Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 257-275Tichem, T. M., Wang, Y., Gameli, R. B. H., Mbage, B., Duwiejuah, A. B., Wang, N., and Bing, L. (2024). “Mono and simultaneous adsorption of aldrin and toxic metals from aqueous solution using rice husk biochar,” BioResources 19(1), 257-275.AbstractArticlePDF
Recent research has explored the potential of rice husk biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions, including aldrin, mercury (Hg2+), lead (Pb2+), and cadmium (Cd2+). Experimentation involved adding varying doses of biochar to wastewater with different contamination levels, agitating the mixture for 60 min, and filtering the solutions for analysis. The experiment revealed impressive removal efficiencies: 100% for aldrin, 99.92% – 99.99% for Hg2+, 95.90% – 99.52% for Pb2+, and 88.60% – 99.46% for Cd2+. In binary and quaternary mixtures, Hg2+ showed higher removal efficiency than Pb2+ and Cd2+, with the exception of aldrin. The adsorption order was identified as aldrin > Hg2+ > Pb2+ > Cd2+. The Freundlich adsorption isotherm best described heavy metals in the mono and quaternary component adsorption, while the Langmuir adsorption isotherm was a better fit for the binary component. Consequently, the study highlights rice husk biochar as an efficient, sustainable, and environmentally friendly option for wastewater treatment.
- Researchpp 276-287Mamaeva, O., and Isaeva, E. (2024). “Composition of alcohol extracts from poplar leaves (Populus balsamifera L.),” BioResources 19(1), 276-287.AbstractArticlePDF
The group composition of alcohol extracts from balsamic poplar leaves Populus balsamifera L, growing in the Krasnoyarsk Krai, Krasnoyarsk (Russia) were examined in this work. Leaves selected in different phases of the growing season were used: June, July, August – fresh, September – fallen leaves. Poplar leaves contain up to 56% of extractive substances, alcohol-soluble substances account for up to 67% of the extract amount. Alcohol extracts were fractionated using solvents with increasing polarity: petroleum ether (boiling point 40 to 70 °C), diethyl ether, ethyl acetate, butanol. The results showed that the alcohol extracts of poplar leaves are dominated by substances extracted with ethyl acetate (up to 60%). The study of the component composition of volatile compounds of individual fractions of alcohol extracts was performed on an Agilent chromatography-mass spectrometer. The presence of various groups of compounds was established: hydrocarbons, alcohols, acids, ketones, etc., including biologically active substances such as megasterol acetate, ℽ-sitosterol, sitosterol, 3,7,11,15-tetramethyl-2-hexadecene-1-ol, diethyltoluamide, 4-methoxy-3-nitrobiphenyl, and other compounds that it can be used in different applications.
- Researchpp 288-305Wang, Q., Hua,J., Hu, J., Zhao, L., Huang, M., Tian, D., Zeng, Y., Deng, S., Shen, F., and Zhang, X. (2024). “Artificial neural network modeling to predict the efficiency of phosphoric acid-hydrogen peroxide pretreatment of wheat straw,” BioResources 19(1), 288-305.AbstractArticlePDF
Phosphoric acid-hydrogen peroxide (PHP) pretreatment is an effective method to obtain a cellulose-enriched fraction from biomass. In this study, artificial neural network (ANN) was used to predict PHP pretreatment efficiency of cellulose content (C-C), cellulose recovery (C-Ry), hemicellulose removal (H-Rl), and lignin removal (L-Rl) under various conditions of pretreatment time (t), temperature (T), H3PO4 concentration (Cp), and H2O2 concentration (Ch). The final optimized topology structure of the ANN models had 1 hidden layers with 9 neurons for C-C and 10 neurons for C-Ry, 10 neurons for H-Rl, and 12 neurons for L-Rl. The actual testing data fit the predicted data with R2 values ranging from 0.8070 to 0.9989. The relative importance (RI) revealed that Cp and Ch were significant factors influencing the efficiency of PHP pretreatment with total RI values ranging from 12% to 62.6%. However, their weights for the three components of biomass were different. The value of T dominated hemicellulose removal effectiveness with an RI value of 78.6%, while t did not seem to be a main factor dominating PHP pretreatment efficiency. The results of this study provide insights into the convenient development and optimization of biomass pretreatment from ANN modeling perspectives.
- Researchpp 306-321Alamsyah, E. M., Abdullah, A. F., Suhaya, Y., Sutrisno, Darwis, A., Sumardi, I., Suheri, A., Munawar, S. S., and Malik, J. (2024). “Effect of impregnation with diammonium phosphate and sodium silicate on some physical and mechanical properties of modified laminated veneer lumber made of jabon wood,” BioResources 19(1), 306-321.AbstractArticlePDF
Laminated veneer lumber (LVL) and laminated veneer board (LVB) panels from jabon wood (Neolamarckia cadamba) were impregnated with fire retardation substances, namely diammonium phosphate (DAP) and sodium silicate (SS). Prior to testing, the boards were conditioned in relative humidity (RH) of 65% and a temperature of 25 °C. The moisture content (MC), bending strength tests in flat wise position, and bonding tests were conducted in accordance with the Japanese Agricultural Standard (JAS:2008). Density tests and hardness tests were conducted in accordance with ASTM D143 standard (2003) in 50 mm x 50 mm. Thickness-swell shrinkage tests were conducted in accordance with the standard BS EN 317:1993, and fire resistance was tested under PS 1-19 standard. The use of 20% DAP and SS solution on jabon wood using impregnation methods affected some of the properties of the panels, especially the moisture content, density, and bonding strength of LVL and LVB compared to the control panels. Both DAP and SS impregnation increased the density. The treatments showed promise for resisting fire, as well as increasing the moisture content and increasing the density compared to the control.
- Researchpp 322-344Huan, J., Sun, Z., Guo, X., Chu, T., Zhou, X., Wang, W., and Yang, Y. (2024), “Study on the seismic performance of through-tenon joints with pullout tenon gaps between mortise and tenon shoulder,” BioResources 19(1), 322-344.AbstractArticlePDF
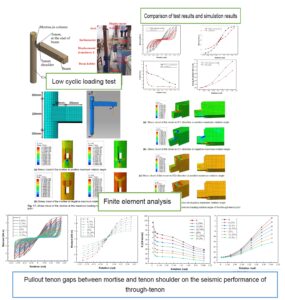
Through-tenon joints are widely used in ancient timber buildings. To study the influence of the gaps between mortise and tenon shoulder on the seismic performance of through-tenon joints, a 1:3.52 scaled model was constructed and used for low cyclic loading test. Finite element analysis was conducted to study the mechanical behavior of the through-tenon joint. The seismic performance parameters of the model such as moment-rotation hysteresis curves, envelope curves, degradation of rigidity, and energy dissipation capacity were compared. The analyses showed similar changing characteristics, which indicated that the finite element analysis results were reliable. Based on the results, 7 through-tenon joint finite element analysis models with different gaps between mortise and tenon shoulder were established. The seismic performance of each of the through-tenon joints with different gaps between mortise and tenon shoulder were studied. The moment-rotation hysteresis curve of the through-tenon joint had an obvious pinching effect, and the through-tenon joint had good rotational loading capacity and good deformation ability. The peak rotational loading capacity, initial stiffness, and energy dissipation capacity of the joint decreased, while the gap between mortise and tenon shoulder increased.
- Researchpp 345-365Bloch, P.-Y., Olejnik, K., Bloch, J.-F., Bloch, A., Hammond, J., and Brissaud, D. (2024). “Time scales of spontaneous imbibition into porous material: From classic models to papers applications,” BioResources 19(1), 345-365.AbstractArticlePDF
Flow and spontaneous imbibition phenomena in porous media are important for various industrial applications, including printing and medical lateral flow assays. Their quantitative characterization is important to better understand and select the appropriate raw materials. However, standard methods often require time-consuming tests, and/or expensive equipment. Different time scales must be considered, limiting the range of possible characterization tools. A novel experimental approach based on image analysis for characterizing spontaneous imbibition processes is presented. Hence, ultra-fast diffusion may be quantitatively characterized. Models are issued from the literature to consider physical phenomena at small (milliseconds) and medium range (seconds) of time scales. The obtained experimental data fit with theoretical results, providing valuable insights into the understanding of fluid flow behavior at different time scales. Furthermore, the identification of some physical properties for either the fluid, or the substrate, based on the theoretical models are possible, as the contact angle, which remains to be otherwise challenging. This study contributes to bridging the gap between spontaneous imbibition and capillary phenomena at different time scales, their modeling, and a characterization of material and/or fluid properties paving the way for enhanced understanding and control of fluid behavior in porous media. Different papers are considered to illustrate the method.
- Researchpp 366-379Kang, X., Ma, F., Sun, P., Gao, A., and Zhang, Y. (2024). “Starch-based active packaging film and its application,” BioResources 19(1), 366-379.AbstractArticlePDF
Montmorillonite (MMT) was used to improve the performance of starch and nano-ZnO was added to act as antibacterial agent for developing a starch-based active packaging material via solution mixing and casting methods. The effect of MMT and ZnO on the performance of starch films was investigated, and then the composite films were used for cherry preservation. The results indicated that the addition of MMT could improve the mechanical and water-vapor barrier properties of starch films, but it had only a slight impact on optical properties. However, the addition of nano-ZnO could reduce the optical, mechanical, and water vapor barrier properties of composite films. In preservation applications, compared to the other films, the composite films containing nano-ZnO could be beneficial to maintain quality and nutritional value of cherries by slowing down the growth of bacteria and thereby delaying weight loss, decreasing hardness, and decreasing pH and soluble solid content, resulting in a better preservation effect. Therefore, a starch-based active packaging film with good properties and preservation effect was developed with nano-ZnO and MMT, which could be applied in the field of preservation.
- Researchpp 380-404Gedikli, H., Akdogan, A., Karpuz, O., Akmese, O., Kobya, H. N., and Baltaci, C. (2024). “Aflatoxin detoxification by biosynthesized iron oxide nanoparticles using green and black tea extracts,” BioResources 19(1), 380-404.AbstractArticlePDF
Researchers have recently been interested in employing nanoparticles (NPs) obtained from herbal extracts through green synthesis for various applications. This study investigated the detoxification of aflatoxins, which are toxic substances produced by molds Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus. The present work examined the levels of aflatoxins in hazelnut and peanut puree. Turkish black tea extract (BTE), Turkish green tea extract (GTE), green synthesized black tea-based iron oxide nanoparticles (BTFeONPs), and green tea-based iron oxide nanoparticles (GTFeONPs) were produced for aflatoxin removal. Characterizations and various antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of the tea extracts and iron oxide nanoparticles (FeONPs) were investigated. The aflatoxin levels of hazelnut puree used for this study were 6.57 ± 0.06 µg/kg for aflatoxin B1 and 13.03 ± 0.16 µg/kg for total aflatoxin, whereas the aflatoxin levels of (AFLB1) peanut puree were 7.79 ± 0.15 µg/kg for AFLB1 and 15.21 ± 0.12 µg/kg for total aflatoxin. Using soluble BTE resulted in a 40 to 50% decrease in aflatoxin levels in hazelnut and peanut purees, while soluble GTE led to a 30 to 45% decrease. Meanwhile, using BTFeONPs and GTFeONPs resulted in a 33 to 48% and 40 to 50% decrease, respectively, in aflatoxin levels in hazelnut and peanut purees.
- Researchpp 405-415Suhaya, Y., Sumardi, I., Alamsyah, E. M., Sutrisno, and Hidayat, Y. (2024). “Environment’s effect on wood characteristics of white jabon grown in West Java and Banten area, Indonesia,” BioResources 19(1), 405-415.AbstractArticlePDF
This study analyzed the diversity of physical properties and mechanical properties of white jabon (Neolamarckia cadamba (Roxb.) Bosser) from various locations and ecological conditions in West Java and Banten Indonesia. White jabon wood samples were taken from 8 locations in West Java and the Banten region. Tree ages ranged from 5 to 6 years. This wood was then tested to compare physical characteristics (density or specific gravity) and mechanical characteristics (modulus of rupture (MOR) and modulus of elasticity (MOE)). The results showed that wood density ranged from 0.29 to 0.43 g.cm-3, MOR ranged from 361 to 641 kg.cm-2, and MOE ranged from 31,117 to 58,910 kg.cm-2. The highest density average (0.43 ± 0.004 g.cm-3) was produced from Cianjur, and the lowest density average (0.29 ± 0.010 g.cm-3) was from Tanjungsari Sumedang. Environmental factors (precipitation and altitude) affect the density of wood. Separately, rainfall has a low effect and a negative relationship to jabon wood density, while altitude has a high influence and a negative relationship to jabon wood density. Andosol soil types tend to produce low density wood.
- Researchpp 416-433Li, H., Zhang, W., Zhang, Y., Zhai, F., and Chen, F. (2024). “Thermal bridging and its mitigation in bamboo panel construction with steel frameworks and mineral wool insulation,” BioResources 19(1), 416-433.AbstractArticlePDF
An energy-efficient and environmentally conscious bamboo-constructed residential structure was created, comprising bamboo composite panels, steel framework, and mineral wool insulation. To ascertain the efficacy of this particular type of wall in enhancing thermal capabilities, the finite element method was employed to analyze the factors influencing the thermal performance of the exterior wall panels, insulation layer, framework, and interior wall panels. A more judicious design and implementation strategy, known as the 3# and 8# combination scheme, was evaluated in practical applications to assess the thermal efficiency of the wall system. The findings indicated that augmenting the thickness of the inner and outer wall panels and insulation layer, reducing the framework thickness, and incorporating wooden framework as a substitute for steel framework within a certain range enhanced the thermal capabilities of bamboo-constructed walls and mitigated the adverse effects of thermal bridges. The thermal performance of the residences employing the newly developed bamboo-constructed walls surpassed that of conventional iron container houses, thereby warranting broader adoption and application in practical projects. These outcomes offer valuable insights for the optimized design of thermal performance in bamboo-constructed walls.
