Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 5385-5398Zakaria, S. M., Idris, A., Chandrasekaram, K., Darji, D., and Alias, Y. (2023). “Rice husk lignin to vanillin: IonoSolv as a way forward for value-added biomass depolymerization,” BioResources 18(3), 5385-5398.AbstractArticlePDF
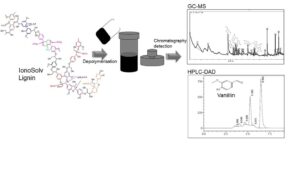
The depolymerization of natural biomass-based lignin is a definitive challenge, as it involves the integral breakdown of complex and well-constructed natural structures. A sustainable method called ‘ionoSolv pretreatment’ employs ionic liquids in biomass processing. In this study, Bronsted acidic IL (BAIL); 1-methyl-3-(3-sulfopropyl)-imidazolium chloride, [C3SO3HMIM]Cl was synthesized and commendably used to both assist the depolymerization of lignin under mild reaction conditions as well as to benefit from the commercially valuable vanillin. About 68% degree of depolymerization (DD) of lignin was achieved under optimized conditions (120 °C, 60 min), yielding ca. 43% of tetrahydrofuran (THF) soluble products. The influence of BAIL on the depolymerization was investigated using chromatographic (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, gel permeation chromatography, and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and spectroscopic techniques (Fourier transform infrared). The HPLC analysis of the depolymerized lignin detected the clear presence of 12% of vanillin was obtained from 2 wt.% of rice husk’s lignin.
- Researchpp 5399-5416Wu, X., Wu, G., Wang, B., and Li, J. (2023). “Classification of alfalfa hay based on infrared spectroscopy,” BioResources 18(3), 5399-5416.AbstractArticlePDF
Alfalfa hay plays a decisive role in the quality and safety of livestock products. Chemical analytical methods for alfalfa hays are laborious, time-consuming, and costly. Therefore, suitable methods are required for rapid and accurate detection of alfalfa hay. This study evaluated the feasibility of infrared spectroscopy (IR) in identifying different alfalfa hays. 105 alfalfa hay samples under three different drying methods were analysed. Results indicated that the full spectra model constructed through standard normal variable transformation (SNV), first-derivative (FD), and second-derivative (SD) preprocessing by BP and SVM had the best performance. The accuracies were all up to 100%. Under the same preprocessing method, the accuracy of BP neural networks was better than that of support vector machine models in most cases. The characteristic wavelength-based SNV-SD-SPA by BP exhibited better performance than the other pretreatment methods, such as: SNV-SPA, SNV-FD-SPA, and SNV-GA, etc. The classification accuracy of moldy-dried alfalfa, sun-dried alfalfa, and shade-dried alfalfa in the training set were 100%, 100%, and 99.5%, respectively, and the accuracy of the prediction set reached 100%, 97.6%, and 97.4%, respectively. Thus, a better theoretical basis was obtained for the grading and online monitoring of alfalfa hay.
- Researchpp 5417-5434Khorramabadi, L. A., Behrooz, R., and Kazemi, S. (2023). “Effects of nanoclay modification with aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) on the performance of urea–formaldehyde resin adhesives,” BioResources 18(3), 5417-5434.AbstractArticlePDF
Urea-formaldehyde (UF) resins, as the most common adhesives for wood-based composites, emit formaldehyde, which is forcing producers to find a solution to this problem. Using scavengers is a practical way of reducing formaldehyde emissions, but sometimes these materials change the properties of the adhesive. This study investigated the effect of adding nanoclay and nanoclay modified with aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES), as scavengers, on the formaldehyde emission and the properties of the urea-formaldehyde resin. Modification of nanoclay with APTES was confirmed by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. After the addition of nanoclay and modified nanoclay to the urea-formaldehyde resin, the emission of formaldehyde decreased by 22% and 61%, and the physical and mechanical properties were improved. The FTIR, XRD, and differential scanning calorimetry results showed that the addition of nanoclay and modified nanoclay improved the characteristics of the adhesive, reduced the crystalline areas, and delayed the curing of the adhesive. Additionally, according to thermogravimetric analysis results, addition of nanoclay and modified nanoclay increased the thermal stability and reduced the weight loss of urea formaldehyde resin.
- Researchpp 5435-5446Kahveci, G. (2023). “Dendrochronological potential of Juniperus foetidissima Willd in central Anatolia, a semi-arid region of Turkey,” BioResources 18(3), 5435-5446.AbstractArticlePDF

The dendrochronological potential of Juniperus foetidissima, growing in central Anatolia, was assessed. Raw, standard, and residual tree-ring chronologies were prepared for J. foetidissima trees in the Eskişehir region using classical dendrochronological methods for the period between 1875 and 2014. All the chronologies were statistically relevant, and the running correlation, expressed population signal, and mean sensitivity values in the residual tree-ring chronology were within the given limits. Therefore, the residual tree-ring chronologies were used to assess the climate-growth relationship. The relationships between tree-ring width growth and climate variables (mean temperature, monthly sum of precipitation) were investigated using response function analysis (moving windows correlations) in the R platform. Positive or negative relations were found between the residual tree-ring widths and the monthly precipitation and mean temperature, but with low coefficient values. The tree-ring width growth showed a significantly negative response to precipitation in August of the current year for the period in 1977-2001 and 1978-2002 and significantly positive to temperature in June of the current year for the period in 1971-1995, 1972-1996, and 1993-1996. In conclusion, despite some problems with cross-dating, J. foetidissima can generally be used for dendrochronological research and is suitable for developing long-term chronologies.
- Researchpp 5447-5465Wijana, S., Ayuningtias, M., Perdani, C. G., and Kartikaningrum, W. (2023). “Formulation of Tengger herbal coffee: Effect of coffee type and fennel seed powder,” BioResources 18(3), 5447-5465.AbstractArticlePDF
The Bromo Tengger Semeru National Park (or Taman Nasional Bromo Tengger Semeru/TNBTS) is a popular tourist destination in Indonesia, and the local authorities encourage the development of new local specialty products. One locally available commodity is coffee. This study investigated the best formula for Tengger herbal coffee. The randomized block design (RBD) consisted of two factors, including the coffee types (i.e., Arabica, Robusta, and Arabica:Robusta (50:50)) and the proportion of coffee:fennel seed powders (i.e., 92:8, 90:10, and 88:12). Physicochemical and organoleptic quality parameters were analyzed. In all coffee types, the addition of fennel seed powder at different concentrations significantly affects the sensory attribute (i.e., color, taste, and aroma) and the physicochemical characteristics of Tengger herbal coffee. The blending of coffee with fennel seed powder improved the taste and aroma of the herbal coffee. The best formulation was obtained from A3B3, a mixture of 44% Arabica coffee: 44% Robusta coffee: 12% fennel seed powder. This formula resulted in Tengger herbal coffee with pH 4.9, 16.6 color lightness, 0.64% total insoluble solids (TIS), 0.07% caffeine content, 47.2 mg GAE/g total phenol, 0.49 ppm antioxidant activity (IC50), and 0.58% reducing sugar. The findings confirmed that Tengger herbal coffee offers health benefits from its antioxidant activity, alongside the potential as a traditional beverage product.
- Researchpp 5466-5475Ulay, G. (2023). “Effects of artificial weathering on some surface properties of Anatolian chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) wood applied with yacht varnish,” BioResources 18(3), 5466-5475.AbstractArticlePDF
Anatolian chestnut wood is an industrial material used in various indoor and outdoor applications in Turkey. This study investigated the effects of artificial weathering (times: 144, 288, 432, and 576 h) conditions on color parameters (L*, ∆L*, a*, ∆a*, b*, ∆b*, ∆E*, ho, ∆H*, C*, and ∆C*), glossiness values at 60° in different directions (║ and ⊥), pendulum hardness (König method) values, and surface adhesion strength (pull-off method, MPa) on the layers of yacht varnishes applied to Anatolian chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) wood. The results showed that the univariate analysis of variance was significant by obtaining the weathering factor for all tests. While the brightness values perpendicular (⊥) and parallel (║) to the fibers increased at 144 and 288 h, they decreased at 432 and 576 h. Adhesion strength to the surface decreased 4.35% at the 576th h of weathering. At the end of weathering, a*, C*, b*, and pendulum hardness values increased, while ho and L* values decreased compared to un-weathered samples. The ∆a* and ∆E* values increased with increased weathering time.
- Researchpp 5476-5493Kocaman, A., Savaş, B. F., and İşler Ceyhan, D. (2023). “Removal efficacy of toxic metals in leachate through micro-organisms isolated from the natural environment,” BioResources 18(3), 5476-5493.AbstractArticlePDF
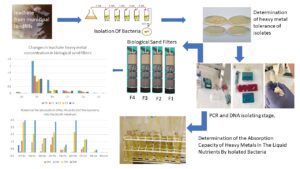
Landfill leachate is a serious contaminant for groundwater and surface water because of its potentially toxic metal content. In many countries, leachate is discharged into the natural environment without treatment because of the high disposal cost. However, this environmental problem can be solved by microorganisms, as they can adsorb the contaminants or convert them into end products, and this is cost-effective. This study focused on determining bacteria capable of efficiently removing toxic metals from leachates. Therefore, bacteria were isolated from nature that have a high adsorption and resistance capacity to a number of toxic metals. This potential was achieved by Enterobacter hormaechei, Priestia aryabhattai, and Mycobacterium sacrum, among others. Their efficiency in removing toxic metals compared to raw leachate was Cd (78%, 67%, 78%), Ni (64%, 57%, 56%), Pb (99%, 75%, 76%), Cr (41%, 46%,19%), Co (45%, 60%, 40%), and Cu (80%, 80%, 60%), respectively. According to the results, these bacterial strains proved to be very effective in the treatment of toxic metals from leachate. Therefore, they are good candidates for the treatment of wastewater by bioremedial methods.
- Researchpp 5494-5511Ushakov, A., Alashkevich, Y., Kozhukhov, V., and Marchenko, R. (2023). “Role of external fibrillation in high-consistency pulp refining,” BioResources 18(3), 5494-5511.AbstractArticlePDF
The mechanical and hydrodynamic phenomena occurring in the refining zones of disc refiners cause fibres to undergo fibrillation. This paper presents a study of the changes occurring during fibre fibrillation as expressed in terms of the fibrillation index when refining pulp with a 10%, 15%, and 20% consistency. The influences of the tangential force of a circular bar and a straight bar on fibre fibrillation were compared. The changes in the tangential force are shown to depend on the angle between the tangent to the cutting edge and the radius from the centre of the disk to the tangency point. Increasing the angle between the tangent to the cutting edge and the radius from the centre of the disk to the tangency point gives higher fibrillation index values. The study revealed a relationship between fibre fibrillation and the strength characteristics of handsheets.
- Researchpp 5512-5530Ashraf, S. R., Afroz, A., and Anwar, Z. (2023). “Physicochemical parameters optimization and peroxidase characterization from Aspergillus niger native strain by solid-state fermentation for improved dye decolorization,” BioResources 18(3), 5512-5530.AbstractArticlePDF
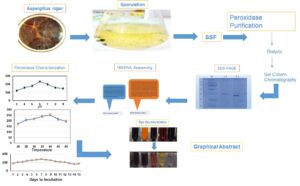
The hyper yield of peroxidase (POX) was investigated for a novel native Aspergillus niger strain identified by 18S RNA analysis. A. niger strains sequences were submitted to GenBank; IDs allotted were MN611114.1 (BMB 17) and MN559756.1 (BMB-18). The identified Aspergillus strains in combination showed enhanced (POX) activity (601.5 U/mL) by solid-state fermentation in comparison to their individual activities. POX was purified by ammonium sulfate, and size exclusion gel chromatography exhibited a 7.83-fold increase in POX concentration (13.3 U/mg) in comparison to BMB17 and BMB 18 (11.8 & 7.6 U/mg respectively). The best POX activity was obtained with pH 6.5, 37 °C, and 5 days of incubation. Using guaiacol as substrate, POX showed maximum activity (Vmax) of 537 U/mL with a corresponding Michaelis constant (Km) value of 126 µM. Calcium chloride worked as a POX activator at 300 & 400 mM. Zinc sulfate (500 mM), EDTA (5 mM); ethanol, propanol, and acetonitrile (50%) inhibited (18-30%) POX. Urea (1M), and copper sulfate (500 mM) strongly inhibited POX up to 40%. Polysorbate-80 (1%) slightly reduced the POX by 10% to 15%. BMB17+18-induced promising dye decolorization (88-98%) against all vat dyes, methylene blue, and phenol red.
- Researchpp 5531-5548Wang, J., Lyu, J., Li, X., Jiang, Y., and Chen, M. (2023). “Optimization of parameters for vacuum heat modification of Cupressus funebris wood,” BioResources 18(3), 5531-5548.AbstractArticlePDF
A full factorial experiment was conducted to analyze the main and interaction effects on the physical and mechanical properties of Cupressus funebris Endl. wood subjected to vacuum heat modification. The response variables evaluated were mass loss rate (ML, %), moisture resistance (MR, %), and modulus of rupture in bending (MOR, MPa). The results reveal significant variations in the effects of modification time, holding temperature, and vacuum pressure as independent factors, along with varying degrees of interaction effects among them. Simplifying the analysis model, a regression equation was derived to describe the relationship between the response variable (mass loss rate) and the factors: The model achieved an R-squared value of 96.0% and an R-squared (predicted) value of 73.7%, indicating good overall predictive performance. Optimal process parameters for mid-temperature vacuum heat modification of cypress were determined based on the mass loss rate and modulus of rupture (MOR), resulting in a modification temperature of 120 °C, holding time of 5 h, and a pressure intensity of 0.1. The reliability of the full factorial experiment was further confirmed through orthogonal testing.
