Volume 19 Issue 1
Latest articles
- Researchpp 1666-1679Yang, S., and Kang, S. (2024). “Assessment of color and contact angle changes in waterborne stained wood under natural weathering condition of South Korea’s summer climate,” BioResources 19(1), 1666-1679.AbstractArticlePDF
This study aimed to develop a waterborne stain (WBS) that protects against weathering and increases resistance of wood to fungi when exposed to heavy rainfall. The WBS was prepared using an antibacterial agent, insect repellent, and copper nanoparticle solution (CN) as a surface coating agent. The WBS was applied on larch and hemlock wood, and changes in color and wettability due to natural and artificial weathering were evaluated. A gray-blue spot developed on the untreated wood surface within 30 d of outdoor exposure, which then spread over the entire wood surface, and the wood eventually turned black. Resistance to fungi increased when CN alone was applied; however, the CN surface was oxidized and turned gray after 30 d and 90 d for larch and hemlock, respectively. The water contact angle was increased due to leaching. The application of CN followed by WBS prevented wood discoloration under ultraviolet light and the wood showed excellent weathering resistance capacity. The prevention of wood discoloration and resistance to fungi by CN were confirmed, which could guide the development of a paint that can prolong protection from weathering of wood exposed to heavy rainfall events.
- Researchpp 1680-1695Ezung, B., Kalivarathan, R., Khusro, A., Agastian, P., Almutairi, B. O., and Arokiyaraj, S. (2024). “In vitro assessment on anti-inflammatory and anti-lipidemic properties of selected plant species,” BioResources 19(1), 1680-1695.AbstractArticlePDF
Preliminary assessment for anti-inflammatory and anti-lipidemic properties was done with different solvent extracts derived from Urtica urens and Polygonum chinense leaves through in vitro experimentation. To evaluate anti-inflammatory properties, the stability of human red blood cells membranes and the denaturation activity of proteins were assessed. For anti-lipidemic effects, an assay was conducted to measure the inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. The results of membrane stabilization showed IC50 values of 480.96 ± 0.02 and 319.41 ± 0.19 µg/mL for ethyl acetate extract of U. urens and P. chinense, respectively. The standard drug Diclofenac sodium exhibited IC50 value of 240.37 ± 0.04 µg/mL. For protein denaturation, IC50 values were determined as 221.75 ± 0.2 and 315.76 ± 0.19 µg/mL for U. urens and P. chinense, respectively. The IC50 value of the standard drug was calculated as 126.7 ± 0.34. The IC50 values towards HMG-CoA reductase inhibition were subsequently determined as 29.84 ± 0.35 µg/mL for U. urens and 24.34 ± 0.04 µg/mL for P. chinense against the standard drug Diclofenac sodium (7.52 ± 0.43 µg/mL). GC-MS chromatograms revealed the presence of bioactive compounds in ethyl acetate extract of P. chinense leaves. This work is substantiation for the traditional therapeutic utilization of these extracts.
- Researchpp 1696-1706Chowdhury, G., Sharma, R., and Sarkar, U. (2024). “Cultural studies and yield attributes of pink oyster mushroom (Pleurotus djamor) in West Bengal,” BioResources 19(1), 1696-1706.AbstractArticlePDF
The pink oyster mushroom, scientifically known as Pleurotus djamor, is characterized by its appealing color, positive sensory qualities, substantial nutritional content, and its possession of antioxidant, antimicrobial, and medicinal properties. Mushrooms degrade lignocellulosic substrates through lignocellulosic enzyme production and utilize the degraded products to produce their fruiting bodies, contributing to sustainable agriculture and forestry and a short-term generation of income. The present study was carried out to assess the effect of various cultural parameters viz. temperatures, pH, solid culture media, carbon, and nitrogen sources on mycelial growth of the fungus and to identify the suitable grain for spawn production, optimum dose of spawn and suitable substrate for obtaining the highest yield of the mushroom. All of the experiments were conducted following standard protocols after procuring the pure culture of P. djamor from DMR-Solan. The optimum temperature for mycelial growth of the fungus was 28 °C at pH 7.5, and the best solid culture media was oat meal agar. Starch was the best carbon source and 0.3% L-asparagine served as the best source of nitrogen. Sorghum grains promoted the fastest spawn production. Out of five different doses of spawn and two assessed substrates, 4% spawn on paddy straw promoted the highest yield.
- Researchpp 1707-1727Xue, G., and Chen, J. (2024). “Strategies for applying shape grammar to wooden furniture design: Taking traditional Chinese Ming-style recessed-leg table as an example,” BioResources 19(1), 1707-1727.AbstractArticlePDF
This paper uses shape grammar to conduct strategic research and innovative translation of existing wooden furniture designs. A traditional Chinese Ming-style recessed-leg table was used as an example to demonstrate its feasibility. The paper applies biological DNA genetic information to furniture products, and combines shape grammar to evolve and mutate them, thereby creating new forms of wooden furniture that maintain the original genes. A DNA gene pool of recessed-leg table was constructed, and an architectural queti replacement pool was constructed based on the rules of shape grammar as backup for subsequent experiments to replace part of the designed genes of the recessed-leg table. Shape grammar was used to deduce the recessed-leg table and generate three plans. A consumer questionnaire was established through the semantic differential method. After evaluating these three design plans, an optimal plan that meets market demand was selected, and modeling, rendering, and concept elaboration were performed. Finally, the paper takes Ming-style recessed-leg table as an example to demonstrate that it is effective and feasible to use shape grammar to guide the design and research of domestic wooden furniture.
- Researchpp 1728-1743Law, J. C. H., Wade, K. R., Parker, K. G., Mutukumira, A. N., and Sloane, M. (2024). “Sustainable paper-based packaging from hemp hurd fiber: A potential material for thermoformed molded fiber packaging,” BioResources 19(1), 1728-1743.AbstractArticlePDF
Hemp hurd fiber, a low-value waste stream from the hemp industry, has potential downstream applications as an alternative to non-renewable plastics for single-use food service ware and packaging applications. Packaging paper substrates made from chemically pulped hemp hurd, mixed in varying ratios with bleached thermomechanical radiata pine pulp were developed and tested. Handsheets were characterized using several mechanical property tests including tensile strength, tearing resistance, burst strength, short-span compression, ring crush, together with Gurley air resistance, contact angle, and Cobb60 tests. Generally, addition of hemp hurd fibers significantly improved handsheet mechanical properties. Hot-pressing of the handsheets so as to approximate molded fiber thermoforming further enhanced their performance, with pure hemp hurd handsheets having the highest mechanical properties and barrier performance. A prototype was successfully thermoformed from hemp fiber, demonstrating overall feasibility of this fibre source for molded fibre objects.
- Researchpp 1744-1756Miric-Milosavljevic, M., Svrzic, S., Nikolić, Z., Djurkovic, M., Furtula, M., and Dedic, A. (2024). “Signal processing and machine learning as a tool for identifying idling noises of different circular saw blades,” BioResources 19(1), 1744-1756.AbstractArticlePDF
This study examines the possible utilization of machine learning and decision-making in the woodworking sector. This refers to the recognition of certain sounds produced during tool idling. The physical and geometric properties of the circular saw blade result in different noises being generated during idling. It was assumed that the respective circular saw blades can be recognized by these noises. The noises of three different circular saw blades were examined while idling at the same speed. In order to obtain useful data for the deep learning process, the coarse signals were subjected to frequency analysis. A total of 240 noise samples were taken for each circular saw blade and later subjected to signal processing. Frequency-power spectra were created using a custom program in Matlab Campus Edition software, such as for the spectrograms. A short Fourier transform was used to create the average spectral density plot using self-made software. The input data for the deep learning network was created in Matlab using a custom program. The GoogleNet deep learning network was used as a data classifier. After training the network, an accuracy of 97.5% was achieved in recognizing circular saw blades.
- Researchpp 1757-1776Mirițoiu, C. M., and Rădoi, A. I. (2024). “Mechanical properties for composites with dammar resin reinforced with crushed corn cob,” BioResources 19(1), 1757-1776.AbstractArticlePDF
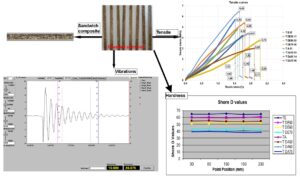
The study focused on the potential use of agricultural waste (corn cob) in the manufacturing of composite materials. In the first stage, composite materials were manufactured and tested using synthetic matrices (epoxy and acrylic) and hybrid matrices based on dammar resin (50% dammar, 60% dammar, and 70% dammar). Since it was observed that the samples had low mechanical properties under tensile and bending loads, the study was expanded to the production of sandwich-type composites with silk fabric facings. It was found that, by utilizing silk fiber, both tensile and bending strength increased from a few hundred percent up to a few thousand percent, compared to the samples that are only reinforced with crushed corn cob.
- Researchpp 1777-1788Fredriksson, M. (2024). “Predicting strength of Norway spruce and Scots pine sawn timber using discrete X-ray log scanning, optical board scanning, traceability, and partial least squares regression,” BioResources 19(1), 1777-1788.AbstractArticlePDF
Recently developed technology in sawmills such as advanced log scanning and traceability concepts enable new ways of grading logs and boards. When it comes to strength grading, this is often done on sawn boards using automatic scanning systems. However, if board scanners were to be augmented with data from log scanners by using traceability, more information on the wood properties is available. In this study, the main objective was to compare the strength prediction capability of board scanning alone, to board scanning augmented with X-ray and 3D data from log scanning, for Norway spruce (Picea abies L. Karst.) and Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.). In that case, data from three different scanning systems was combined, two for logs and one for boards. A further objective was to investigate whether pre-sorting logs for strength grading can be done using either 3D log data alone, or 3D log data augmented with X-ray data. The results show an improved strength prediction when adding log data to board data, and that 3D log data alone is not enough to pre-sort logs for strength, while adding X-ray log data makes it possible. Strength prediction on Scots pine performed somewhat better than prediction on Norway spruce.
- Reviewpp 1789-1813Palanisamy, S., Murugesan, T. M., Palaniappan, M., Santulli, C., Ayrilmis, N., and Alavudeen, A. (2024). “Selection and processing of natural fibers and nanocellulose for biocomposite applications: A brief review,” BioResources 19(1), 1789-1813.AbstractArticlePDF
In this study the recent developments in raw materials, manufacturing processes, and applications of natural fiber composites (NFCs) were reviewed. Natural fibers can represent a substitute for man-made fibers (including glass, aramid, and carbon) in a variety of biocomposite applications. Physical and chemical properties of the natural fibers are given and compared with the synthetic fibers. Advantages and disadvantages of NFCs in comparison with synthetic fibers such as glass and carbon fibers have been proposed. Criteria are described for the selection and processing of natural fibers for polymer composites used in different sectors such as automotive and building industries. The nanocellulose production methods, unique properties, and its recent industrial application in various sectors are given. This short review on NFCs considers their chemical, physical, and mechanical characteristics, as well as their various applications.
- Reviewpp 1814-1843Sanoja-López, K. A., Loor-Molina, N. S., and Luque, R. (2024). “Rice waste feedstocks: A review of alternatives for their conversion into high-value added products,” BioResources 19(1), 1814-1843.AbstractArticlePDF
The increase in global population, expected daunting energy demands, and scarcity of resources has driven the search for new sustainable sources of materials, energy, and chemicals. In this context, biomass valorization has emerged as a promising technology to obtain high-value products in recent years. This research focuses on the valorization of rice production waste including straw, husk, and bran, due to their abundance, underutilization, and potential in generating a wide range of valuable products such as biofuels and materials. A systematic review was conducted regarding the valorization of rice production waste. The characteristics of biomass obtained from post-harvest rice production were explored, as well as the primary products derived from each of the discussed biomass feedstocks. Furthermore, the economic viability of the obtained products in their respective fields of application was evaluated, providing a solid foundation for future research and industrial applications. Different rice waste materials studied hold significant potential to obtain high‑value products including silica, adsorbent materials, biofuels, and various bioactive compounds.
