preservative resistance to leaching (Zhang and Cai 2006; Yu 2010). A freezing treatment is known as an environmentally friendly treatment and is used to reduce wood shrinkage, enhance wood stability, structural properties, and permeability, as well as increase the rate and extent of moisture and modifier migration within the wood, and contribute to wood modification treatments (Furuta et al. 2001; Awoyemi et al. 2010). Silica sol is a type of inorganic polymer with a large adsorption capacity, high specific surface area, high dispersibility, and strong permeability, which can be used as a suitable dispersant for nano-metal particles under certain conditions. In addition, it can increase the mechanical properties and thermal stability of the treated material (Mahltig et al. 2008; Pfeffer et al. 2012). Propylene glycol (PG) is a relatively non-toxic dispersant, which can also be used as a wood stabilizer and a carrier for inorganic chemicals into wood.
Very little information is available on improving the performance of nano-sized wood preservatives by physical treatments without sacrificing the original properties of the wood. In this study, PG and silica sol were employed as the base solution for the preparation of nano dispersions, and the nano-CuO/silica sol wood preservatives were prepared via mechanical co-blending. The effects of different times and temperatures on the compressive properties, water resistance, and thermal stability of the specimens were investigated by two different post-treatment methods, i.e., steaming at 100 °C (the highest steaming temperature that can be reached at atmospheric pressure) and freezing at a temperature of -30 °C (the lowest average winter temperature in northeast China is approximately -30 °C). This research provides a theoretical basis for the application of different treatment methods in the industrial production of nano preservatives.
EXPERIMENTAL
Materials
Sapwood lumber of poplar (Populus tomentosa Carr.) specimens were cut into 20 mm (longitudinal) × 20 mm (tangential) × 20 mm (radial) pieces; the wood was purchased from the Dongfanghong Forest Farm in Heilongjiang Province. All wood specimens were selected to ensure that they were free from knots, cracks, or other obvious defects. The CuO nanoparticles (50 nm) were purchased from Hebei Xinhu Metal Ltd., China, the propylene glycol (PG) was purchased from Tianjin Fuyu Fine Chemical Technology Ltd., China, and the silica sol was purchased from Shandong Yousuo Chemical Technology Ltd., China. All the chemicals used in the experiments were analytically pure.
Preparation of the Nano-CuO /Silica Sol Wood Preservative
The nano-CuO/silica sol wood preservative was prepared by adding 1.5 g of CuO nanoparticles to 100 g of a PG and silica sol complex reagent, where the mass ratio of PG to silica sol was 4 to 1. The mixture was then vigorously stirred in a high-speed homogenizer (FJ200, Shanghai Specimen Model Factory, Shanghai, China) at 20000 rpm to 23000 rpm for 30 min to obtain a homogeneous solution. The dispersion was then sonicated for 60 min via an ultrasonic generator (AK-080S Shenzhen Yujie Cleaning Equipment Ltd., Shenzhen, China) to prevent agglomeration. Finally, a stable nano-CuO/silica sol wood preservative was obtained.
Preservative Treatment
The wood specimens were immersed in an excess of solution and subjected to a minus 0.09 MPa vacuum for 1 h and then left in the solution for 24 hours at room temperature. Excess solution was wiped from the specimens which were weighed to obtain the control impregnated specimens (labeled as CIS). According to AWPA E10, the initial CuO or Si retention levels of the specimens were calculated using the following Eq. 1:
(1)
where m1 is the specimens weight before treatment (in g), m2 is the specimens weight after treatment (in g), C is the CuO or Si concentration in the solution (in g) per 100 g of treating solution and V is the volume of the treating wood sample (in cm3).
Post-treatments of Specimens
The obtained control impregnated specimens (labeled as CIS) were put into an autoclave (YXQ-LS-50SI, Shanghai Boxun Industrial Ltd., Shanghai, China) and a refrigerator (DB/C-100A, Guangdong Hisense Rongsheng Cold Storage Ltd., Yingkou, China) for the steaming and freezing post-treatments, respectively. The steaming post-treatment temperature was set at 100 °C and the treatment time was set to 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90 min to obtain the steaming impregnated specimens (labeled as SIS). The freezing post-treatment temperature was set at -30 °C, and the treatment time was 4 h, 6 h, 8 h, 10 h, 12 h, and 24 h to obtain the freezing impregnated specimens (labeled as FIS). The unimpregnated and post-treatment free control specimens were labeled as CS.
Pyrolysis Characteristics
The thermal degradation processes of the post-treatment impregnated materials were studied via thermogravimetric (TG) and differential thermogravimetric (DTG) methods using a thermogravimetric analyzer (SDT-Q600 Thermogravimetric Analyzer, TA Instruments, New Castle, DE).
Compression Parallel to the Grain
According to Chinese national standard GB/T 1935 (2009), the 30 mm (longitudinal) × 20 mm (tangential) × 20 mm (radial) size wood blocks were tested for compression parallel to the grain using an electronic universal mechanical testing machine (CMT-6305, Zhuhai Sansi Measuring Instruments Ltd., Zhuhai, China). The data were subjected to an analysis of variance and then means were compared using Tukey’s multiple comparison’s test (α=0.05).
Water Resistance Properties
According to Chinese national standards GB/T 1934.1 (2009), GB/T 1934.2 (2009), and GB/T 1932 (2009), the water absorption (WA), volume expansion extent (α), and anti-shrinkage efficiency (ASE) were measured to evaluate the waterproof performance of the different post-treatment specimens. The WAR, volume expansion (α), and ASE were calculated according to Eq. 2, Eq. 3, and Eq. 4, respectively,
(2)
(3)
(4)
where W1 and W0 are the weights of the wood samples before and after soaking in water for 20 d (g), respectively, Va is the volume of the sample that has reached dimensional stability after absorption of water (cm3), Vb is the volume of the dried sample (cm3), α0 and α1 are the volume expansion extents of the sample from dried to water absorption to dimensional stability for the control and different post-treatment specimens, respectively.
Characterization of Wood Specimens
Selected samples were used to examine the morphology and surface chemistry of the treated wood. The blocks were cut open and then sputter coated with gold before being examined via scanning electron microscopy (SEM) using a Quanta 20 scanning electron microscope (FEI, Hillsboro, OR) operated at 5 kV. The specimens were observed for differences in morphology around the ray parenchyma and vessels.
Two specimens subjected to a given post-treatment process were ground and passed through a 200 to 300 mesh screen and a small aliquot of the wood powder was analyzed via X-Ray diffraction (XRD) using a Shimadzu XRD-6100 (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). A second aliquot of wood powder was thoroughly mixed with KBr and compressed into a pellet that was analyzed via Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) on a Nicolette 6700 FTIR Spectrometer (Shenzen Risheng Technology Ltd, Shenzen, China) using 64 scans per sample that were averaged and baseline corrected. The resulting peaks were compared between the treated and non-treated poplar samples, as well as between the scans of wood from blocks subjected to different post-treatment processes.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Microscopic Distribution of the Preservatives under Different Post-treatments
No significant differences were found in the initial retention levels of CuO and Si among the different post-treatments, with mean retention levels of 9.47±0.02 kg/m3 and 37.03±4.07 kg/m3, respectively. The SEM observations (Fig. 1) clearly demonstrated the microstructural impregnation and filling effects of the different post-treatment specimens. In contrast to the CS, the conduits of the CIS were filled with a thick layer of preservative and unevenly distributed large particles of preservative. The steaming post-treatment improved the diffusion process of the preservative, thus promoting the penetration and diffusion of the copper ions into the wood structure. The preservative in the specimens adhered more uniformly and densely to the wood conduits and filled the grain pores in large quantities, and few uneven large particles of preservative were detected. The distribution of the preservatives in the FIS was uneven, and the form appeared granular, with only a small amount of preservative entering the grain pores.
Fig. 1. SEM images and spectrum of the impregnated specimens (a through d); the steaming treatment specimens (e through h); the freezing treatment specimens (i through l); and the corresponding SEM-EDS maps of Cu (c, g, and k) and Si (d, h, and l)
Fig. 2. XRD and FTIR spectral patterns of the wood specimens: (a) the FTIR spectral patterns of the SIS; (b) the FTIR spectral patterns of the FIS; (c) the XRD spectral patterns of the SIS; and (d) the XRD spectral patterns of the FIS
Characteristics and Schematic of Chemical Bonding
Figures 2a and 2b illustrate the variation in the intensity of the FTIR absorption peaks for different specimens. The absorbance peaks at approximately 560 and 934 cm-1 of the impregnated specimens represent the stretching vibration peak of Cu-O and the bending vibration peak of Cu-O-H, respectively (Sun 2012). In addition, the 1112 and 800 cm-1 absorbance peaks represent the anti-symmetric stretching vibration peak of Si-O-Si and the symmetric stretching vibration peak of Si-O-Si, respectively (Wang 2014). These peaks suggest that a large number of Cu-O, Si-O-Si, and Cu-O-H functional groups were available in the modified wood. The absorbance peaks at 1370 and 899 cm-1 are the characteristic peaks of C-H bending vibration and the hydroxyl group of cellulose, while 1736 and 1160 cm-1 are the characteristic peaks of carbonyl stretching vibration and C-O vibration in hemicellulose carboxylic acid; 1226, 1327, and 1424 cm-1 are the characteristic peaks of C-O stretching, -CH2 bending vibration of lignin acetyl, and -CH2 bending vibrations in hemicellulose carboxylic acid, respectively (Pandey 1999; Pandey and Nagveni 2007).
The intensity of the correlation bands at 1160 cm-1 almost completely disappeared in the steaming and freezing post-treatment specimens, and the intensity of the correlation bands at 1226 and 899 cm-1 decreased to some extent. In addition, the absorbance bands at 1736, 1424, 1370, and 1327 cm-1 also decreased in the freezing post-treatment specimens. According to previous studies, the binding of silica sol to wood is primarily a chemical reaction between the hydroxyl groups of the silica sol and the cell wall components (as shown in Fig. 3) (Xue et al. 2016; Sun et al. 2021). Furthermore, the CuO nanoparticles, which produce copper ions in wood, interact with the carboxyl, phenolic, carbonyl, and ether groups in the hemicellulose, lignins, and some hydroxyl groups of cellulose in the specimens. This in turn affects the fixation properties of the wood preservatives (Yu 2010; Xue et al. 2016).
Figures 2c and 2d display the XRD maps of the control and treated specimens. Based on the diffraction peak analysis, obvious diffraction peaks appeared at approximately 17°, 22°, and 34°, referring to the crystalline surfaces of lignocellulose (100), (002), and (040), respectively. According to the standard pattern of CuO, the diffraction peaks appeared at 33°, 35°, and 39° for the composite wood, which indicated the crystalline surfaces of CuO (110), CuO (002), and CuO (111), respectively (Yi et al. 2020). The diffraction peaks of (002) and (040) in the crystalline region and (101) in the non-crystalline region were still clearly visible in the post-treated wood compared to the control specimens. This indicated that the post-treatment did not change the coexistence of the crystalline and non-crystalline regions of the cellulose. Thus, the structure of the wood was not destroyed during the process. It is also apparent from Fig. 2c and 2d that the difference in the diffraction peak intensities between the groups of samples in the (002) and (040) planes was not substantial, which implies that the different post-treatments had little effect on the cellulose crystalline regions within the wood. Thus, both post-treatment samples retained the basic properties of the wood.
Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of the composite wood
Compression Parallel to the Grain
The results of the different post-treatment wood compressive strength analyses are shown in Fig. 4. The compressive strength of the CIS increased by 25.4% compared to the CS. The steaming post-treatment and the nano-CuO/silica sol preservative exhibited a good synergistic effect in terms of improving the compressive strength of the wood. With the SIS showing an increase of 22.8% to 32.1% compared to the CS, SIS45 showed the best results (Fig. 4a). However, according to statistical analysis, this result was not significant. After the steaming post-treatment time increased from 15 min to 90 min, the compression parallel to the grain of the post-treated specimens tended to increase and then decrease. In the steaming post-treatment specimens, the heat could be transferred more quickly through the CuO nanoparticles, and as the treatment time increased, the microgel particles and microfibers within the wood cell walls became fixed against each other and are relatively plasticized due to the drainage of water. This effect resulted in a slight increase in the smooth grain compressive strength (Hill 2006; Awoyemi et al. 2010).
As the freezing time increased from of 4 h to 24 h, the compression parallel to the grain of the FIS exhibited a gradual increase, but all the FIS had a lower compression parallel to the grain than the CIS (as shown in Fig. 4b). This can be explained by the expansion of the size of the free water crystallization zone in the cell lumen and the destruction of the cell wall structure during the slow freezing, which reduces its mechanical properties (Szmutku et al. 2013). In addition, the freezing treatment allowed the preservative to be unevenly distributed throughout the wood specimens, which did not permit greater effectiveness of the preservative (Fig. 1). Due to the presence of preservatives, the compression parallel to the grain of the FIS increased by 5.60% to 8.07% compared to the CS after 8 h to 24 h of freezing treatment, which alleviated the adverse effects of freezing on the mechanical properties of wood.
Fig. 4. Compression parallel to the grain of control and post-treated specimens: (a) the compression parallel to the grain of the SIS; and (b): the compression parallel to the grain of the FIS (Note: CS: control specimens; CIS: control impregnated specimens; SIS15: 15 min steaming treatment; and FIS4: 4 h freezing treatment). Columns with the same letter do not differ significantly using Tukey’s studentized range test (α = 0.05).
The water resistance and moisture absorption resistance of the different post-treatment specimens were examined by evaluating the water absorption (WA), volume expansion extent (α), and anti-shrinkage efficiency (ASE) (Fig. 5). The nano-CuO/silica sol preservative filled the cell cavity of the wood and cured to form a thick film in the cell walls, blocking most microscopic channels and limiting the diffusion of water throughout the wood (Fig. 1). Moreover, the SiO2 in the preservative was either found in the cell wall or filled the cell lumens or was bound to the hydroxyl groups in the amorphous zone of the cell wall, which limited the water absorption of the wood. The ability to absorb water molecules decreased, thus, the swelling extent decreased. In comparison with the CS, the CIS showed a 20.78% reduction in WA, a 21.96% reduction in volumetric swelling, and a 21.96% increase in ASE.
Fig. 5. Water resistance properties of the different post-treatment specimens: (a) the WAR and α of the SIS; (b) the WAR and α of the FIS; (c) the ASE and moisture content of the SIS; (d) the ASE and moisture content of the FIS (Note: CS: control specimens; CIS: control impregnated specimens; SIS15: 15 min steaming treatment; and FIS4: 4 h freezing treatment)
The WA of the SS decreased by 4.92% to 12.13% and the volume expansion decreased by 1.72% to 12.01% compared to the CIS, where the steaming post-treatment for 30 min yielded the greatest reduction in the WA and volume expansion (Fig. 5a). Within a high temperature and high humidity environment, the microgum particles and microfibers within the cell walls of wood were not only held close to each other due to the discharge of water, but also fixed by relative plasticization due to the high temperature. The structure of a specimen is not easy to recover once changed, so once a certain degree of moisture absorption capacity is lost, the dimensional stability of the wood is relatively improved (Diniz et al. 2004; Salmén and Stevanic 2018). Additionally, the hydroxyl groups in the wood cell walls are highly water absorbent, and the high temperature treatment may reduce the utilization of hydroxyl groups, which in turn reduced the water absorption strength of the wood cells (Thybring et al. 2017). The WA and volume swelling of the SIS shows a decreasing and then increasing trend, likely due to the decrease in the binding of SiO2 to the hydroxyl groups of the wood cell wall (Fig. 3).
The ASE of the specimens treated via steaming increased 6.10% by 42.71% as the treatment time increased from 15 min to 75 min compared to the CIS, with the best ASE occurring after 30 min of steaming treatment (Fig. 5b). Research has previously shown that the presence of infiltrates in the wood ducts and the presence of grain pore membranes are the primary reasons why wood is prone to wrinkling, and that heat treatment using steam, hot water, or other means as a medium can open the micro-pores blocked by infiltrates in the grain pore membranes and cell cavities of wood; in addition, it can break the airtightness and the improve wood permeability, thus increase the ASE of wood (Zhao 2013). With the extension of the total steam treatment time, the volume resistance to dry shrinkage of the SIS showed a gradual decrease, with the decrease in water content and saturation of the specimen may be the reason for this change (Chafe 1993; Peng et al. 2012).
The WA and the volume expansion of the FIS gradually decreased with time, while the ASE gradually increased (Fig. 5c). The WAE and volume expansion of the 4 h to 24 h FIS decreased by 2.79% to 9.02% and 3.66% to 13.27%, respectively, compared to the CIS. The wood WA decreased as the extractive content increases, and wood extractives migrate into the cell wall during freezing, which considerably decreased the hydrophilicity of the material (Awoyemi 2006, 2010). In particular, the freezing treatment resulted in wood xylem embolism, which reduced the hydraulic conductivity of the wood cells and contributed to the reduction of the WA and volume swelling extent of the specimens (Mayr et al. 2006).
The ASE of the FIS was increased by 13.02% to 47.17% compared with the CIS (Fig. 5d). One of the reasons for the freezing treatment reducing the extent of shrinkage is that the cell cavities with a high water content expand due to freezing, which leads to the rupture of the grain pore membrane. In addition, air bubbles are generated in the wood cell cavity, which destroys the air tightness of the wood cells. However, the migration and redistribution of the adsorbed water and extractables in the cell wall and microcapillaries caused the “cold contraction” of the wood cell wall, which increased the strength of the cell wall and reduced the extent of shrinkage of the specimen (Wang et al. 2003).
Pyrolysis Characteristics
The comparative analysis of the TG and DTG for the different post-treatment specimens is presented in Fig. 6. In relation to the CS, the weight loss of the CIS was reduced, the carbonization onset temperature (pyrolysis termination temperature) was decreased, and the pyrolysis residue was increased. The maximum weight losses of the CS and CIS were 26.53%/min and 16.78%/min, respectively. The thermal degradation residues were 8.66% and 18.16%, respectively, and the carbonization onset temperatures were 405 °C and 385 °C, respectively (Table 1; Fig. 6a, 6b). The carbonization temperature was lowered, which indicated that the SiO2 in the preservative was either chemically cross-linked with the cellulose and other components or covered on its surface, accelerating the carbonization procedure, and exerting a certain protective effect on the wood. In addition, the nano-CuO in the preservative enhanced the thermal conductivity of the wood, making the CIS uniformly heated, unlike the CS which were susceptible to local heating, thus retarding the burning of the wood.
Fig. 6. TG and DTG comparison analysis of the different post-treatments
The thermal degradation onset temperature (T1) of the different post-treatment specimens shifted towards a high temperature, and the temperature corresponding to the maximum degradation rate (T2), as well as the final decomposition temperature (T3), shifted towards a low temperature compared to the CS, which indicated the enhancement of the thermal stability of the specimens, as shown in Table 1 and Fig. 6c through 6f. The degradation temperatures of the specimens (T1, T2, and T3) were not drastically affected by the different post-treatment methods. In terms of the residue mass fraction (Table 1), the FIS had more residue mass fraction, which may be due to the fact that the freezing treatment affected the moisture content of the specimens less and the SiO2 could bind more to the wood, which raised the thermal stability of the specimens. In addition, the migrating decomposition of the wood cell extracts led to a decrease in the wood pH, and the released acidic chemicals can serve as flame retardants, carbonizing the wood at low temperatures and forming an insulating layer on the surface, enhancing the thermal stability of the specimens (Pries and Mai 2013).
Table 1. Thermal Degradation Temperature and Residue Mass of the Post-Treatment Specimens
CONCLUSIONS
- The CuO/silica sol preservative improved the water resistance, smooth grain compressive strength, and thermal stability of poplar wood. The compression parallel to the grain of the steaming treatment specimens increased and then decreased with an increasing treatment time. The best results were found after 45 min of steaming treatment. However, according to statistical analysis, this result was not significant. The compression parallel to the grain of the freezing treatment specimens were lower than that of the impregnated specimens.
- Both the steaming and freezing treatments considerably improved the water resistance of the specimens, especially the steaming treatment for 30 min and the freezing treatment for 24 h, which had the best result. Compared with the steaming treatment, the freezing treatment was more effective in improving the thermal stability of the specimens.
- The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images disclosed that the steaming treatment resulted in a more uniform and dense distribution of the nano preservative in the wood, while the freezing treatment created a granular appearance of the preservative. The Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) results showed that the different post-treatments facilitated the binding of the active ingredients in the preservative to the wood and had little effect on the crystallinity of the wood, preserving the basic properties of the wood.
- The experimental results provided a new reference for improving the effectiveness of nano wood preservatives and can serve as a basis for the selection of different treatments in the industrial production of nano preservatives.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful for the support of the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31500470) and the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province, China (Grant No. C 2016014).
REFERENCES CITED
Awoyemi, L. (2006). “Influence of prefreezing on the fibre saturation point, sorption and swelling properties of birch (Betula pubescens) wood,” Journal of the Institute of Wood Science 17(4), 225-227. DOI: 10.1179/wsc.2006.17.4.225
Awoyemi, L., Femi-Ola, T. O., and Aderibigbe, E. Y. (2010). “Pre-freezing as a pre-treatment for thermal modification of wood. Part 2: Surface properties and termite resistance,” Journal of the Indian Academy of Wood Science 7(1-2), 19-24. DOI: 10.1007/s13196-010-0004-1
Chafe, S. C. (1993). “The effect of boiling on shrinkage, collapse and other wood-water properties in core segments of Eucalyptus regnans F. Muell,” Wood Science and Technology 27(3), 205-217. DOI: 10.1007/BF00192817
Clausen, C. A. (2012). Enhancing Durability of Wood-Based Composites with Nanotechnology (FPL-GTR-218), U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Products Laboratory, Madison, WI, USA.
Diniz, J. M. B. F., Gil, M. H., and Castro, J. A. A. M. (2004). “Hornification – Its origin and interpretation in wood pulps,” Wood Science and Technology 37, 489-494. DOI: 10.1007/s00226-003-0216-2
Furuta, Y., Obata, Y., and Kanayama, K. (2001). “Thermal-softening properties of water-swollen wood: the relaxation process due to water soluble polysaccharides,” Journal of Materials Science 36(4), 887-890. DOI: 10.1023/A:1004838831791
GB/T 1932 (2009). “Method for determination of the shrinkage of wood,” Standardization Administration of China, Beijing, China.
GB/T 1934.1 (2009). “Method for determination of the water absorption of wood,” Standardization Administration of China, Beijing, China.
GB/T 1934.2 (2009). “Method for determination of the swelling of wood,” Standardization Administration of China, Beijing, China.
GB/T 1935 (2009). “Methods of testing in compressive strength parallel to grain of wood,” Standardization Administration of China, Beijing, China.
Gérardin, P. (2016). “New alternatives for wood preservation based on thermal and chemical modification of wood- a review,” Annals of Forest Science 73(3), 559-570. DOI: 10.1007/s13595-015-0531-4
Goffredo, G. B., Accoroni, S., Totti, C., Romagnoli, T., Valentini, L., and Munafo, P. (2017). “Titanium dioxide based nanotreatments to inhibit microalgal fouling on building stone surfaces,” Building and Environment 112, 209-222. DOI: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2016.11.034
Hill, C. A. (2006). Wood Modification: Chemical, Thermal and Other Processes, John Wiley and Sons, Hoboken, NJ.
Huang, Y. G., Li, G., and Chu, F. (2019). “Modification of wood cell wall with water-soluble vinyl monomer to improve dimensional stability and its mechanism,” Wood Science and Technology 53, 1051-1060. DOI: 10.1007/s00226-019-01112-0
Kookandeh, M. G., Taghiyari, H. R., and Siahposht, H. (2014). “Effects of heat treatment and impregnation with zinc-oxide nanoparticles on physical, mechanical, and biological properties of beech wood,” Wood Science and Technology 48(4), 727-736. DOI: 10.1007/s00226-014-0627-2
Li, J., Wang, Y., Zhao, H., and Qi, D. (2021). “Research on the gradual process of the structure and mechanical properties of NanoZnO-coated veneer,” Wood Science and Technology 55(1), 243-25. DOI: 10.1007/s00226-020-01241-x
Mahltig, B., Swaboda, C., Roessler, A., and Böttcher, H. (2008). “Functionalising wood by nanosol application,” Journal of Materials Chemistry 18(27), 3180-3192. DOI: 10.1039/b718903f
Matsunaga, H., Kiguchi, M., and Evans, P. D. (2009). “Microdistribution of copper-carbonate and iron oxide nanoparticles in treated wood,” Journal of Nanoparticle Research 11(5), 1087-1098. DOI: 10.1007/s11051-008-9512-y
Mattos, B. D., Tardy, B. L., Magalhães, W. L. E., and Rojas, O. J. (2017). “Controlled release for crop and wood protection: recent progress toward sustainable and safe nanostructured biocidal systems,” Journal of Controlled Release 262, 139-150. DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.07.025
Mayr, S., Cochard, H., Améglio, T., and Kikuta, S. B. (2006). “Embolism formation during freezing in the wood of Picea abies,” Plant Physiology 143(1), 60-67. DOI: 10.1104/pp.106.085704
Mohanraj, V. J., and Chen, Y. (2007). “Nanoparticles – A review,” Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 5(1), 561-673. DOI: 10.4314/tjpr.v5i1.14634
Nair, S., Nagrajappa, G. B., and Pandey, K. K. (2018). “UV stabilization of wood by nano metal oxides dispersed in propylene glycol,” Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology 183, 1-10. DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.04.007
Nair, S., Pandey, K. K., Giridhar, B. N., Vijayalakshmi, G. (2017). “Decay resistance of rubberwood (Hevea brasiliensis) impregnated with ZnO and CuO nanoparticles dispersed in propylene glycol.” International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation 122, 100-106. DOI: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.05.008
Pandey, K. K. (1999). “A study of chemical structure of soft and hardwood and wood polymers by FTIR spectroscopy,” Journal of Applied Polymer Science 71(12), 1969-1975. DOI: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4628(19990321)71:12<1969::aid-app6>3.0.co;2-d
Pandey, K. K., and Nagveni, H. C. (2007). “Rapid characterisation of brown and white rot degraded chir pine and rubberwood by FTIR spectroscopy,” Holz als Roh-und Werkstoff 65(6), 477-481. DOI: 10.1007/s00107-007-0181-9
Peng, Y. Q., Li, F., Yi, S. L., Zeng, L. D. (2012). “Effects of steaming on dimensional stability and transverse permeability of poplar,” Forestry and Grassland Machinery 23(6), 23-26+62. DOI: 10.13594/j.cnki.mcjgjx.2012.06.008
Pfeffer, A., Mai, C., and Militz, H. (2012). “Weathering characteristics of wood treated with water glass, siloxane or DMDHEU,” European Journal of Wood and Wood Products 70(1-3), 165-176. DOI: 10.1007/s00107-011-0520-8
Pries, M., and Mai, C. (2013). “Fire resistance of wood treated with a cationic silica sol,” European Journal of Wood and Wood 71(2), 237-244. DOI: 10.1007/s00107-013-0674-7
Salmén, L., and Stevanic, J. S. (2018). “Effect of drying conditions on cellulose microfibril aggregation and hornification,” Cellulose 25, 6333-6344. DOI: 10.1007/s10570-018-2039-1
Schwarzkopf, M. (2019). “Densified wood impregnated with phenol resin for reduced set-recovery,” Wood Material Science & Engineering 16(1), 35-41. DOI: 10.1080/17480272.2020.1729236
Stirling, R., and James, D. (2009). “Re-distribution of copper in the cell walls of wood treated with micronized copper quat,” in: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the International Research Group on Wood Protection, 24-28 May, Beijing, China,
Sun, H. Y. (2012). The Research of Synthesis and Surface Complexation of Copper Oxide and Basic Cupric Carbonate Nano Mineral (in Chinese), Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Jinan, Jinan, China.
Sun, Z., Lv, J., Wang, Z., Wu, Y., Yuan, G., and Zuo, Y. (2021). “Sodium silicate/waterborne epoxy resin hybrid-modified Chinese fir wood,” Wood Science and Technology 55(3), 837-855. DOI: 10.1007/s00226-021-01287-5
Szmutku, M. B., Campean, M., and Porojan, M. (2013). “Strength reduction of spruce wood through slow freezing,” European Journal of Wood and Wood Products 71, 205-210. DOI: 10.1007/s00107-013-0667-6
Teng, T.-J., Arip, M. N. M., Sudesh, K., Nemoikina, A., Jalaludin, Z., Ng, E.-P., and Lee, H.-L. (2018). “Conventional technology and nanotechnology in wood preservation: A review,” BioResources 13(4), 9220-9252. DOI: 10.15376/biores.13.4.Teng
Thybring, E. E., Thygesen, L. G., and Burgert, I. (2017). “Hydroxyl accessibility in wood cell walls as affected by drying and re-wetting procedures,” Cellulose 24, 2375-2384. DOI: 10.1007/s10570-017-1278-x
Wang, W. (2014). Fast-Growing Poplar Wood Modified with Silica Sol/VAE (in Chinese), Ph.D. Dissertation, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, Changsha, China.
Wang, X., Liu, X., Xue, Z., and Zhao, G. (2003). “Study on mechanism of decreasing wood collapse by pre-freezing,” Scientia Silvae Sinicae 39(5), 95-99+182
Xu, E., Zhang, Y., and Lin, L. (2020). “Improvement of mechanical, hydrophobicity and thermal properties of Chinese fir wood by impregnation of nano silica sol.” Polymers 12(8), 1632. DOI: 10.3390/polym12081632
Xue, W., Ruddick, J. N. R., and Kennepohl, P. (2016). “Solubilisation and chemical fixation of copper (II) in micronized copper treated wood,” Dalton Transactions 45(9), 3679-3686. DOI: 10.1039/c5dt03159a
Yang, H., Gao, M., Wang, J., Mu, H., and Qi, D. (2021). “Fast preparation of high-performance wood materials assisted by ultrasonic and vacuum impregnation,” Forests 12(5), 1-12. DOI: 10.3390/f12050567
Yi, T., Guo, C., Zhao, S., Zhan, K., and Du, G. (2020). “The simultaneous preparation of nano cupric oxide (CuO) and phenol formaldehyde (PF) resin in one system: Aimed to apply as wood adhesives,” European Journal of Wood and Wood Products 78(3), 471-482. DOI: 10.1007/s00107-020-01514-z
Yona, A. M. C., Žigon, J., Matjaž, P., and Petrič, M. (2021). “Potentials of silicate-based formulations for wood protection and improvement of mechanical properties: A review,” Wood Science and Technology 55, 887-918. DOI: 10.1007/s00226-021-01290-w
Yu, L. L. (2010). Effects of Post-Treatments on Leaching and Fixation Mechanism of ACQ-D Treated Wood (in Chinese), Ph.D. Dissertation, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China.
Zhang, Y., and Cai, L. (2006). “Effects of steam explosion on wood appearance and structure of sub-alpine fir,” Wood Science and Technology 40(5), 427-436. DOI: 10.1007/s00226-005-0053-6
Zhao, X. L. (2013). Study on the Collapse Recovery Technology and Mechanism of Poplar Plantation (in Chinese), Ph.D. Dissertation, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Huhhot, China.
Article submitted: August 5, 2021; Peer review completed: September 8, 2021; Revised version received and accepted: September 12, 2021; Published: September 23, 2021.
DOI: 10.15376/biores.16.4.7444-7460
