Volume 18 Issue 2
Latest articles
- Researchpp 3802-3814Chen, Z., White, M., Mack, R., Rider, D., Reddy, V., and O’Neill, S. (2023). “International supply chain handling practices and the quality of heat-treated, white oak veneer logs,” BioResources 18(2), 3802-3814.AbstractArticlePDF
The most promising alternative to the methyl bromide fumigation of exported logs is steam-heating the log in a vacuum. Research has confirmed that steam heating to 56 °C for 30 minutes kills all viable propagules of oak wilt pathogen (Bretziella fagacearum) in the sapwood of oak logs. The purpose of this study was to determine whether this heat-treatment method has any effect on the quality or value of white oak veneer logs shipped between the US and EU. Seventeen steam- and vacuum-treated and seventeen untreated control logs were shipped from Baltimore, Maryland to the Czech Republic, for processing into veneer, between December 2021 and February 2022. The treated and untreated logs were sawn into flitches, soaked in hot water vats, sliced, dried, and the veneer from each log was graded for quality. Each log was assigned a value based on the veneer quality and yield. The average value of treated log was 1,547 €/m³, and the average value of the untreated logs was 1,539 €/m³. The null hypothesis was statistically confirmed. Therefore, it is concluded that the 56 °C/30 min, sapwood heat treatment using vacuum and saturated steam had no adverse impact on the value of the white oak veneer logs.
- Researchpp 3815-3826Ji, L., Liu, Y., Zhou, J., Lei, Y., and Feng, H. (2023). “Factors affecting the temperature variation rate of bamboo during high-frequency heating,” BioResources 18(2), 3815-3826.AbstractArticlePDF
High-frequency electromagnetic fields refer to electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from 100 kHz to 300 MHz. High-frequency medium heating has the advantages of uniform heating, rapid energy consumption, and environmental protection. While it has a wide range of applications, the use of high-frequency dielectric heating in the bamboo industry is rare. Understanding the influence of bamboo temperature rise rate in high-frequency heating could promote bamboo industry development. In this work, curved bamboo was tested with high-temperature energy for continuous heating. The influence of moisture content of bamboo, sample thickness, and high-frequency processing power on temperature rise rate were studied. The results showed that the water content of bamboo affected the temperature rise rate. The effect of high-frequency heating was highest when the moisture content of bamboo was close to 11%. The thickness of sample had little effect on the temperature rise rate, but the high-frequency power had a significant effect on the temperature rise rate. The temperature rise rate of the lower and higher frequency power levels increased slowly and was close to constant. The heating power was 11 kW, and the temperature rise rate was the highest.
- Researchpp 3827-3837Liu, W., Zhang, X., Ren, H., Hu, X., Yang, X., Zhu, B., and Liu, H. (2023). “Synthesis of silsesquioxanes with methacryloyloxy and phenyl groups using corn stover ash as the major precursor,” BioResources 18(2), 3827-3837.AbstractArticlePDF
To address the challenges associated with corn stover utilization and the synthesis of phenyl- and methacryloyloxy-based silsesquioxanes (SQs) with difficulty and poor controllability, the authors present a novel approach that combines advanced biorefining techniques and innovative chemical synthesis methods. Spirocyclic alkoxysilane synthesized from corn stover ash was subsequently utilized for the synthesis of phenylSQs. The resulting phenylSQs were then subjected to fluorine ion-catalyzed rearrangement with 3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl methacrylate (KH570) to yield SQs containing phenyl and methacryloyloxy functional groups. Through manipulating the ratio of phenylSQs and KH570, the authors successfully achieved a desired ratio of functional groups on individual SQ cages. Optimization of the ratio significantly impacted product collection, with a range of 5.5:1 to 8.5:1 recommended for efficient and effective synthesis. This study represents an important advancement in the field of high-value conversion of biomass, offering an easy means of tailoring the structure of phenyl- and methacryloyloxy-based cage SQs.
- Researchpp 3838-3855Pang, S.-J., and Oh, J.-K. (2023). “Bending behavior of separable glued-laminated timber (GLT)-steel beam combined with inclined screws,” BioResources 18(2), 3838-3855.AbstractArticlePDF
A separable glued-laminated timber (GLT, Larix kaempferi Carr.)-steel beam system is presented in this work for easy recycling at the time of disposal. The minimum thickness of steel required to induce compressive GLT failure was assembled with GLT by inclined screws. In a total of 8 GLTs, 3 GLTs were not reinforced (control group), and 5 GLTs were reinforced with steel plates (comparison group). In the GLT in the comparison group, a steel plate (SPHC, yield strength: 227 MPa, modulus of elasticity 166.33 GPa) was installed with screws (∅9x160mm, 45°). The deflection and load of specimens were measured by a third-point bending test to derive their bending stiffness and load-carrying capacities. All specimens in the control group showed brittle tensile failure, but all specimens in the comparison group showed ductile behavior and maintained a load-carrying capacity of about 30 kN. After the compression failure of the GLT, there was no damage to the screw connection, while the steel plate was extended. Based on the behavior of the steel, a GLT-steel beam prediction model was developed, similar to the structural design method for reinforced concrete.
- Researchpp 3856-3869Sjöstrand, B., Karlsson, C.-A., Barbier, C., and Henriksson, G. (2023). “Hornification in commercial chemical pulps: Dependence on water removal and hornification mechanisms,” BioResources 18(2), 3856-3869.AbstractArticlePDF
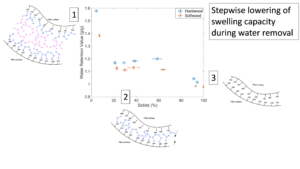
Understanding cellulose hornification provides crucial information regarding drying of pulp, paper, and other cellulosic materials as well as recycling them. By measuring drainage, fiber width, and water retention value of hardwood and softwood pulps before and after sheet forming and after different drying procedures at different achieved levels of solids, the hornification was evaluated. The water retention value was also measured for the pulps when dried from acetone to observe what happens when hydrogen bonds are not available in the liquid phase. The drainage and fiber width decreased with increasing solids content; the fibers became increasingly stiff with increased water removal. Water retention measurements indicated that hornification is a stepwise process with large drops in fiber flexibility as soon as the fibers are being processed and later after a certain amount of water has been removed. In sum, the fibers must achieve a certain solids content to show hornification, and hydrogen bonds in water draw the cellulose surfaces together to create hornification. The mechanism of hornification is believed to be driven by hydrogen bonds and related to the distance between cellulose chains inside the fiber wall. Other types of bonds are probably also present and help with the irreversibility of hornification.
- Researchpp 3870-3884Su, M., Li, N., Huang, T., and Zhu, B. (2023). “Competitive interactions of NH3 and toluene with biochar modified by pre- and post-treatments of H3PO4 in dual adsorption systems,” BioResources 18(2), 3870-3884.AbstractArticlePDF
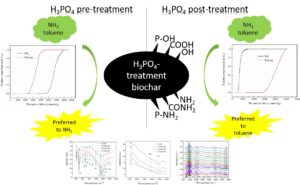
Biochar modified by H3PO4 treatment can be used to purify malodorous gases during bio-drying of sludge, but the current understanding of multi-component adsorption of malodorous gases through biochar is limited. This study examined the adsorption mechanism of mixed malodorous gases including toluene and ammonia (NH3) on two kinds of biochar modified via H3PO4 pretreatment before and after pyrolysis. The biochar obtained by H3PO4 pretreatment of biomass before pyrolysis (C550) preferred to adsorb NH3 whether in the single or the dual system. In contrast, the biochar obtained by H3PO4 reprocessing after pyrolysis of biomass (C350-550) tended to adsorb toluene in the dual system but was more efficient in absorbing NH3 in the single system. The pseudo-second-order kinetic model indicated the synergistic adsorption between NH3 and toluene for all biochar samples. In-situ DRIFTS of C350-550 during adsorption demonstrated the formation of amino functional groups caused by NH3 chemical adsorption with -OH (or -COOH) in the dual system. These increases in basic groups on C350-550 could enhance the surface zero potential point of C350-550, thereby improving the non-polarity of C350-550 and benefit the adsorption of weak polar toluene.
- Researchpp 3885-3894Hosseini, A. (2023). “Comparison of variability in leaves and roots nutrient contents of Persian oak (Quercus brantii Lindl.) in drought affected declining forests,” BioResources 18(2), 3885-3894.AbstractArticlePDF
Drought-induced crown dieback depends on plant nutrient status. This research examined the leaves and roots nutrients of Persian oak trees (Quercus brantii Lindl.) under the effects of drought and tree decline. The leaves and roots of oak trees were sampled randomly on the four main sides of their crown to analyze the N, P, K, Ca, and Mg. In healthy and declining trees, the N, P, and K content in the leaves was higher than in the roots, while the Ca content in the leaves was lower than in roots. The N and P in the roots of healthy trees had decreasing temporal changes, but these elements did not have significant temporal changes in the roots of declining trees. Leaf P showed decreasing temporal changes. The temporal decrease of root N and P and leaf P showed a negative effect of drought on Persian oak trees by reducing their ability to absorb water and nutrients and transfer them to their leaves. The higher concentration of elements in the leaves of oak trees, in addition to showing the decrease in the absorption of elements by the roots from the soil, can indicate a protective mechanism of oak trees against drought stress.
- Researchpp 3895-3908An, Q., Zhou, Z.-G. Wang, Y.-H., Guo, S., Chen, Z., Yuan, Y.-N., Sun, X.-Q., Yang, Y.-L., Zhang, T.-X., and Han, M-L. (2023). “Laccase produced by Coriolopsis trogii and Cerrena unicolor with the mixed of metal ions and lignocellulosic materials,” BioResources 18(2), 3895-3908.AbstractArticlePDF
Coriolopsis trogii and Cerrena unicolor were investigated for laccase production in submerged fermentation with different nutrient medium containing metal ions and lignocellulosic materials. The maximum laccase activity of C. trogii Han751 was 8584.44 ± 98.45 U/L and was obtained from nutrient medium 7. However, the maximum laccase activity of C. unicolor Han 849 was 16144.26 ± 635.30 U/L from nutrient medium 9. Thus, the capacity of secreting laccase of C. unicolor Han 849 was superior to that of C. trogii Han751. Different fungal species have different medium components suitable for laccase production. The content of CuSO4·5H2O and MnSO4 in nutrient medium with the concentration of 0.25 g/L and 0.151 g/L, respectively, was more beneficial to C. trogii Han751 secreting laccase. However, the vital components of nutrient medium that contribute to the laccase activity of C. unicolor Han 849 were corncob, glucose, and CuSO4·5H2O, with the corresponding concentrations of 1 g/flask, 5 g/L, and 0.25 g/L, respectively. The results will contribute to the development of new methods to produce low-cost laccase.
- Researchpp 3909-3922Zhou, S., Cao, J., Zhang, Z., Wang, H., and Liu, J. (2023). “Thermal properties of radiant floor surface materials and numerical evaluation of the thermal performance,” BioResources 18(2), 3909-3922.AbstractArticlePDF
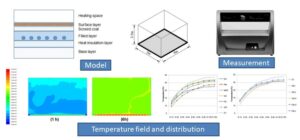
A Hot Disk thermal constant analyzer was used to obtain the thermal parameters of composite boards, solid wood floor, and ceramic tiles (CT). FLUENT software was used for the model establishment and the temperature field simulation, and the effects caused by different surface materials were analyzed. A 2D unsteady model was constructed to analyze floor surface temperature and indoor temperature fields in an enclosure space. Comparison of temperature fields caused by different materials showed that both steady indoor temperature and surface temperature of CT were the highest, which is due to its good thermal properties. Thermal conductivity and thermal capacity are the two main factors affecting floor thermal performance in the initial hours, while thermal conductivity is the key factor in the steady period. For the compared floor materials, CT and Sindora glabra (SG) are the optimal choices from the perspective of thermal performance, while composite boards are almost the same in thermal performance.
- Researchpp 3923-3937Čavlović, A. O., Bešlić, I., Pervan, S., and Prekrat, S. (2023). “Characteristics of thermally modified hardwood dust in determining workers’ occupational exposure,” BioResources 18(2), 3923-3937.AbstractArticlePDF
Thermal modification of wood changes its mechanical properties, generally reducing its strength, such that it is more easily chipped during processing than untreated hardwood. This study presents specific parameters used in the determination of mass concentration of thermally modified (TM) hardwood by gravimetric and photometric methods. An optical device, the Split 2, was used in the active mode, of which the holder of the inhalable dust IOM (Institute of Occupational Medicine) filter was the input part. Side-by-side determination of the respirable and inhalable mass concentration was made using the Higgins-Dewell respirable dust cyclone and an inhalable dust IOM sampler. Side-by-side determination of inhalable and total dust mass concentration was made using an IOM and open-faced (OF) filter holder to establish an IOM / OF sampling ratio. A correction factor of 1.16 was calculated for applying the photometric method as the ratio of mass concentration determined by gravimetric and photometric methods. Minimal concentrations of respirable and inhalable wood dust (geometric mean: cr = 0.058 mg/m3; cinh = 0.882 mg/m3) and a 12.76% share of respirable dust in the inhalable concentration cr / cinh, had a significant influence on the efficiency of the photometric method. The mass concentration obtained by IOM and OF samplers did not significantly differ (p = 0.36).
