Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 1781-1793Cao, J., Li, R., Qu, H., Wang, P., Fu, J., Chen, M., and Chen, Y. (2022). "Effects of the membrane-covered technology and superphosphate on the compost quality and nitrogen-containing gas emissions during aerobic composting," BioResources 17(1), 1781-1793.AbstractArticlePDF
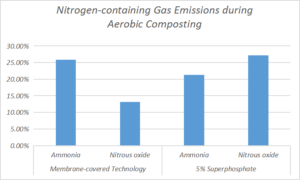
A lab-scale experiment was conducted to assess effects of the membrane-covered technology and superphosphate on the compost quality and emissions of nitrogen-containing gases during aerobic composting. The results showed that the membrane-covered technology increased the temperature of the compost pile and accelerated degradation of organic matter. The membrane-covered (T1) sample attained a germination index (GI) of 50% and 80%, approximately 2 and 9 d earlier, respectively, relative to the control (CK) sample. However, the application of superphosphate might have an adverse effect on the GI value. The NH3 and N2O emissions during the aerobic composting were decreased by 25.8% and 13.1%, respectively, for the T1 sample compared to the CK sample, while these were reduced correspondingly by 21.3% and 27.2% for the superphosphate addition (T2) sample. Compared with the superphosphate addition, the membrane-covered approach reduced the NH3 emission but not the N2O emission. Thus, the membrane-covered aerobic composting is a potential technology for the adequate utilization of organic waste as a resource.
- Researchpp 1794-1804Doczekalska, B., Bartkowiak, M., Łopatka, H., and Zborowska, M. (2022). "Activated carbon prepared from corn biomass by chemical activation with potassium hydroxide," BioResources 17(1), 1794-1804.AbstractArticlePDF
With the depletion of fossil fuel feedstocks, the lignocellulosic biomass, including the agro-wastes, can serve as the best alternative source to produce activated carbons (ACs). Corn biomass (corn leaves, stalks, cobs without kernels, silk, and kernels) were used to produce ACs in a two-step process. Crushed plant material was carbonized at 600 °C and then the obtained carbon was activated using potassium hydroxide at 750 °C. The content and type of surface oxygen functional groups were determined by the Boehm method and infrared spectroscopy. The porous structure of the obtained AC was determined by the nitrogen adsorption/desorption method at -196 °C, and the thermal resistance by the thermogravimetric method. The iodine number was also determined. The ACs derived from corn biomass were characterized with surfaces rich in chemical groups and revealed a highly developed porous structure. The specific BET surface area ranged from 1600 m2/g to 1965 m2/g. High values of iodine number approx. 1300 mg/g, indicated an extensive system of pores and their good adsorption properties.
- Researchpp 1805-1817Taheri, A. A., Rahmaninia, M., and Khosravani, A. (2022). "Interaction of the electrical conductivity of recycled pulp colloidal suspension with chitosan and bentonite as a papermaking additive system," BioResources 17(1), 1805-1817.AbstractArticlePDF

The performance of chitosan biopolymer-bentonite microparticle system in recycled pulp colloidal suspension of old corrugated containers with different electrical conductivities was considered. Various instrumental analyses (atomic force microscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy, dynamic light scattering, and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy) were applied to characterize the applied chemicals. The results indicated that the mentioned system could increase the process and mechanical properties in comparison to the control sample. Although increasing the electrical conductivity of the recycled pulp decreased the performance of chitosan-bentonite system to some extent, the system was successful in its mission even at the highest electrical conductivity, i.e., increasing the retention, drainage, tensile index, tear index, bending strength and internal bonding strength, with improvement of approximately 41%, 32%, 8%, 16%, 26%, and 57% in comparison with the control samples, respectively. Therefore, this method can be a fascinating approach to the papermaking process. Moreover, the probable reasons of the mentioned achievements were considered and discussed.
- Researchpp 1818-1835Mihailovic, V., Miric-Milosavljevic, M., Djurkovic, M., Mladenovic, G., Milosevic, M., and Trajkovic, I. (2022). "Loading rate effects on MOE and MOR distributions in testing of small clear beech wood specimens," BioResources 17(1), 1818-1835.AbstractArticlePDF
Distributions of the modulus of elasticity (MOE) and modulus of rupture (MOR) were characterized at three loading rates for small clear beech specimens in static bending. The correlation between MOE and MOR for all three loading rates was significant, but it weakened with increasing load rates. The analysis of the characteristics of empirical distributions, as well as the preliminary selection of the theoretical distributions for MOE and MOR, were performed on the basis of L-moments and L-moment diagrams. According to the standard for testing small specimens, MOE and MOR are determined as the arithmetic mean of the sample. Usage of the arithmetic mean is justified when the analyzed quantity is symmetrically distributed. It was found that the distribution of MOE and MOR is not always symmetric. The loading rate influences the shapes of the MOE and MOR empirical distributions, and consequently the choice of theoretical distribution. The general extreme value distribution stood out as the best one for both MOE and MOR, regardless of the loading rate, and the second overall ranked distribution is the three-parameter Weibull distribution. The loading rate affected the value of the fifth percentile in MOR, when determined from both the empirical and theoretical distributions.
- Researchpp 1836-1854Alvarez Valverde, M., Horvath, L., and Bouldin, J. (2022). "Wood pallet performance analysis with palletized drums in distribution and warehousing," BioResources 17(1), 1836-1854.AbstractArticlePDF
As an integral part of the supply chain, wooden pallets are produced in large quantities, with 849 million new and recycled wooden pallets being manufactured annually in the industry. Pallets are currently designed using a uniformly distributed load to determine the load capacity. This highly generalized approach often leads to overdesign and increased material utilization. Due to a phenomenon called load bridging, when discrete packages such as corrugated boxes or industrial drums are shipped on a pallet, the weight of the load tends to distribute unevenly. This can lead to an increased load capacity for the pallet. Industrial drums are commonly used to transport large amounts of liquids and chemicals; however, their load bridging effect has not been previously researched. The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of 55-gallon drums on the pressure distribution and deflection of stringer class wooden pallets using multiple support conditions and pallet designs. Results of the study indicated that loading pallets with drums significantly reduces the deflection of the pallet in all support conditions when compared to a uniformly distributed load. It was also observed that plastic and metal drums distributed their load to the pallets differently, which resulted in significantly different load bridging effects for each drum type.
- Researchpp 1855-1867Filgueira Amorim França, T. S., Nistal França, F. J., Seale, R., Ross, R. J., and Shmulsky, R. (2022). "Flexural properties of visually graded southern pine 2x4 and 2x6 structural lumber," BioResources 17(1), 1855-1867.AbstractArticlePDF
Flexural properties of visually graded southern pine structural lumber were evaluated. Several grade controlling characteristics were considered relative to bending properties and compared with current design values. A total of 751 southern pine lumber specimens were obtained from a broad spectrum of regions in the southeastern United States. Visually graded No. 2, nominally two inch thick specimens, in four and six inch widths, were obtained from commercial sawmills. All specimens were evaluated by a certified grader in the laboratory. Actual dimensions, weight, and moisture content (MC) were measured. Growth and manufacturing related characteristics were identified and classified into two categories: strength reducing characteristics (SRC) and grade reducing characteristics (GRC). Specific gravity (SG), bending modulus of elasticity (MOE), and modulus of rupture (MOR), were determined for each specimen. The presence of knots was identified as the most significant SRC; their presence had the most significant impact on SG, MOE and MOR. For GRC, specimens with knots, warp and specimens that fell into the category none, were significantly lower in SG, MOE and MOR. MOE and the allowable design bending strength values yielded in this study met the current design value criteria for both widths tested.
- Researchpp 1868-1880Wan Abdul Rahman, W., Md Yatim, A., Mansor Manshor, R., and Yuziah Mohd Yunus, N. (2022). "Performance of particleboard made with Neolamarckia cadamba, Leucaena leucocephala, and their 50:50 Admixtures," BioResources 17(1), 1868-1880.AbstractArticlePDF
The performance of a particleboard seems to be related to the chemical constituents of the species and the size distribution the particles. Neolamarckia cadamba (NC) and Leucaena leucocephala (LL) are fast growing species and good potential resources for particleboard production. This study examined the chemical contents of both species, as well as the mechanical and physical performance of particleboard made with 100% NC, 100% LL, and their 50:50 admixtures. High moisture resistance boards were prepared using melamine urea formaldehyde (MUF) at a content of 10, 12, and 14 %. The 30% extra buffering of LL translated to its lower performance for both mechanical and physical properties. The 50:50 admixtures provided enticing results, as it counteracts the impact of lowered performance of 100% LL. All boards passed the mechanical requirements of the BS EN 312 (2003) standard, but they did not meet the requirement for thickness swelling. The internal bond for cyclic test only failed for 100% LL with 10% resin added. With use of wax, the potential of improvement in swelling properties is possible.
- Researchpp 1881-1891Cajova Kantova, N., Caja, A., Belany, P., Kolkova, Z., Hrabovsky, P., Hecko, D., and Micko, P. (2022). "Mechanical and energy properties of pellets formed from walnut shells blended with spruce sawdust," BioResources 17(1), 1881-1891.AbstractArticlePDF
Various waste materials have energy potential. It is important to make use of this potential and prepare the product for further use by treating the waste. Treatments such as compressing waste into pellets leads to increasing the energy density of this fuel, which benefits transport and storage costs. However, low bulk density, high ash content, low-ash melting temperatures, and low calorific values of non-woody pellets can cause problems during their combustion. This article deals with the energy usage of walnut shells, which were blended with spruce sawdust in various amounts and compressed into pellets. The mechanical and energy properties of these were measured and compared with recommended or standardized values. The formed pellets met the quality limit for bulk density, ash content, moisture content, the content of nitrogen and sulfur, and net calorific value according to ISO 17225. However, low ash melting temperatures were noticed for pellets from pure walnut shells, and also lower mechanical durability for produced pellets with walnut shells contents higher than 10% were detected.
- Researchpp 1892-1904Bandao-Antonio, J., and Diaz, J. M. A. (2022). "Sayote (Sechium edule) fiber isolated at varying acid hydrolysis time and reinforcement to starch/PVOH composite blends," BioResources 17(1), 1892-1904.AbstractArticlePDF
The chemo-mechanical extraction of sayote (Sechium edule) fibers and their use as reinforcement to biodegradable starch/polyvinyl alcohol composite blends were studied. Fourier transform infrared analysis revealed the removal of hemicelluloses from the fiber surface after 7 and 10 h of acid hydrolysis time. Scanning electron micrographs show the removal of surface impurities during chemical-mechanical treatment. There was a more exposed fiber surface after 7 and 10 h of acid hydrolysis time. However, fibers acid hydrolyzed for 10 h revealed the presence of more cracks on the fiber surface. X-ray diffraction analysis showed that 7 h acid hydrolyzed fiber had the highest relative crystallinity index of 64.9% as compared to the fiber that was acid hydrolyzed for 10 h with a relative crystallinity index of 58.6%. Both 7 h and 10 h acid hydrolyzed fibers gave 20% yield after extraction. The fiber that was hydrolyzed for 7 h was used as reinforcement to starch/polyvinyl alcohol composite and gave a bending and tensile strength of 5.36 MPa. The unreinforced composite gave a bending and tensile strength of 2.85 MPa. The scanning electron micrograph of the reinforced composite revealed a more homogeneous surface and lesser starch granule exposure as compared to the unreinforced composite with a rough and bumpy surface. The onset of degradation and carbonization of the fiber reinforced composite was seen at around 280 and 580 °C respectively.
- Researchpp 1905-1915Zhang, D., Liu, H., Jin, Y., Pan, D., Yu, W., Lu, L., Lü, T., and Zhao, H. (2022). "The simultaneous and synergistic sorption of phenanthrene and cadmium using biomass derived from rice roots," BioResources 17(1), 1905-1915.AbstractArticlePDF
Evaluating the sorption performance of coexisting phenanthrene and cadmium on rice roots is critical for a better understanding of plant sorption and uptake of combined pollutants. Batch sorption kinetics and isotherms of phenanthrene and cadmium on rice root biomass, as well as key factors in both single and binary systems, were evaluated to access any potential synergistic effects. Results showed that rice root biomass effectively and simultaneously removed phenanthrene and cadmium from aqueous solutions. The presence of a co-solute led to synergistic effects on the sorption, enhancing the affinity parameters, i.e., the Kd (linear model), from 2530 to 3970 L/kg for phenanthrene, and the KF (Freundlich model), from 640 to 777 L/kg for cadmium. The well fitted pseudo-second-order kinetics implied that the coexisting pollutants slowed the sorption rates, decreasing the sorption rate (k2) from 0.185 to 0.155 g/mg/min for phenanthrene and from 0.0361 to 0.00146 g/mg/min for cadmium. The results suggested that further studies should carefully evaluate the remediation and risk-assessment in rice-arable soil under combined pollution.
