Volume 18 Issue 4
Latest articles
- Researchpp 7769-7795Gupta, A., Jain, L., Dutt, B., Kumar, R., and Sharma, S. (2023). “Behavioral change in physical, anatomical, and mechanical characteristics of thermally treated Pinus roxburghii wood,” BioResources 18(4), 7769-7795.AbstractArticlePDF
Thermal treatment of pine wood was carried out at 80, 120, 160, and 200 °C for 2, 4, and 6 hours. The highest mean values were, for specific gravity (0.492), moisture content (29.1%), and maximum moisture content (191%), whereas the lowest mean values were for specific gravity (0.418), moisture content (1.20%), and maximum moisture content (127%). The maximum mean values were for shrinkage in longitudinal plane (0.42%), radial plane (4.63%), volumetric shrinkage (9.28%), and maximum mean value tangential plane (3.67%). The minimum mean values were for shrinkage in longitudinal plane (0.04%), radial plane (2.22%), tangential plane (1.55%), and volumetric shrinkage (4.88%). Maximum mean values were for swelling in longitudinal (0.41%), radial (5.22%), and tangential plane (3.15%) and maximum mean volumetric swelling (7.71%), while minimum mean values were for swelling in longitudinal plane (0.08%), radial plane (2.26%), and tangential plane (1.29%) and minimum mean volumetric swelling (3.15%). The highest mean values were for tensile strength (57.3 MPa) and compression parallel to the grain (50.3 MPa), the maximum mean value of bending strength (84 MPa) and compression strength perpendicular to grain (27 MPa), whereas the lowest values were for tensile strength (42.7 MPa), bending strength (7.33 MPa), compression parallel to the grain (7.33 MPa) and compression strength perpendicular to grain (12.3 MPa).
- Researchpp 7796-7804Çakıcıer, N., and Ulay, G. (2023). “Determination of color characteristics of some wood species treated with bleaching chemicals,” BioResources 18(4), 7796-7804.AbstractArticlePDF
With the application of bleaching treatments, the color of the wood material changes. When different bleaching agents are applied to the same wood, different results are likely to be obtained. In this study, wood species doussié (Afzelia africana), iatandza (Albizia ferruginea), merbau (Intsia bijuga (Colebr.) O. Kuntze), mahogany (Swietenia mahagoni L.), and hornbeam (Carpinus betulus L.) along with one and two component (B-One-C and B-Two-C) wood bleaching chemicals were applied to the wood material surfaces with sponge technique. Then, color parameters (ho: hue angle, a*: red color tone, b*: yellow color tone, C*: chroma, and L*: lightness) were determined on bleached and unbleached materials. According to the results obtained, B-One-C application increased ho, a*, b*, C*, and L* values in all wood species. The highest ∆E* values were determined in mahogany, doussié, hornbeam, and merbau wood species treated with B-Two-C. The chemicals used in the study showed different results on the same wood.
- Researchpp 7805-7817Xu, Q., Lan, X., Ali, M., Ding, Y., and Wang, Z. (2023). “Dynamic test study of twelve elastic constants of larch timber,” BioResources 18(4), 7805-7817.AbstractArticlePDF
The elastic modulus, shear modulus, and Poisson’s ratio of timber are the elastic constants characterizing its material properties. In this paper, the transient excitation method was used to dynamically measure the 10 elastic constants of the falling larch wood under the condition of the free board and cantilever board, that is, 3 elastic moduli E, 3 shear moduli G, and 4 Poisson’s ratios μ. The other two Poisson’s ratios μ were derived using the principle of orthogonality. At the same time, the elastic modulus, shear modulus, and Poisson’s ratio under static conditions were tested and verified by symmetrical four-point bending, asymmetrical four-point bending, and tensile methods. This study is expected to have good application value and practical significance for timber as an engineering structural material, which is widely used in architecture, decoration, furniture, transportation, musical instruments, and in other fields.
- Researchpp 7818-7838Zhao, Y., and Xu, Y. (2023). “Evaluation model for modular children's wooden storage cabinet design,” BioResources 18(4), 7818-7838.AbstractArticlePDF
The design evaluation method of furniture products was explored for modular children’s wooden storage cabinets. An evaluation model consisting of the Kano model, hierarchical analysis, and grey relational analysis is proposed. A 25-member panel of experts was involved in the development of the evaluation guidelines and the scoring of the program. The expert group used the KJ method to obtain evaluation guidelines for modular children’s wooden furniture that met the requirements of the hierarchical analysis method and screened the functional indicators through 103 validated questionnaires for the Kano model. The evaluation guidelines of modularized children’s wooden storage cabinets were thus obtained, which are both comprehensive and targeted. Then, hierarchical analysis and grey relational analysis were combined to select the solution with the highest grey weighted correlation result as the best solution. The feasibility of the grey comprehensive evaluation method, which combines subjective preference and objective empowerment, in the field of furniture was confirmed through the practice of selecting the best of the three modular children’s wooden storage cabinet design solutions, and the evaluation preference of the modular children’s wooden storage cabinet was uncovered. The design model provides an innovative evaluation tool for children’s furniture manufacturers to optimize their sales strategies.
- Researchpp 7839-7855Jo, H. M., Lee, S. H., and Lee, J. Y. (2023). “Evaluation of structure and compressive properties of eco-friendly cushioning materials based on starch and cellulose types,” BioResources 18(4), 7839-7855.AbstractArticlePDF
A reinforced eco-friendly cushioning material (ECM) comprising starch and cellulose material was developed. The ECM was prepared based on the starch type and cellulose material content; it was compared with commercial CMs. Different sizes of refined pulp (RP) and microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) were manufactured from hardwood bleached kraft pulp via beating and grinding, respectively. Thereafter, amylose-containing corn starch (CS) or amylopectin-only-containing glutinous rice starch (GS) was mixed with the manufactured cellulose materials. A slurry comprising starch and cellulose materials was homogenized for 2 min and lyophilized to prepare the ECM, after which the structure and strength characteristics of the prepared ECM were evaluated. The GS-prepared ECM produced a plate-like internal structure because of its amylopectin content, and amylose-containing CS exhibited a net-like shape. The cellulose materials offered support between starches with plate-like or net structure ECMs, and the pore shape was formed by adding MFC. As the cellulose material content increased, the strength of the ECM increased compared with that of the commercial CMs. Thus, ECMs with higher strength than their commercial counterparts could be manufactured with GS and cellulose materials.
- Researchpp 7856-7876Yildirim, I., and Han, M. (2023). “Determining the motivation levels of employees in the forest products industry,” BioResources 18(4), 7856-7876.AbstractArticlePDF
This research assessed employee motivation levels within the forest products industry. A total of 1,175 individuals engaged in diverse roles across the sector were involved in the study. Data collection relied on the administration of questionnaires. The findings highlighted key motivational factors. Notably, “wages, social rights, and work environment” emerged as the primary contributors to mood and motivation. Similarly, the factors encompassing “wages, social rights, reward systems, and bonuses” ranked highest in terms of motivational tools. Job satisfaction was primarily influenced by “wages and the fulfillment of individual needs.” Furthermore, the study revealed that “education, talent, industriousness, and self-sacrifice” were predominant among influential factors. When it came to desired managerial qualities, “staffing and interpersonal skills” took precedence. Material rewards like “leave entitlements and wage increases” were the foremost considerations for recognizing achievement. During the company selection process, employees considered wage conditions, insurance, social opportunities, health and safety measures, job security, management approach, and growth prospects as vital factors, in descending order of importance.
- Researchpp 7877-7888Choowang, R., Rodpan, W., Raknarong, J., and Noopum, N. (2023). “Glycerol-based liquefied palm kernel shell product and its blend with citric acid as bio-based wood adhesive,” BioResources 18(4), 7877-7888.AbstractArticlePDF
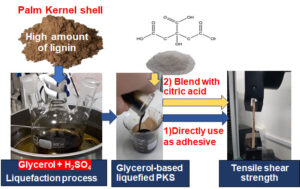
Concerns for the environment and for human health have become critical factors that motivate creating bio-based wood adhesives. Therefore, this study proposes replacing toxic chemicals with alternative adhesives. In the first step, glycerol was added to the natural phenolic compounds from liquefaction of palm kernel shell (PKS), having a high content of lignin. The obtained glycerol-based liquefied PKS, and its blend with citric acid, were tested for bonding in a study on the effects of hot-pressing conditions (temperature and time). The results revealed that the liquefaction system in this study achieved an 83% conversion of the PKS components into glycerol-based liquefaction. According to the Fourier transform infrared and carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance analyses, the glycerol-based PKS contained lignin derivatives and furan products. This accounted for its great performance in bonding rubberwood veneers. The tensile shear strength was improved by blending with 15% citric acid, especially when applying the high 190 °C pressing temperature for 15 min.
- Researchpp 7889-7904Zhang, N., Xu, W., and Tan, Y. (2023). “Multi-attribute hierarchical clustering for product family division of customized wooden doors,” BioResources 18(4), 7889-7904.AbstractArticlePDF
To improve the production system for customized wooden doors and to gain research and development efficiency, this paper proposed the feasibility of using hierarchical clustering algorithms to cluster a company’s customized wooden door products and its application to rational product family architecture. The particular use of multi-attribute feature data to locate products and the integration of image data into the database can make the original hierarchical clustering more compatible and adaptable for application to customized wooden doors. The preprocessed data was analyzed by clustering to obtain the clustering results and similarity relationships. Hierarchical clustering results were uneven and not entirely interpreted. However, the internal order structure of clusters and the clustering process could be clearly observed, and the distance hierarchical relationship between the products could be obtained, which was beneficial to the division of the product architecture. The results illustrated that processing using hierarchical clustering of multi-attribute data is feasible for optimizing customized wooden door product systems. In addition, the product architecture, product coding rules, and front-end development process were established to improve standardization and research and development efficiency. There is still great potential for developing the custom wooden door category in custom furniture companies.
- Researchpp 7905-7914Sinin, A. E., Hamdan, S., Said, K. A. M., Abdul Aziz, D. S., and Musib, A. F. (2023). “Acoustics of the forgotten Tapi two-strings lute of Lun Bawang,” BioResources 18(4), 7905-7914.AbstractArticlePDF
The Tapi two-strings lute is typically made from Pulai (Alstonia spp.), a light hardwood in the Apocynaceae family. This study determines the tuning retrieval of the Tapi two strings lute instrument. This work investigated the string notes using a microphone for recording the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) of the signal to determine the fundamental and the partial frequency of Tapi two strings lute instrument. The Tapi was tuned to the E major key with F#, C#, G#, and D# note. The time frequency analysis (TFA) showed that each open string has its own timbre characteristics. The open string 1 showed only 3 important partials, whereas open string 2 showed 6 important partials. Frets 2, 4, 6, and 8 showed more partials than frets 1, 3, 5, and 7. Both fret 9 and 10 showed a similar number of partials. Frets 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, and 16 showed less partials and were evenly distributed, whereas fret 17 clearly showed only 4 partials.
- Researchpp 7915-7922Fauzi, B., Mohd Nawawi, M. G., Fauzi, R., Mohd Ismail, N. I., Mohd Noor, S. F., Yahaya, I., Suhaimy, S. H. M., and Roslan, M. S. (2023). “Glucose tolerance of Clostridium acetobutylicum fermentation in the anaerobic system,” BioResources 18(4), 7915-7922.AbstractArticlePDF
Solvent-producing Clostridium acetobutylicum was purified and used in an acetone-butanol-ethanol (ABE) fermentation process. The objective of this study is to design a fermentation medium for the synthesis of butanol and determine the ideal glucose concentration for appropriate microbe ingestion. The fermentation medium was incubated at 37 °C for up to 90 h before inoculation while being sparged with nitrogen gas under anaerobic conditions. Based on the optical density of fermentation media, the growth rate was also monitored. At 60 g/L of glucose, which was the optimum condition for fermentation, the process followed a log phase pattern until the death phase, with the largest growth taking place between 10 h and 50 h after incubation. The C. acetobutylicum steadily consumed the glucose content, reaching its maximal consumption with only around 12 g/L remaining. In contrast to acetone and ethanol, which produced the highest concentrations at 6.4 g/L and 5.2 g/L, respectively, butanol productions were seen appropriately, with the greatest concentration yielding 11.2 g/L of butanol. This shows that C. acetobutylicum expressed its active metabolism for up to 60 g/L and further increase of glucose content will deteriorate the performance of butanol production.
