Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 4006-4031Brito, A., Suarez, A., Pifano, A., Reisinger, L., Wright, J., Saloni, D., Kelley, S., Gonzalez, R., Venditti, R., and Jameel, H. (2023). “Environmental life cycle assessment of premium and ultra hygiene tissue products in the United States,” BioResources 18(2), 4006-4031.AbstractArticlePDF
Under the controversial concern of using virgin fibers in hygiene tissue products, mostly Bleached Eucalyptus Kraft (BEK) and Northern Bleached Softwood Kraft (NBSK), consumers are responding by purchasing self-labeled sustainable products. As of today, there are no established sustainability reported results to inform consumers about the carbon footprint of hygiene tissue. To fill this gap, this study used Life Cycle Assessment to evaluate the environmental impacts across the supply chain (cradle to gate) to produce Premium and Ultra grades of bath tissue, including the production of feedstock, pulp production, and tissue production stages, with focus on Global Warming Potential (GWP). The results showed that one air-dried metric ton (ADmt) of BEK pulp had an associated GWP of 388 kgCO2eq, whereas one ADmt of NBSK pulp presented values ranging between 448 and 596 kgCO2eq, depending on the emissions allocation methodology used. It was estimated that the GWP of one finished metric ton of tissue weighted average could range from 1,392 to 3,075 kgCO2eq depending on mill location, electricity source, and machine technology. These results provide an understanding of the factors affecting the environmental impact of hygiene tissue products, which could guide manufacturers and consumers on decisions that impact their carbon footprint.
- Researchpp 4032-4054Bao, M.-H., Yu, F.-L., Yuan, B., Xie, C.-X., and Yu, S.-T. (2023). “Aqueous-phase hydrogenation of α-pinene to cis-pinane using an amphiphilic Ni-based catalyst,” BioResources 18(2), 4032-4054.AbstractArticlePDF
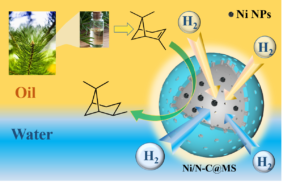
Alpha-pinene is an important forest chemical resource, and the cis-pinane obtained by its hydrogenation reaction is used in spices, medicine, and other industries. A hollow nanospheric material with amphiphilic properties in a two-sided structure was prepared, with a nitrogen-doped carbon layer towards the inside and mesoporous silica in the outer layer of the nanospheres. The amphiphilic catalyst with non-precious nickel as the active component was synthesized by loading nickel onto the nanospheres using a simple impregnation method and applied to the aqueous phase hydrogenation reaction of α-pinene. The mesoporous structure of the catalyst shortened the mass transfer distance and thus reduced the mass transfer resistance. The nitrogen atoms doped in the carbon matrix provided anchor points for stabilizing the metal nanoparticles; the hydrophilic outer surface and hydrophobic hollow cavity enabled the catalyst to be well dispersed in water while still enriching the organic matter in aqueous solution. The effect of various reaction conditions on the catalytic reaction was investigated. The catalysts showed excellent activity and good stability, suggesting a new green and efficient method for more effective exploitation of biomass pine resin resources, and providing a reference for expanding the application of non-precious metal catalysts.
- Researchpp 4055-4070Jo, H. M., Lee, S. H., and Lee, J. Y. (2023). “Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from paper mulberry fibers,” BioResources 18(2), 4055-4070.AbstractArticlePDF
The applicability of paper mulberry fiber (PM-FB), which is bast fiber, for manufacturing cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) with high-yield was investigated. The PM-FB and hardwood bleached kraft pulp (Hw-BKP) were hydrolyzed under different sulfuric acid concentrations, reaction times, and reaction temperatures. The dependence of the CNC yield on the hydrolysis conditions and crystallinity of the raw materials was analyzed. The functional groups of the CNCs and their zeta potentials were determined. The fiber length and width of the individual CNCs were determined by transmission electron microscopy image analysis. The PM-FB showed a higher crystallinity of 86.8% compared to that of Hw-BKP and exhibited a high CNC yield of 55% under strong hydrolysis conditions. The sulfate group was introduced into the CNCs, which increased their negative charge. The fiber width of PM-FB-based CNCs (PM-CNCs) was larger than that of Hw-BKP-based CNCs (Hw-CNCs), and the aspect ratio ranged from 29.0 to 12.2 depending on the hydrolysis conditions. The yield of PM-CNCs was higher than that of Hw-CNCs under the same hydrolysis conditions. In addition, both CNCs exhibited similar quality. Therefore, PM-FB is a promising raw material for efficient CNC manufacturing.
- Researchpp 4071-4084Lv, H., Yang, S., Zhu, Y., Shu, X., Cao, W., Xu, B., and Fei, B. (2023). “Effects of microwave drying on the cell wall structures of round bamboo,” BioResources 18(2), 4071-4084.AbstractArticlePDF
Effects of microwave irradiation on bamboo cell wall structures were studied. Microwave treatment resulted in samples exhibiting smoother surfaces, deformed parenchyma cells, and increased porosity. Microwave treatment altered microfibril orientation through the formation of hydrogen bonds. The peak at 3440 cm-1, assigned to O-H stretching, decreased. Meanwhile, intermolecular and intramolecular bonds were formed, increasing the uniformity of microfibrils. Condensation reactions in surface hydroxyl groups and the formation of intramolecular hydroxyl groups in the amorphous region under microwave irradiation also improved the fiber arrangement uniformity. After treatment, the HCH and HOC bonds were reduced and the ester bonds were broken down. The methoxy and aromatic ring hydroxyl groups were oxidized, as indicated by the increase in the absorption peak at 148 ppm. The hydroxyl groups in the amorphous region near the fiber surface decreased, as did hemicellulose content, but there was an increase in secondary crystalline fibers.
- Researchpp 4085-4103Vasudevan, V., Karthikeyan, A., Rajamuthu, T. P., Sarkar, A., Parnjothi, G., Krishnan, N., Sakthivelu, M., Velusamy, P., Anbu, P., and Raman, P. (2023). “Bioactive metabolites from germinated Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. seeds after treating with different concentrations of salicylic acid,” BioResources 18(2), 4085-4103.AbstractArticlePDF
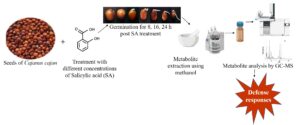
Salicylic acid (SA) is an effective elicitor for enhancing product formation in various agricultural practices. This study examined the diverse responses to physiological metabolites and the pathway modifications in broad-spectrum resistance-1 (BSR1) of Cajanus cajan after treatment with SA using a metabolomics technique. The significance of the SA function at the metabolite level was examined by treating C. cajan with various concentrations of SA and germinated by soaking in water for different time periods. The secondary metabolites were recovered and investigated by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for all the periodic conditions. Chemometric analysis of the collected samples showed that the seeds responded to the SA treatment. Acetic acid increased in germinated seeds after the SA treatment. In addition, the up-regulated metabolite production was downregulated in the C. cajan seeds before germination. The levels of metabolites, including hyacinthin, furaneol, citramalic acid, palmitate, stearate, linoleate, tocopherol, glucobrassicin, syringol, and hydroxy acetophenone, were increased after the SA treatment compared to control. Hence, the SA-treated seedling is a potential bio-factory for nutraceutical products to provide significant health benefits to the human population.
- Researchpp 4104-4115Wang, Q., Liu, S., Chen, H., Liu, J., Liu, H., and Zhu, Q. (2023). “Carboxylated cellulose silica hybrid beads for efficient dye removal,” BioResources 18(2), 4104-4115.AbstractArticlePDF
Highly efficient and environmentally friendly carboxylated cellulose silica hybrid adsorbents were prepared by combining the advantages of cellulose and silica. The surface property and chemical composition of produced cellulose silica hybrid adsorbents were extensively characterized via different techniques. The results indicated that silica particles were densely deposited on the surface of composite adsorbents. Because of their porous structure and large specific surface area, the carboxylated cellulose silica hybrid adsorbents demonstrated a high capacity of methylene blue (MB) adsorption, exceeding 990 mg·g-1. This adsorption capacity was more than 45% higher than that of carboxylated cellulose adsorbent. The cellulose silica hybrid adsorbents were able to maintain an MB adsorption efficiency of up to 70% even after undergoing five cycles. This study developed cellulose silica hybrid adsorbents for wastewater treatments. High adsorption capacity and stability make them sustainable and cost-effective alternatives to traditional adsorbents.
- Researchpp 4116-4131Silva, G. A. O., Curvo, K. R., Oliveira, A. C., Neto, P. N. M., Vasconcelos, L. G., Carvalho, A. M. M. L., Silva, M. J., Natalino, R., and Pereira, B. L. C. (2023). “Effect of age on heartwood proportion, color, chemical composition, and biological resistance of teakwood,” BioResources 18(2), 4116-4131.AbstractArticlePDF
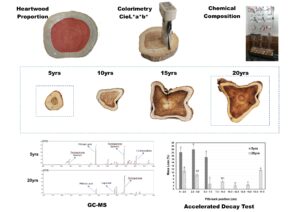
Teakwood from fast-growth plantations is commercialized at increasingly younger ages for economic reasons. However, wood features are influenced by the age of the tree. This study examined how age affects heartwood proportion, color parameters, chemical composition, and natural teakwood durability. Trees with 5, 10, 15, and 20 years of fast-growth at commercial plantations located in Mato Grosso, Brazil were evaluated. The base diameter of the trees ranged from 13.1 (5 years) to 28.3 cm (20 years), and the heartwood percentage increased from 16.3 to 60.0%, respectively. The color parameters in the CIELab system indicated that wood became darker and more saturated, and the predominance of yellow color decreased compared with red as age advanced. The total extractive content ranged between 7.4 (5 years) and 9.6% (15 years), without a clear trend of age affecting the extractive content. The extractives from five-year-old wood were mainly composed of tectoquinone (43.3%), phthalic acid (19.1%), and 1,3-indandione (9.2%), while those from 20-year-old wood were mainly composed of tectoquinone (60.7%), lapachol (13.8%), and phthalic acid (9.7%). Teakwood can be classified as resistant (5 years) to very resistant (20 years) after being submitted to an accelerated decay test.
- Researchpp 4132-4142Zuo, L., Qu, M., Song, Z., Zhang, Y., Su, X., Yue, X., Li, C., and Xu, B. (2023). “Decay resistance of Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir. and the antifungal properties of its extract,” BioResources 18(2), 4132-4142.AbstractArticlePDF
The processing residue of Pterocarpus erinaceus was used to obtain an ethanol-extract, whose anti-fungal properties and mode of action was investigated using multi-omics principles and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The results showed that the decay resistance of the heartwood of Pterocarpus erinaceus was in Grade I; it showed strong decay resistance. The effective concentration of 70% ethanol extract of the heartwood of Pterocarpus erinaceus was 13.8%. It showed high inhibition against Coriolus versicolor and Gloeophyllum trabeum, and the content of the extract was positively correlated with the diameter of the inhibition zone. Transcriptomics analysis showed there were 93 genes differentially expressed in Gloeophyllum trabeum. Among them, 42 genes were up-regulated and 51 genes were down-regulated. These genes were mainly related to oxidoreductase activity, integral components of the membrane, carbohydrate metabolism, lipid metabolism, and other related Gloeophyllum trabeum life activities. In total, 31 substances were separated and observed using GC-MS, and their peak areas accounted for 91.8% of the total peak area. Of these, 16 substances including ketones, esters, amines, alkanes, olefins and aromatic compounds showed a relatively high content. Ketones accounted for the most abundance at 29.1%. These compounds may represent the main active components of antifungal and decay resistance.
- Researchpp 4143-4152Chai, H., Cai, L., Xu, T., and Ma, Y. (2023). “Digital image correlation method for detecting strain in wood drying process,” BioResources 18(2), 4143-4152.AbstractArticlePDF
Stress and strain monitoring is of great significance for wood drying. Using digital image correlation (DIC), this study measured displacement and strain changes during wood drying in real time. The results showed that when wood is dried below the fiber saturation point, the difference of the radial and tangential shrinkage ratio gradually increased. An analysis of tangential and radial shrinkage ratio revealed that in the early stage of drying, the tangential and radial shrinkage ratio was relatively flat; in the middle stage of drying, the shrinkage ratio began to gradually increase; and in the later stage of drying, the tangential shrinkage ratio was approximately twice as large as that in the radial direction. Further, regarding the tangential and radial strain distribution, the radial strain distribution was more scattered than that in the tangential direction. The radial strain distribution exhibited compressive strain on both ends of the specimen, and the tensile strain was in the center. The tangential strain distribution was tensile strain on the left side of the specimen and compression strain on the right. Overall, DIC is stable and reliable, and it can be used to monitor well the stress and strain changes during wood drying.
- Researchpp 4153-4167Ghahrani, N., Nazarnezhad, N., Ramezani, O., and Asadpour, G. (2023). “The impact of an acidic post-treatment on surface-modified old corrugated cardboard (OCC) with NaOH-urea as a reinforcing agent,” BioResources 18(2), 4153-4167.AbstractArticlePDF
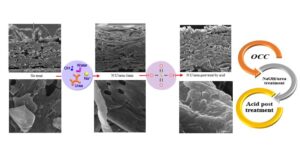
Chemical surface modification is one method for enhancing the mechanical and barrier properties of packaging paper. The NaOH/urea solvent system has been deemed an effective, inexpensive, and cost-effective solvent for paper modification and cellulose dissolution due to its unique self-reinforcing qualities and the fact that it can be utilized on an industrial scale, although it is ineffective for porous paper and requires pre- or post-treatment. This study examined the influence of acid as a post-treatment on the surface modification of paper with NaOH/urea to improve properties relative to packaging uses. The results indicated that NaOH/urea modification on OCC as a semi-crystalline material did not result in materials with superior resistance and barrier qualities. While acid treatment increased tensile and burst strength and air permeability, it was ineffective at increasing tear strength. Properties of control, NaOH/urea treatment, and acidic post treatment papers were respectively 33.31, 29.4, and 37.46 mn/g in the tensile index, 1.7, 1.58, and 1.74 Kpa.m2/g in burst index, 9.94, 9.07 and 8.87 mn.m2/g in tear index, 2.04, 1.34 and 1.32 s-1 in smoothness, 37.2, 38.2 and 45.4 s in air resistance, and 77.5, 90.8 and 80.5 water absorption. Therefore, with or without acidic post-treatment, the sheets became hydrophilic.
