Volume 16 Issue 4
Latest articles
- Researchpp 8049-8059Acosta, R., Calle Trujillo, G., and Marulanda Arévalo, J. L. (2021). "Synthesis and mechanical behavior of composite material reinforced with Guadua fiber and with a polyurethane or polyester matrix," BioResources 16(4), 8049-8059.AbstractArticlePDF
A reactive hot-melt resin (polyurethane) was used to manufacture Guadua composites with a certain flexibility, high processing speed, good initial rigidity, and high temperature performance. These composites can support a moderate tensile stress, allow for large strains at low stresses, and have a low density and a working temperature range of -40 °C and 110 °C. During the flexural test, bamboo composites with reactive polyurethane matrix do not break or fail during the test. A polyurethane-based reactive hot-melt resin was characterized by tensile tests, Shore hardness tests, differential scanning calorimetry, and thermogravimetry. Besides, a composite material was made with Guadua fiber and polyester matrix, which had a greater strength in the test of tension and flexion, although it had a lower percentage of elongation than the composite material with reactive polyurethane. Guadua fiber can increase the strength by 266% of polyurethane matrix and 228% of polyester matrix.
- Researchpp 8060-8081Xu, J., Wu, J., Qi, J., Li, J., Liu, Y., Miao, Z., Qiu, G., and Jia, W. (2021). "Microwave-assisted extraction of flavonoids from Phyllostachys heterocycla leaves: Optimization, mechanism, and antioxidant activity in vitro," BioResources 16(4), 8060-8081.AbstractArticlePDF
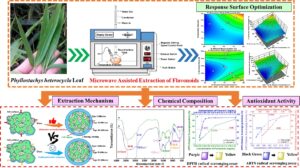
Flavonoids were extracted from Phyllostachys heterocycla leaves by adopting microwave-assisted extraction technology. Based on the single factor experiment and Plackett-Burman design results, the extraction process of flavonoids was further optimized using the response surface methodology. The optimum conditions were as follows: an ethanol concentration of 78.1%, an extraction time of 24.9 min, and a microwave power of 559 W. Under these conditions, the extraction yield of flavonoids was 4.67%, which was in close proximity to the predicted value (4.70%) and higher than the extraction yield from traditional Soxhlet extraction (3.35%). Moreover, the possible extraction mechanisms of these two extraction methods were further derived to explain why the microwave-assisted extraction of flavonoids was more efficient compared with traditional Soxhlet extraction. Ultimately, the antioxidant activities in vitro of flavonoids from Phyllostachys heterocycla leaves were evaluated via DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging assay. The flavonoids from Phyllostachys heterocycla leaves exhibited excellent antioxidant activities in vitro and Phyllostachys heterocycla leaves could be a new natural source for developing antioxidants. Overall, the findings of this research could provide a theoretical reference for the further comprehensive development and utilization of bamboo resources.
- Researchpp 8082-8097Huang, Y., Huang, Z., Liu, J., Wu, F., Li, Q., and Yan, S. (2021). "Optimal instar and method of meta-tolyl-N-methyl-carbamate application for killing Aphrophora costalis Matsumura," BioResources 16(4), 8082-8097.AbstractArticlePDF
For determining the effects of meta-tolyl-N-methylcarbamate (MTMC, metolcarb) on Aphrophora costalis Matsumura (ACM) and the migration and leaching law of MTMC in soil, the thin-layer chromatography method was used. The characteristics of migration and leaching of MTMC in the dark brown soils, and the most critical influences such as soil type, pH, and amount of water were considered to evaluate the impact of leaching rate. The results showed that 25% MTMC diluted 1,000 times was most effective in controlling ACM, with a mortality reaching 87.8% by root irrigation, and a mortality of up to 94.4% by root burial. For dark brown soil, clay minerals are primarily quartz, as well as small amounts of agalmatolite, mica, and kaolinite. Adsorption of MTMC by dark brown soil begins within 2 h, which increases rapidly in capacity before 16 h, and tends to balance with a decrease in the gradient concentration after 16 h. The desorption capacity of MTMC exhibits a gradual increase within 2 h, showing a maximum around 12 μg·g-1, which tends to stabilize after 12 h. MTMC has moderate mobility in dark brown soil. This research has important practical significance for controlling tree diseases and insect pests and protecting the environment.
- Researchpp 8098-8110Bildik Dal, A. (2021). "Refining of crude sulfate turpentine obtained from a kraft pulp mill: A pilot scale treatment," BioResources 16(4), 8098-8110.AbstractArticlePDF
Crude sulfate turpentine (CST), a by-product of the kraft process, has commercial value that depends on the removal of sulfur compounds. The current study investigates desulfurization of CST using basic process steps for a paper mill at a pilot scale treatment. In another aspect, the sulfurous compounds in CST were removed by passing to the aqueous phase with terpin hydrate production, followed by α-terpineol conversion with citric acid catalysis. The goal was to design an environmentally friendly, low-cost, zero waste process and thereby refine the CST or byproducts to a quality that can produce chemical raw materials. Refining processes included hypochlorite oxidation, air oxidation, washing with water, and distillation. The sulfur content was decreased to 170, 106, and 29 ppm from respectively by 1260 ppm initial sulphur content of CST. The chlorine amount, due to treatment with hypochlorite oxidation, did not decrease with refining processes, even in distilled fraction. By obtaining α-terpineol from terpin hydrate, the sulfur compounds were completely removed. According to the GS-MS analysis results, distilled sulfate turpentine (DST) as the final product of the refining process of the CST sample increased the ratio with pinenes. On the other hand, with two reaction steps by obtaining terpin hydrate from CST and then α-terpineol, pinenes were converted to α-terpineol.
- Researchpp 8111-8124Hsieh, P., Liu, C., Ko, C., Yang, B., and Lin, P. (2021). "Effects of residual phenolic compounds on xylanase-assisted ClO2 bleaching of hardwood kraft pulp," BioResources 16(4), 8111-8124.AbstractArticlePDF
In both pulping and bleaching processes, lignin in the pulp fiber is degraded into smaller molecules that need to be rinsed away. However, despite the installation of automatic washing equipment, the small phenolic compounds among other lignin degradation products can hardly be completely removed from the brownstock. Among the myriad of small phenolic compounds degrading from lignin, some are water-soluble and highly reactive with bleaching reagents. To understand the impact of residual phenolic compounds from black liquor on pulp bleaching, six monomeric phenolic model compounds were tested in this study. Catechol and vanillin showed inhibitory effects on xylanase activity, while catechol, vanillin, and guaiacol interfered with the delignification reaction in the chlorine dioxide (D) and alkaline extraction (E) stages of the bleaching sequence, thereby preserving the integrity of cellulose in the pulp. Because the efficiency of xylanase and bleaching reagents is hindered by the presence of these phenolic compounds, higher operational cost and more bleaching reagents are needed, which are incompatible with modern environmental policies in the world. Nonetheless, the presence of remaining soluble phenolic compounds in the brownstock can improve the bleaching selectivity important for the production of high-quality pulp with less-degraded cellulose chains.
- Researchpp 8125-8151Krishnadev, P., Subramanian, K. S., Lakshmanan, A., Ganapathy, S., Raja, K., and Rajkishore, S. K. (2021). "Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose nanocomposites containing nano fibrillated cellulose (NFC) from Agave americana L. for food packaging applications," BioResources 16(4), 8125-8151.AbstractArticlePDF
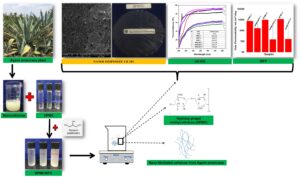
Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) is popularly known as a hydrocolloid for potential use as a biopolymer film. The films of HPMC exhibit brittleness, lacking flexibility, but they can provide a gas barrier. With the aim of improving the HPMC film properties, nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) from the succulent plant Agave americana L was incorporated as reinforcement material using the solution casting method. The films were prepared with three different amounts of NFC with glycerol as a plasticizer. The incorporation of the NFC into the nanocomposite films showed a 1,000-fold reduction in the gas permeability. However, significant improvements in the tensile strength (TS), the elongation at break (EAB), and Young’s modulus (YM) were only observed with 1% NFC. A higher moisture content (24.5%) and a higher solubility (59.5%) were observed in the HPMC/NFC-1 film, which also exhibited the best biodegradability loss of the films that were observed with a 92.8% degradation rate in 15 d of soil burial studies. Therefore, the results evidence that the HPMC/NFC films might be potentially suitable as food wrap packaging on perishable produce of fruits and vegetables to maintain their quality attributes and prolong the storage life.
- Researchpp 8152-8171Matygulina, V., Natalya, C., Vititnev, A., and Chistov, R. (2021). "Dry grinding of waste wood fiberboard: Theoretical and practical aspects affecting the resulting fiber quality," BioResources 16(4), 8152-8171.AbstractArticlePDF
This paper presents the results of research on the treatment of secondary wood fibre semi-finished materials using a dry-grinding-type rotary cutting mill and the possibility of their use in finished products for various purposes. The physical phenomena, processes, and regularities of the treatment of secondary wood fibre materials in dry processing conditions were determined and evaluated. The influence of grinding plant design parameters on wood fibre quality indices was evaluated. Mechanical effects on wood fibre waste of face-cross cutting (cutting, crumpling, collapsing, and breaking) and the dry grinding environment (breaking, collision, defibering, and fibrillation) was studied. These phenomena contribute to the formation of external and internal fibrillation of secondary wood fibre and an increase in the specific surface area. This is achieved in the absence of high temperatures and pressure, in the absence of chemical additives, and without the application of water and vapour. The effectiveness of secondary wood fibre semi-finished material treatment was demonstrated under dry processing conditions, thus confirming the environmental and economic feasibility of this method.
- Researchpp 8172-8183Jin, D., and Wei, K. (2021). "Machinability of Scots pine during peripheral milling with helical cutters," BioResources 16(4), 8172-8183.AbstractArticlePDF
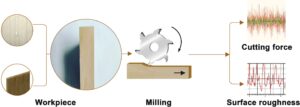
Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) is a fast-growing wood that has been widely manufactured into various furnishing products. To improve the machinability of Scots pine, the cutting force and surface roughness during peripheral milling with helical cutters was assessed via an orthogonal experimental design. Experimental results revealed that the resultant cutting force is positively related to the depth of cut, but negatively correlated with inclination angle of cutting edge and cutting speed. However, surface roughness first declines and then increases with increasing inclination angle, and it also shows an increasing trend with the increasing depth of cut and decreasing cutting speed. Furthermore, the depth of cut significantly contributes to the resultant force and surface roughness, while both the cutting speed and inclination angle have insignificant impacts on the resultant force and surface roughness. Finally, the optimized milling parameters were determined as 62° inclination angle of cutting edge, 45 m/min cutting speed, and 0.2 mm depth of cut, and these parameters are proposed for the quality finishing of Scots pine machining.
- Researchpp 8184-8196Lee, C. J., and Eom, C.-D. (2021). "Effects of knife-incising and longitudinal kerfing pretreatments on high-temperature drying of red pine and pitch pine timbers," BioResources 16(4), 8184-8196.AbstractArticlePDF
Effects of knife-incising and longitudinal kerfing pretreatments were analyzed relative to the high-temperature drying of red pine and pitch pine timbers with cross-sections less than 15 cm. Specimens were prepared as round and square timbers with thicknesses of 9, 12, and 15 cm. They were divided into four groups: control, longitudinal kerf, knife-incised, and a combination of knife-incised and longitudinal kerf. Some results from this study, such as commercial availability and application methods of drying schedules, have immense commercial importance. The incising and kerfing treatment can be used not only to improve drying quality but also as a tool for deriving an optimal drying schedule. The kerfing treatment noticeably reduced the surface checks in square timber. However, the incising treatment caused a phenomenon in which the incisions connect to each other and develop into surface checks. The wood characteristics, such as species, type, thickness, and initial MC, had more influence on determining the drying defects than the pretreatments. For the commercial use of the drying schedule used in this study, it can be useful to determine the appropriate drying time in the third step according to the species, thickness, and shape.
- Researchpp 8197-8204Ning, Y., Li, Y., Zhao, S., Liu, H., Deng, L., and Wang, F. (2021). "Applications of one-step environmentally-friendly fermentation method to produce fumaric acid with immobilized Rhizopus arrhizus in stirred-tank reactor," BioResources 16(4), 8197-8204.AbstractArticlePDF
The traditional two-step cultivation mode for fungal cultivation is commonly divided into the seed stage (usually 24 to 48 h) and the production stage (usually 96 to 144 h). The use of two stages prolongs the total production cycle and generates excess wastewater. In this work, an efficient and environmentally friendly one-step fermentation method was applied for the production of fumaric acid by immobilized Rhizopus arrhizus in a stirred-tank reactor. The nitrogen source content and the agitation speed of the reactor were optimized as the two critical factors in the one-step fermentation process; the fumaric acid production of 51 g/L with a yield of 0.42 g/g glucose was comparable with the product from the traditional two-step fermentation process. Furthermore, the total production cycle was shortened to 96 h, and the amount of wastewater was reduced due to the avoidance of the seed culture process. Thus, utilization of the one-step fermentation method to produce fumaric acid was shown to be preferable feasibility and environmental-friendliness. This is a promising method for industrial production of fumaric acid and other high-value biochemicals by fungus.
