Volume 18 Issue 2
Latest articles
- Researchpp 3654-3665Yamada, T., Matsumoto, Y., Nge, T. T., and Yamada, T. (2023). “Acid-catalyzed solvolysis of softwood using polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether to produce functional lignin derivatives,” BioResources 18(2), 3654-3665.AbstractArticlePDF
Glycol lignins (GLs) produced through acid-catalyzed solvolysis of softwood meal using glycols, such as polyethylene glycol (PEG), have been used for the development of functional materials. In this study, GLs with various physical and chemical properties were synthesized via solvolysis with monomethyl ethers of polyethylene glycol (MPEG), such as MPEG-n4 and MPEG-n8. The effects of the reaction time and temperature on the yield, molecular weight, and thermal properties of MPEG-lignin were studied. The yield of MPEG-lignin increased with the solvolysis time. Acid-catalyzed solvolysis using MPEG-n4 occurred faster than that using MPEG-n8. Higher reaction temperature resulted in a higher yield of MPEG-lignin with a higher glass transition temperature (Tg) and viscous thermal flow temperature (Tf). The Tg and Tf of MPEG-lignins increased with the solvolysis time. The MPEG-lignins synthesized at higher reaction temperatures showed a relatively strong carbonyl absorbance band in the infrared spectra, which was ascribed to decomposed sugar derivatives.
- Researchpp 3666-3680Guo, H., Yi, B., Xu, H., Dong, L., Guo, G., and Gong, L. (2023). “Numerical simulation on influencing factors of co-firing of municipal solid waste and leather,” BioResources 18(2), 3666-3680.AbstractArticlePDF
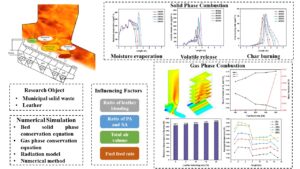
Incineration is an important method of recycling municipal solid waste (MSW). As an industrial waste, leather has a higher calorific value and more combustible components than MSW. The blending of leather can make up for the high moisture content and insufficient calorific value of MSW, providing a good solution to reduce the capacity of MSW and industrial waste. This study predicts the effect of blending combustion by means of numerical simulation; the effects of leather blending ratio, the ratio of primary air and secondary air, total air volume, and fuel feed rate were analyzed. The results showed that the appropriate increase of blending ratio improves the furnace chamber temperature, and the best blending amount of leather is approximately 10%. The best primary and second air ratio is 0.72:0.28. Insufficient airflow caused inadequate combustion, and excessive airflow reduced the furnace temperature. The feed volume in the range of 500 to 550 t/d had a good burning effect.
- Researchpp 3681-3693Liu, W., Zhang, X., Ren, H., Hu, X., Yang, X., and Liu, H. (2023). “Synthesis of biomass-based adsorbent from rice husk ash for copper ions adsorption,” BioResources 18(2), 3681-3693.AbstractArticlePDF
To solve the problems of low utilization of agricultural waste rice husk and heavy metal pollution, this investigation prepared a cheap copper ion adsorbent using rice husk ash (RA). The maximum Cu2+ adsorption capacity was 19.8 mg/g. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and surface area and porosity analyses were used to characterize the composition and structure of the material of silica-depleted rice husk ash (SDRA). The thermodynamics and kinetics of Cu2+ adsorption by SDRA were studied for their relevance to the adsorption mechanism. The adsorption of copper ions by SDRA was in accordance with the Langmuir model and the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. Furthermore, the increases in specific surface area and oxygen-containing functional groups following silica removal were primarily responsible for SDRA’s enhanced adsorption ability. And this is the first time that Cu2+ adsorbent has been prepared from the by-product of the synthesis of silane from rice husk ash. So, its synthesis cost is very low. Moreover, the preparation technique of SDRA is a revolutionary method of adsorbent creation that is both economical and environmentally benign.
- Researchpp 3694-3708Xiao, F., Li, D., Zhang, L., Du, Y., Xue, Y., Gong, P., Song, Y., Zhang, K., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, J., and Cui, Y. (2023). “Effect of seaweed extracts from different sources combined with urease and nitrification inhibitors,” BioResources 18(2), 3694-3708.AbstractArticlePDF
Urease inhibitors (UIs) and nitrification inhibitors (NIs) still have limitations in increasing crop yield. Therefore, to improve the application effect of inhibitors, the combination of seaweed extracts (SE) from different sources and inhibitors was added to urea to provide a theoretical basis for the development of a new generation of efficient stabilized urea fertilizer with both biostimulant and inhibitor technologies. The combinations were tested in outdoor pots with no N- fertilizer (CK), application of urea alone (U) as control, and kelp polysaccharide (KP), margin polysaccharide (MP), N−(n−propyl) thiophosphoric triamide (NPPT), dicyandiamide (DCD), and combinations of SE with inhibitor were added to urea to make eight fertilizer prototypes. Compared with KP, MP showed better application effect, with significantly higher grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) (P < 0.05). Compared with the addition of inhibitor alone, the combinations of NPPT with KP and MP, respectively, had opposite effects on urea−N transformation, meanwhile NPPT+KP had a positive effect. However, NPPT+MP significantly decreased yield, plant nitrogen uptake, and NUE (P < 0.05); DCD+MP decreased plant N uptake and NUE to some extent. Therefore, the addition of NPPT with KP and DCD with KP to urea significantly improved yield when planting maize in black soil.
- Researchpp 3709-3723Liu, W., Zhang, X., Ren, H., Hu, X., Yang, X., Zhu, B., and Liu, H. (2023). “Facile production of highly active rice straw bioadsorbent to remove Cu in wastewater,” BioResources 18(2), 3709-3723.AbstractArticlePDF
A bioadsorbent with a high specific surface area and high content of oxygen-containing functional groups was prepared from silica depleted rice straw ash (SDRSA). The starting material was a by-product of rice straw after alkoxysilane extraction. The maximum adsorption capacity of SDRSA for copper ions was 26.7 mg/g, which was higher than previously reported biomass adsorbents. The effects of adsorbent dose, pH, contact time, and other conditions on the adsorption performance of SDRSA on Cu2+ were investigated. The adsorption process of Cu2+ on SDRSA was well fitted by the Langmuir isotherm model and the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The physicochemical properties and adsorption mechanism of SDRSA were investigated by specific surface area testing (BET), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and Boehm titration methods. Electrostatic interaction, complexation, ion exchange, and precipitation are the possible Cu2+ removal mechanisms. The preparation method requires only simple washing and drying, and the alcohol can be distilled and recycled. Thus, SDRSA is very low cost and convenient to prepare in large quantities. This work presents a novel approach to optimize adsorbent production to mitigate heavy metal pollution.
- Researchpp 3724-3735Guo, P., Zhao, X., Zhu, X., Liu, Y., and Feng, Q. (2023). “Flame retardancy and physical-mechanical properties of poplar veneers impregnated by calcium carbonate,” BioResources 18(2), 3724-3735.AbstractArticlePDF
Fast-growing poplar (Populus tomentosa Carr) can produce wood veneers, but their poor quality restricts their application in construction and building. Modification of wood has the potential to improve its properties. In this study, poplar veneers were impregnated with calcium carbonate (CaCO3) to reinforce their performance. The results showed that CaCO3 was uniformly distributed in cell lumens in impregnated veneers. After impregnation, the maximum weight gain rate was up to 41.4%, and water uptake decreased from 6.82% to 0.94%. The hardness increased from 7.6 to 10.0 MPa, and the extent of wear fell from 0.91% to 0.05%. The ignition time was prolonged, and the heat release rate and total heat release were low. Experimental results demonstrated that CaCO3 improved the physical-mechanical properties and flame retardancy of poplar veneers.
- Researchpp 3736-3749Ouattara, A. Y., Soro, D., Kakou, E. K., Kone, K., Assidjo, E., Mabia, G., and Kamagate, M. (2023). “Synthesis and characterisation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae immobilised cells from cashew apple bagasse,” BioResources 18(2), 3736-3749.AbstractArticlePDF
Cashew apple bagasse is biomass rich in little-exploited lignocellulosic material. This study used this biomass as a support for cell immobilisation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. For this purpose, the immobilisation technique by attachment to a surface was applied. The bagasse used in this study contained 32.6% lignin. After delignification, the lignin content of the bagasse was 3.33%. The cell density was 1.21 × 108 cells g-1 for the immobilised cells prepared for 24 h. For the immobilised cells prepared for 48 h, the cell density was 1.71 × 108 cells g-1. Microscopic observations showed that the adhesion of the yeast cells to the surface of the support occurred on all layers with the cells immobilised for 48 h. These results highlight the efficiency of cell immobilisation of S. cerevisiae on cashew apple bagasse.
- Researchpp 3750-3767Yang, Y., Song, C., Liang, L., Tao, M., Wang, F., and Zhao, Y. (2023). “Material deterioration detection of wooden columns at the Nanyang Fuya Museum using a combination of macroscopic visual inspection and moisture content testing,” BioResources 18(2), 3750-3767.AbstractArticlePDF
Wooden columns, as an important load-bearing wooden component of traditional wooden structures, determine the safety of an entire building. With the increase in material deterioration, the overall health and life of ancient buildings is affected. In this study, the deterioration of wooden columns of ancient buildings in the central axis of the Nanyang Fuya Museum was detected through a combination of macroscopic visual inspection and moisture content testing. The result was that the deterioration degrees and MCs of wooden columns located in the south direction, with good ventilation effect or with oil paint protection were lower than those of wooden columns located in the north direction, with poor ventilation effect or without oil paint protection. The deterioration degree increased with the increase of MC. The results of this research provide the basis for the analysis of the causes and risks of material deterioration.
- Researchpp 3768-3782Yücel, G., and Erken, K. (2023). “Germination methods and characteristics of endemic Centaurea olympica DC. Koch grown in cultural conditions,” BioResources 18(2), 3768-3782.AbstractArticlePDF
The most suitable generative production method was selected in this work by applying different treatments to endemic Centaurea olympica seeds. The development performance and adaptation ability of the species in natural and cultural conditions (in the natural population, in pots and in the garden) were determined, with the goal to protect the species under ex situ conservation. The growth performance of the plant was monitored, and its ornamental plant potential was evaluated. The obtained data were compared with the data from the natural population. All morphological and phenological observations showed that the species can easily adapt to cultural conditions. For 2 months in the summer period, it is a lilac-flowered herbaceous plant that can be preferred for gardens with increasing number of shoots and flowers in parallel with its development. Among the different pretreatments applied to the seeds of the species, the highest germination percentage (73.5%) and germination speed (T50=8 days) was found with 600 ppm GA3 treatment for 24 h after cold-wet stratification at 4 °C for 3 months. The appropriate germination temperature was determined as 20 °C.
- Researchpp 3783-3801Ab Latib, H., Amir, M. A., Othman, K., Ratnasingam, J., and Liat, L. C. (2023). “Dichotomy of predictor variables of indoor air quality and prevailing public perception of green living space – A preliminary assessment,” BioResources 18(2), 3783-3801.AbstractArticlePDF
Indoor environmental quality has a profound effect on human health and productivity. In this respect, this study evaluates indoor air quality in terms of its various parameters in sustainably built homes in three different locations. A supplementary study to examine the formaldehyde emission levels from furniture with three different finishes was also undertaken. A questionnaire-based survey was then conducted to evaluate the general public perception of the prevailing indoor air quality in the three locations. The results revealed that temperature, relative humidity, indoor air speed, particulate matter (PM10), CO2, NO2, and total volatile organic compounds (TVOC) and formaldehyde (HCHO) readings were not significantly different between the three locations and were below the existing limit allowed for indoor environmental quality. However, the HCHO emission was the highest from furniture with the two-layer coatings, followed by single layer coating, and finally the furniture with the veneer overlay. It was noteworthy that the general public’s awareness and knowledge of indoor air quality was relatively poor, except for the tertiary level educated respondents. In this regard, policymakers need to increase the awareness and knowledge of indoor environmental quality among the general public, if non-compliance is to be detected and promptly addressed.
