Volume 17 Issue 1
Latest articles
- Researchpp 750-762Rahayu, I., Prihatini, E., Maddu, A., Kurniati, M., and Darmawan, W. (2022). "Density and dimensional stability of a wood-polymer nano-composite from fast-growing wood," BioResources 17(1), 750-762.AbstractArticlePDF
The characteristics of ganitri wood can be improved via wood impregnation. The objective of this research was to analyze the density and dimensional stability of a wood polymer nano-composite, i.e., impregnated ganitri wood with a mixture of melamine formaldehyde furfuryl alcohol and nano-SiO2. The results showed that the impregnation process improved the physical properties of the impregnated ganitri wood. Impregnation with 0.5% melamine-formaldehyde furfuryl alcohol (MFFA)-nano SiO2 had a significant effect on the density, weight percent gain, anti-swelling efficiency, bulking effect (BE), and water uptake (WU). Increased percentage of density and BE values after being treated by MFFA with 0.5% nano-SiO2 were 51.2% and 311.7%, respectively. The percentage decrease in WU was 47.5% (MFFA with 0.5% nano-SiO2). X-ray diffraction analysis verified a decrease in the crystallinity of the wood cellulose. The melamine formaldehyde furfuryl alcohol and nano-SiO2 polymers were found to cover the wood cell walls and lumens (based on scanning electron microscopy images). The formaldehyde emissions of the wood polymer nano-composite decreased. Therefore, it is possible to produce more environmentally friendly materials through wood polymer nano-composites.
- Researchpp 763-784Ferritsius, O., Ferritsius, R., Rundlöf, M., Reyier Österling, S., and Engberg, B. A. (2022). "Heterogeneity of thermomechanical and chemi-thermo-mechanical pulps described with distributions of an independent common bonding factor on particle level," BioResources 17(1), 763-784.AbstractArticlePDF
Particles in mechanical pulp show a wide variety but are commonly described using averages and/or collective properties. The authors suggest using distributions of a common bonding factor, BIND (Bonding INDicator), for each particle. The BIND-distribution is based on factor analysis of particle diameter, wall thickness, and external fibrillation of several mechanical pulps measured in an optical analyser. A characteristic BIND-distribution is set in the primary refiner, depending on both wood and process conditions, and remains almost intact along the process. Double-disc refiners gave flatter distributions and lower amounts of fibres with extreme values than single-disc refiners. More refining increased the differences between fibres with low and high BIND. Hence, it is more difficult to develop fibres with lower BIND. Examples are given of how BIND-distributions may be used to assess energy efficiency, fractionation efficiency, and influence of raw material. Mill scale operations were studied for printing-grade thermomechanical pulp (TMP), and board-grade chemi-thermomechanical pulp (CTMP), both from spruce.
- Researchpp 785-801Aytin, A., Çakıcıer, N., and Birtürk, T. (2022). "Chemical, hygroscopic, and mechanical properties of various wood species heat treated via the ThermoWood® method," BioResources 17(1), 785-801.AbstractArticlePDF
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), energy dissipation spectrometry, dimensional stability, and compressive strength tests were conducted parallel to the fibers on various heat-treated trees, i.e., narrow-leaved ash (Fraxinus angustifolia Vahl), aspen (Populus tremula L.), Oriental spruce (Picea orientalis (L.) Link.), and Uludağ fir (Abies bornmüelleriana Mattf.), which grow naturally in forests in Turkey. Panels made from these trees were first heat treated via the ThermoWood® method, producing ThermoWood® panels. Then, FTIR, as well as energy dissipation spectrometry analysis, dimensional stability, and compressive strength tests were performed on test samples prepared from the panels. The FTIR data showed that the hemicelluloses were degraded in the ThermoWood® test samples and the proportion of cellulose increased. The energy dissipation spectrometry results showed that the amount of carbon increased, the amount of oxygen decreased, while the amount of hydrogen remained approximately the same in the ThermoWood® panels compared to the control samples. It was determined that the proportion of silicon increased in the narrow-leaved ash panels. In addition, among the physical properties, the amount of shrinkage and swelling decreased in all the tested ThermoWood® panels compared to the control samples, whereas the compressive strength values, which are considered a mechanical property, increased.
- Researchpp 802-825Wang, X., Wang, X., Pan, Y., Zhao, B., and Liang, Z. (2022). "Preparation and properties of paint prepared with nanofibrillated cellulose and waterborne epoxy resin," BioResources 17(1), 802-825.AbstractArticlePDF
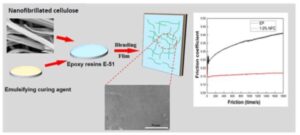
A new type of water-based paint was prepared with Salix nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC), epoxy resin (E-51), and emulsified curing agent as raw materials. The mechanical blending of coated films was characterized. The mechanical properties and friction and wear properties of the coated film were tested. Microstructure was studied by scanning electron and transmission electron microscopies, thermogravimetric analysis, and other methods. The results showed that when the amount of NFC was 1.0%, the overall performance of the coated film was improved. Herein, the flexibility was 1 mm, the adhesion was 0, the hardness was 4 H, the wear value was 15 mg/100 r, the impact resistance was 49 cm, and the gloss was 85 Gs. The friction and wear coefficient of the composite coated film after the addition of cellulose nanofibers was reduced to 0.171, which was 58.5% lower than that before the addition of cellulose nanofibers. The surface observation after abrasion indicated that the composite coated film mainly experienced abrasive wear.
- Researchpp 826-848Ouattara, L. Y., Soro, D., Fanou, G. D., Kouassi, E. K. A., Bamba, M., Yao, K. B., Adouby, K., Drogui, A. P., and Tyagi, D. R. (2022). "Optimization of the autoclave-assisted alkaline delignification of cocoa (Theobroma cacao) pod husks using KOH to maximize reducing sugars," BioResources 17(1), 826-848.AbstractArticlePDF
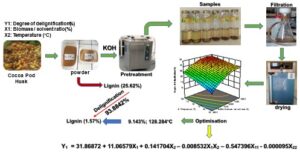
Cocoa pod husks are a type of biomass that is still poorly explored. This work was carried out as part of the optimization of the delignification process for this residue with potassium hydroxide, to maximize the reducing sugars content. Screening for potentially influencing factors showed that the biomass to solvent ratio and the temperature had the greatest effect on the delignification process. Optimization of these factors using a composite central plan revealed that the quadratic model was the most suitable for predicting the rate of delignification. The predicted R² (0.815) was in good agreement with the adjusted R² (0.906). The correlation coefficient (R2 = 0.945) between the predicted and experimental results confirmed the fit of the model. The optimal conditions were a biomass to solvent ratio of 9.14% and a temperature of 128 °C, which resulted in a maximum degree of delignification of 93.9%, with 80% of the solids recovered. This study found that the removal of extractables before the pretreatment considerably improved the delignification of cocoa pod husks and the production of reducing sugars, which increased from 3.15 ± 0.006 mg/mL to 5.33 ± 0.143 mg/mL. Scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction confirmed physicochemical changes in the biomass after pretreatment.
- Researchpp 849-861Jia, S., Wang, M., Ma, J., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., and Xu, Z. (2022). "Metal chloride mediated efficient conversion of hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) into long-chain levulinate ester," BioResources 17(1), 849-861.AbstractArticlePDF
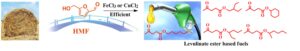
Levulinate esters are a class of promising alternative fuels derived from biomass. The synthesis of levulinate esters from carbohydrates generally undergoes a route with hydroxymethylfurfural as an intermediate product. The conversion of hydroxymethylfurfural is an intrinsic limiting step for the formation of levulinate esters from carbohydrates. Recent work focuses more on the synthesis of short-chain levulinate esters from biomass, but long-chain levulinate esters have superior properties as fuels. In this work, the synthesis of n-hexyl levulinate, a representative long-chain levulinate ester, was investigated with a series of metal chloride catalysts. Iron chloride (FeCl3) and copper chloride (CuCl2) were found to be the most effective amongst the tested catalysts. An n-hexyl levulinate yield of approximately 65% with 100% hydroxymethylfurfural conversion could be achieved at a temperature of 160 °C after 240 min. This system was also applied to the conversion of hydroxymethylfurfural and other hexanols such as 2-ethyl-1-butanol, cyclohexanol, 2-hexanol, and 3-hexanol. The catalyst in the system was reusable in a consecutive batch mode. Mechanistic study indicated that the production of levulinate ester from hydroxymethylfurfural probably went through levulinic acid as the intermediate.
- Researchpp 862-889Moore, R. K., Dietenberger, M. A., Mann, D. H., Lebow, P. K., and Weise, D. R. (2022). "Utilizing two-dimensional gas chromatography time of flight mass spectrometry (GCxGC ToFMS) to characterize volatile products from pyrolysis of living vegetation foliage," BioResources 17(1), 862-889.AbstractArticlePDF
Wildland fire can cause significant damage but is also a natural process that is key to the healthy functioning of many ecosystems worldwide. Primary fuels for a wildland fire are the dead foliage and small branches which accumulate as litter on the ground. A cone calorimeter was used to measure the various aspects of these fuels. A single sample of preignition gases from the live leaves of seven plant species were vacuum collected on quality filters and within super-chilled solvent mixtures. GC-TOFMS (1D) and GCxGC-TOFMS (2D) were used to characterize the “white” smoke emissions. The vegetation chemicals were separated into 4 categories: hydrocarbons (CH), oxygenated organics (CHO), unknown peaks (UNK), and organic non-metals (ONM). The multivariate paired Hotelling T2 test determined that the composition of the white smoke as described by the relative number of peaks in the four chemical groups differed significantly between 1D and 2D (Prob > F3,4 = 0.00004). In contrast, the relative peak area percentages in the four chemical groups did not differ between 1D and 2D (Prob > F3,4 = 0.1258). The Molecular Chemical Maps (MCMs) were used to identify chemical trends between the known and unknown chemicals in live oak and longleaf pine. Application of the 2D technique may provide more detailed information necessary to improve the numerical modeling of wildland fire behavior and emissions production.
- Researchpp 890-907Guan, M., and Huang, Z. (2022). "Direct strain distribution and finite-element-analysis simulation of the bonding interface of bamboo laminated lumber with ultrasound-treated bamboo strips," BioResources 17(1), 890-907.AbstractArticlePDF
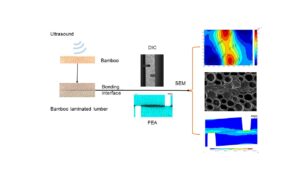
An ultrasonic cavitation treatment was used to increase the permeability of phenol formaldehyde resin adhesive on the surface of bamboo strips, and two-ply laminated bamboo lumber was manufactured. The strain distribution along the bamboo interface under stretching conditions was investigated using the digital image correlation technique. The effect of the ultrasonic treatment on the bamboo strips in terms of the shear strain of the laminated bamboo lumber was investigated, and a finite-element analysis for the bonding interface was carried out to evaluate whether the deformation measurement could predict the mechanical behavior differences of the laminated bamboo lumber. The digital image correlation and shear strength results show that the strain was lower in the bamboo bonding interface after ultrasonic treatment and the shear strength was enhanced due to the increased adhesive penetration. The digital image correlation measurement and finite-element analysis simulation both showed that stress was more concentrated, and the strain value and strain zone width was higher in the carbonized bamboo bonding interface than in the bleached bamboo bonding interface. The finite-element analysis results appeared to be in agreement with the digital image correlation test results.
- Researchpp 908-921Ngene, G. I., Roux, J.-C., and Lachenal, D. (2022). "Influence of Hollander beater refining on xylan extraction from hardwood paper pulp by cold caustic extraction and xylanase treatment," BioResources 17(1), 908-921.AbstractArticlePDF
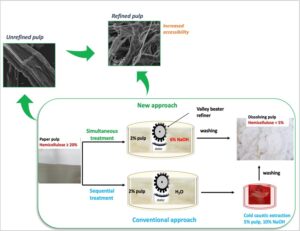
Cellulose fibers’ complex and compact structure hinders the quantitative extraction of residual hemicelluloses from the fiber wall. In this study, hardwood kraft paper pulp was subjected to refining with a Hollander beater at different refining loads (3, 4.5, and 5.5 kg) in order to assess the impact of refining load on xylan removal by cold caustic extraction. The refined pulp showed high water retention values and specific surface area, which increased accessibility and a correspondingly high degree of xylan removal. Coupling refining and cold caustic extraction (100 g/L soda) achieved over 50% more xylan removal than the unrefined pulp (3% against 7%, respectively). Furthermore, an improvement in xylan removal (79%) was achieved by implementing a one-pot simultaneous refining and cold caustic extraction treatment at half the time required for the sequential treatment and low soda concentration (60 g/L). Finally, the benefit of beating was also observed for xylanase treatment. Overall, the combined extractions made it possible to remove 85% of xylan from a conventional hardwood paper pulp giving rise to a high purity cellulose pulp with unimodal and narrow molecular mass distribution.
- Researchpp 922-938Sutrisno, E., Tanpichai, S., and Chuangchote, S. (2022). "Production of esterified nanofibrillated cellulose from a lesser-known wood Species (Macaranga hypoleuca)," BioResources 17(1), 922-938.AbstractArticlePDF
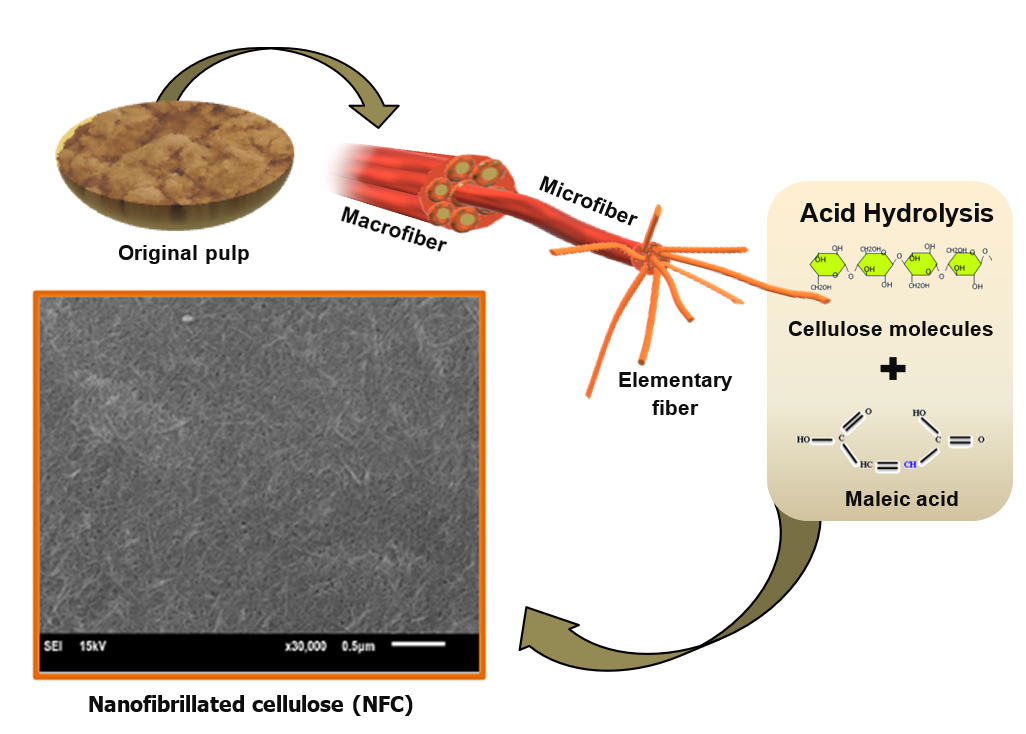
Macaranga hypoleuca, a lesser-known and rarely used wood species, is a pioneer species in the secondary succession that is classified as a fast-growing plant with long fibers. M. hypoleuca was composed of holocellulose, lignin, and extractives, at contents of 68.1 ± 0.5%, 25.5 ± 0.6%, and 4.7 ± 0.1%, respectively. In this study, refined M. hypoleuca pulp was treated by alkali treatment, delignification, and maleic acid hydrolysis. The pre-treated pulp was further disintegrated by mechanical treatment, which produced nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) with a yield of 53.5 ± 2.7%. The average diameter of the NFC was 43.0 ± 4.9 nm. The use of maleic acid (C4H4O4) hydrolysis also reduced the hydrophilicity of the NFC, as confirmed by the Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectra. It was determined that the Macaranga tree is a suitable lignocellulose source to produce NFC, which can be used in transparent flexible substrates, coating, and composite applications.
