Volume 18 Issue 2
Latest articles
- Researchpp 3938-3960Zhang, Y., Luo, M., Yuan X., Yang, Z., Wang, Y., and Zheng, Y. (2023). “The transcriptome and metabolic pathways of Persea americana under drought and low-temperature stress,” BioResources 18(2), 3938-3960.AbstractArticlePDF
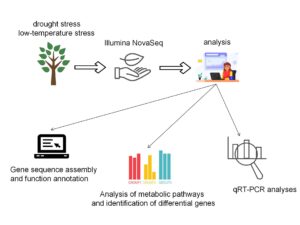
Persea americana Mill. is an important cash crop that contains effective ingredients to reduce cholesterol and protect the cardiovascular system. Presently, the gene regulation mechanism and signal pathway of stress response in P. americana are unclear. To explore the gene expression changes of P. americana under drought and low-temperature stress, the transcripts of P. americana were sequenced under these conditions. The results produced 42,815,960 bp raw reads. Analysis of the related metabolic pathways and differentially expressed genes showed that under drought stress, the gene expression of beta-amylase 3, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and hexokinase were upregulated, while the gene expression of UDP-glycosyltransferase superfamily protein isoform, glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase, and glucose-6-phosphate 1-epimerase were downregulated. Under low-temperature stress, the expression of beta-amylase and shikimate O-hydroxycinnamoyl transferase genes was downregulated. In addition, WRKY, MYB, bHLH, and NAC transcription factors were expressed under drought and low-temperature stress. Finally, the RNA-Seq data were validated using real-time fluorescence quantitative analysis to identify the key genes of P. americana regulated at the transcriptional level under drought and low-temperature stress. This study provides a theoretical basis for the selection of drought-resistant and low-temperature tolerant P. americana varieties.
- Researchpp 3961-3977Katuwal, S., Rafsan, N-A-S., Ashworth, A. J., and Kolar, P. (2023). “Poultry litter physiochemical characterization based on production conditions for circular systems,” BioResources 18(2), 3961-3977.AbstractArticlePDF
Poultry litter is a useful product as a fertilizer, energy feedstock for thermochemical conversion, and a precursor for synthesis of adsorbents and catalysts. Detailed characterization of baseline properties is necessary for enhanced environmental and economic utilization of this valuable resource. Baseline physicochemical characterization was carried out at two broiler production facilities (Arkansas, PL1, and North Carolina, PL2). Greater concentrations of inorganic nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium were obtained for PL1, suggesting greater nutrient value compared to PL2. PL2 had greater carbon content and water-holding capacity than PL1. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) of PL1 and PL2 indicated a similarity between litters in terms of the presence of carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen bonds. Both poultry litters had oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorous functional groups, as confirmed by infrared spectroscopy. Time of flight – secondary ion mass spectroscopy of negative ions also indicated similarity of the surface charge distribution between PL1 and PL2. Overall, poultry litters evaluated had similar surface chemistries, with nutrient composition varying based on rearing conditions, which has implications for downstream use in thermochemical conversion and other value-added products.
- Researchpp 3978-3994Lee, Y. J., Ko, Y. C., Moon, B. G., and Kim, H. J. (2023), “Surface characterization of paper products by profilometry with a fractal dimension analysis,” BioResources 18(2), 3978-3994.AbstractArticlePDF
A surface profilometry technique was used to characterize the surfaces of paper products. A stylus-contact type profilometer capable of simultaneously generating both surface roughness- and friction-profiles was used. As a stylus for the profilometer, a conical shape whose tip was rounded to have a 0.5 mm curvature radius was designed and successfully employed in both printing & writing (P&W) papers and hygiene papers such as bathroom tissues and kitchen towel. From the profiles, the mean absolute deviation (MAD) from the averages, i.e., R-MAD from the roughness average and F-MAD from the average coefficient of friction, were suggested as the new surface characterization parameters. To elucidate the surface roughness profiles by fractal dimension analysis, the variogram method was applied to get the fractal dimensions of the paper products. Generally, the value of the fractal dimension increased as the surface roughness increased. The surface profilometry technique with the fractal dimension analysis with the variogram method looks promising to gain additional insight on the surface characteristics of paper products.
- Researchpp 3995-4005Liu, X., Dong, X., Wang, H., Wu, M., and Huang, Y. (2023). “Transparent nanopaper from nanofibrillated bamboo pulp,” BioResources 18(2), 3995-4005.AbstractArticlePDF
Bamboo pulp was used to produce modified cellulose nanofiber (M-CNF) with 3,4-dichlorophenyl isocyanate through a one-step mechano-chemical method by ball milling. The structural variations of bamboo cellulose with different degrees of substitution (DS) for hydroxyl groups were studied by FTIR, XRD, TEM, AFM, and elemental analysis. The DS was as high as 0.88 after just 2 h of ball milling, and the diameter of M-CNF was 2 to 3 nm after just 1 h of ball milling. The modified nanocellulose was hydrophobic, with a water contact angle as high as 87°. The nanopaper made from the nanocellulose by vacuum filtration was transparent, with an optical transparence up to 88.8% at 550 nm. However, the transmittance of the modified nanopaper decreased to nearly 0 over the wavelength range of 200 to 300 nm. This nanopaper can be used as flexible optoelectronic material, packing material, or ultraviolet shielding material.
- Researchpp 4006-4031Brito, A., Suarez, A., Pifano, A., Reisinger, L., Wright, J., Saloni, D., Kelley, S., Gonzalez, R., Venditti, R., and Jameel, H. (2023). “Environmental life cycle assessment of premium and ultra hygiene tissue products in the United States,” BioResources 18(2), 4006-4031.AbstractArticlePDF
Under the controversial concern of using virgin fibers in hygiene tissue products, mostly Bleached Eucalyptus Kraft (BEK) and Northern Bleached Softwood Kraft (NBSK), consumers are responding by purchasing self-labeled sustainable products. As of today, there are no established sustainability reported results to inform consumers about the carbon footprint of hygiene tissue. To fill this gap, this study used Life Cycle Assessment to evaluate the environmental impacts across the supply chain (cradle to gate) to produce Premium and Ultra grades of bath tissue, including the production of feedstock, pulp production, and tissue production stages, with focus on Global Warming Potential (GWP). The results showed that one air-dried metric ton (ADmt) of BEK pulp had an associated GWP of 388 kgCO2eq, whereas one ADmt of NBSK pulp presented values ranging between 448 and 596 kgCO2eq, depending on the emissions allocation methodology used. It was estimated that the GWP of one finished metric ton of tissue weighted average could range from 1,392 to 3,075 kgCO2eq depending on mill location, electricity source, and machine technology. These results provide an understanding of the factors affecting the environmental impact of hygiene tissue products, which could guide manufacturers and consumers on decisions that impact their carbon footprint.
- Researchpp 4032-4054Bao, M.-H., Yu, F.-L., Yuan, B., Xie, C.-X., and Yu, S.-T. (2023). “Aqueous-phase hydrogenation of α-pinene to cis-pinane using an amphiphilic Ni-based catalyst,” BioResources 18(2), 4032-4054.AbstractArticlePDF
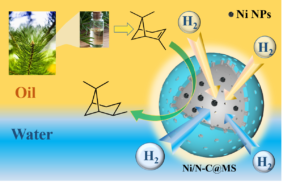
Alpha-pinene is an important forest chemical resource, and the cis-pinane obtained by its hydrogenation reaction is used in spices, medicine, and other industries. A hollow nanospheric material with amphiphilic properties in a two-sided structure was prepared, with a nitrogen-doped carbon layer towards the inside and mesoporous silica in the outer layer of the nanospheres. The amphiphilic catalyst with non-precious nickel as the active component was synthesized by loading nickel onto the nanospheres using a simple impregnation method and applied to the aqueous phase hydrogenation reaction of α-pinene. The mesoporous structure of the catalyst shortened the mass transfer distance and thus reduced the mass transfer resistance. The nitrogen atoms doped in the carbon matrix provided anchor points for stabilizing the metal nanoparticles; the hydrophilic outer surface and hydrophobic hollow cavity enabled the catalyst to be well dispersed in water while still enriching the organic matter in aqueous solution. The effect of various reaction conditions on the catalytic reaction was investigated. The catalysts showed excellent activity and good stability, suggesting a new green and efficient method for more effective exploitation of biomass pine resin resources, and providing a reference for expanding the application of non-precious metal catalysts.
- Researchpp 4055-4070Jo, H. M., Lee, S. H., and Lee, J. Y. (2023). “Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from paper mulberry fibers,” BioResources 18(2), 4055-4070.AbstractArticlePDF
The applicability of paper mulberry fiber (PM-FB), which is bast fiber, for manufacturing cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) with high-yield was investigated. The PM-FB and hardwood bleached kraft pulp (Hw-BKP) were hydrolyzed under different sulfuric acid concentrations, reaction times, and reaction temperatures. The dependence of the CNC yield on the hydrolysis conditions and crystallinity of the raw materials was analyzed. The functional groups of the CNCs and their zeta potentials were determined. The fiber length and width of the individual CNCs were determined by transmission electron microscopy image analysis. The PM-FB showed a higher crystallinity of 86.8% compared to that of Hw-BKP and exhibited a high CNC yield of 55% under strong hydrolysis conditions. The sulfate group was introduced into the CNCs, which increased their negative charge. The fiber width of PM-FB-based CNCs (PM-CNCs) was larger than that of Hw-BKP-based CNCs (Hw-CNCs), and the aspect ratio ranged from 29.0 to 12.2 depending on the hydrolysis conditions. The yield of PM-CNCs was higher than that of Hw-CNCs under the same hydrolysis conditions. In addition, both CNCs exhibited similar quality. Therefore, PM-FB is a promising raw material for efficient CNC manufacturing.
- Researchpp 4071-4084Lv, H., Yang, S., Zhu, Y., Shu, X., Cao, W., Xu, B., and Fei, B. (2023). “Effects of microwave drying on the cell wall structures of round bamboo,” BioResources 18(2), 4071-4084.AbstractArticlePDF
Effects of microwave irradiation on bamboo cell wall structures were studied. Microwave treatment resulted in samples exhibiting smoother surfaces, deformed parenchyma cells, and increased porosity. Microwave treatment altered microfibril orientation through the formation of hydrogen bonds. The peak at 3440 cm-1, assigned to O-H stretching, decreased. Meanwhile, intermolecular and intramolecular bonds were formed, increasing the uniformity of microfibrils. Condensation reactions in surface hydroxyl groups and the formation of intramolecular hydroxyl groups in the amorphous region under microwave irradiation also improved the fiber arrangement uniformity. After treatment, the HCH and HOC bonds were reduced and the ester bonds were broken down. The methoxy and aromatic ring hydroxyl groups were oxidized, as indicated by the increase in the absorption peak at 148 ppm. The hydroxyl groups in the amorphous region near the fiber surface decreased, as did hemicellulose content, but there was an increase in secondary crystalline fibers.
- Researchpp 4085-4103Vasudevan, V., Karthikeyan, A., Rajamuthu, T. P., Sarkar, A., Parnjothi, G., Krishnan, N., Sakthivelu, M., Velusamy, P., Anbu, P., and Raman, P. (2023). “Bioactive metabolites from germinated Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. seeds after treating with different concentrations of salicylic acid,” BioResources 18(2), 4085-4103.AbstractArticlePDF
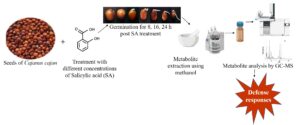
Salicylic acid (SA) is an effective elicitor for enhancing product formation in various agricultural practices. This study examined the diverse responses to physiological metabolites and the pathway modifications in broad-spectrum resistance-1 (BSR1) of Cajanus cajan after treatment with SA using a metabolomics technique. The significance of the SA function at the metabolite level was examined by treating C. cajan with various concentrations of SA and germinated by soaking in water for different time periods. The secondary metabolites were recovered and investigated by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for all the periodic conditions. Chemometric analysis of the collected samples showed that the seeds responded to the SA treatment. Acetic acid increased in germinated seeds after the SA treatment. In addition, the up-regulated metabolite production was downregulated in the C. cajan seeds before germination. The levels of metabolites, including hyacinthin, furaneol, citramalic acid, palmitate, stearate, linoleate, tocopherol, glucobrassicin, syringol, and hydroxy acetophenone, were increased after the SA treatment compared to control. Hence, the SA-treated seedling is a potential bio-factory for nutraceutical products to provide significant health benefits to the human population.
- Researchpp 4104-4115Wang, Q., Liu, S., Chen, H., Liu, J., Liu, H., and Zhu, Q. (2023). “Carboxylated cellulose silica hybrid beads for efficient dye removal,” BioResources 18(2), 4104-4115.AbstractArticlePDF
Highly efficient and environmentally friendly carboxylated cellulose silica hybrid adsorbents were prepared by combining the advantages of cellulose and silica. The surface property and chemical composition of produced cellulose silica hybrid adsorbents were extensively characterized via different techniques. The results indicated that silica particles were densely deposited on the surface of composite adsorbents. Because of their porous structure and large specific surface area, the carboxylated cellulose silica hybrid adsorbents demonstrated a high capacity of methylene blue (MB) adsorption, exceeding 990 mg·g-1. This adsorption capacity was more than 45% higher than that of carboxylated cellulose adsorbent. The cellulose silica hybrid adsorbents were able to maintain an MB adsorption efficiency of up to 70% even after undergoing five cycles. This study developed cellulose silica hybrid adsorbents for wastewater treatments. High adsorption capacity and stability make them sustainable and cost-effective alternatives to traditional adsorbents.
