Volume 19 Issue 2
Latest articles
- Researchpp 2609-2625Palaniappan, M., Palanisamy, S., Murugesan, T., Tadepalli, S., Khan, R., Ataya, S., and Santulli, C. (2024). “Influence of washing with sodium lauryl sulphate (SLS) surfactant on different properties of ramie fibres,” BioResources 19(2), 2609-2625.AbstractArticlePDF
Green composite materials are a means of reducing reliance on synthetic and especially single-use plastics (SUP) and raising public awareness of the need for urgent action to protect the planet. Natural (lignocellulosic) fibres are increasingly utilized as the reinforcement in polymer matrix composites, in search for increased renewability and sustainability. This work concerns the effect of washing ramie (Boehmeria nivea) fibres using sodium lauryl sulphate (SLS) surfactant. The SLS-treated ramie fibres were examined for their morphological, physical, thermal, structural, and mechanical properties by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and tensile testing. SLS treated ramie fibres density and crystallinity index values were 1.23 g/cc and 84.5%, respectively, with a very high cellulose content of 81.3%, because hemicellulose and loose particles were dissolved. SEM images depicted the relevant changes, with no significant damage on treated fibre surfaces. With some assistance from the treatment, fibres initiated their degradation only above 250 °C, culminating at 327 °C, which appears suitable for the manufacturing of composites with the most common matrices.
- Researchpp 2626-2638Wang, S., Ma, P., Lin, J., Hou, T., Wang, F., Que, Z., and Gong, M. (2024). “Mechanical properties of glulam moment-resisting joints reinforced by inclined self-tapping screws,” BioResources 19(2), 2626-2638.AbstractArticlePDF
Self-tapping screws (STS) are an effective fastener to enhance wooden moment-resisting joints. However, the effects of the arrangement and insertion angle of STS on the mechanical properties of wooden joints are less studied. Therefore, this study investigated the influence of these two factors on the mechanical properties of wooden joints by conducting cyclic loading tests using glulam moment-resisting joints reinforced by STS with different arrangements (round and square) and insertion angles (45° and 90°). The failure modes, bearing performances, and energy dissipation capacities were considered. The results showed that the insertion angle affected the bearing and energy dissipation capacity of the joints significantly, while the effect of arrangement was slight. The anti-rotation bending moments of the joints reinforced by inclined STS were higher by 31.7% and 13.5% when the arrangement of STS was circular and rectangular respectively compared with the joints reinforced by vertical STS under compression state, and were lower by 17.5 % and 22.9 % under tensile state. The restoring force characteristics of the joints were similar when the insertion angle of STS was the same. Furthermore, the joints had optimal ductility and stiffness when the arrangement was rectangular, and the insertion angle was 45°.
- Researchpp 2639-2659Yu, S., Zhang, H., Zheng, Q., Chu, D. D., Chen, T., and Chen, X. (2024). “Consumer behavior based on the SOR model: How do short video advertisements affect furniture consumers’ purchase intentions?” BioResources 19(2), 2639-2659.AbstractArticlePDF
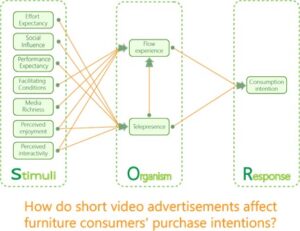
Short video advertisements are a novel and influential medium for promoting furniture products, but their effects on consumers’ purchase intentions remain underexplored. This study applies the extended stimulus-organism-response (SOR) framework, a psychological theory that elucidates how stimuli (short video ads), organisms (consumers), and responses (purchase intentions) are interrelated. This study quantitatively examines these relationships using structural equation modeling (SEM). The results reveal that the Flow experience and Telepresence experience significantly affect purchase intentions, indicating that consumers who experience high levels of engagement and immersion while viewing short furniture-related video ads are more likely to exhibit buying behavior. This study also identifies three critical antecedents of the Telepresence experience: social influence, perceived entertainment value, and perceived interactivity. These factors may enhance the effectiveness of short-form video advertising by increasing consumer interaction and engagement. Moreover, convenience conditions, perceived entertainment value, and media richness significantly influence consumers’ flow experience. This suggests that these factors should be considered when designing short video advertisements to optimize consumers’ flow experience and thus increase purchase intentions. This study provides empirical evidence for the SOR framework, investigates the impact of short video advertisements on furniture consumers’ purchase intention, and offers practical implications and recommendations for marketing practitioners.
- Researchpp 2660-2669Wang, C., Yu, J., Jiang, M., and Li, J. (2024). “Effect of selective enhancement on the bending performance of fused deposition methods 3D-printed PLA models,” BioResources 19(2), 2660-2669.AbstractArticlePDF
The top and bottom shells of fused deposition 3D-printed PLA models are exposed to the highest stresses. To improve the bending performance of PLA models under three-point bending conditions, the models were strengthened by a selective enhancement method. Several sets of PLA models were fabricated using FDM technology, and three-point bending experiments were conducted to compare the bending strength of PLA models when the layer height, top/bottom shell thickness, and extrusion rate were varied. The bending strength of the PLA models increased as the layer height of the top/bottom shell decreased, the thickness increased, and the extrusion rate increased. The average bending strength of the PLA models after selective enhancement was 84.4 MPa, and the average bending modulus of elasticity was 0.816 GPa, which were higher than the average bending strength of 68.6 MPa and the average bending modulus of elasticity of 0.736 GPa of the conventional groups. These results indicated that the selective enhancement method improved the bending performance of 3D-printed PLA models, and it also provided a reference for the improvement of the mechanical properties of the 3D-printed models with cellulose composite reinforced materials.
- Researchpp 2670-2684Kocatürk, E., Şen, F., Zor, M., and Candan, Z. (2024). “Development and characterization of nanocellulose/ carbonized waste rubber nanocomposites,” BioResources 19(2), 2670-2684.AbstractArticlePDF
Recycling is one of the most popular research topics today. In this study, in addition to the evaluation of waste tires, which are frequently encountered in the industry and difficult to dispose of, a green biomaterial, nanocellulose-based new generation nanocomposite was produced and characterized for the first time. Carbonized waste rubber, obtained by pyrolysis of tire wastes, was reinforced with nanocellulose at levels of 0.10%, 0.25%, 0.5%, and 1% by weight. The prepared nanocellulose-based nanocomposites were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), morphological properties by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), thermal properties by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and dynamic mechanical thermal (DMTA). In addition, the percentage of gel contents of the produced nanocomposites were determined. Thermal analyses revealed that the sample containing 1% carbonized waste rubber showed the highest thermal stability and at 750 °C the ash yield increased up to 25% compared to nanocellulose. The fabricated nanocomposites had about 10 times higher storage modulus compared to pure NC. All results show that the green nanocellulose-based nanocomposites can be used for future applications in industry.
- Researchpp 2685-2700Alwala, W., Perju, A., Schwarz, M., Bonhotal, J., Pires, S., Ankeny, M., Daystar, J., and Frey, M. (2024). “The compostability of denim fabrics dyed with various indigos,” BioResources 19(2), 2685-2700.AbstractArticlePDF
Denim fabric samples representing current indigo dye sources and fabric structures were biodegraded in feedstock including food waste, manure, and animal bedding, which are typically composted at the Cornell Farm Services Composting Facility and processed under laboratory conditions for 77 days. Indigo types including dry denim, pre-reduced, and natural did not inhibit degradation as compared to undyed 100% cotton fabric. Additionally, fabrics tested as received from the mill and those tested post scouring degraded effectively. As expected, denim containing 24% polyester and 2% spandex retained overall fabric structure despite degradation of the cotton portion of the yarns.
- Researchpp 2701-2713Al-Rajhi, A. M. H., Ganash, M., Alshammari, A. N., Alsalamah, S. A. and Abdelghany, T. M. (2024). “In vitro and molecular docking evaluation of target proteins of lipase and protease for the degradation of aflatoxins,” BioResources 19(2), 2701-2713.AbstractArticlePDF
The consumption of food contaminated with aflatoxins causes severe harmful health effects, which can lead to death, in both humans and livestock. Therefore, the degradation of aflatoxins, particularly by biological methods, is considered a feasible technology for remediation of aflatoxin-contaminated products. In vitro, aflatoxin B1, B2, G1, and G2 were degraded by 25 U/mL of lipase with reduction percentages of 57.5, 71.7, 80.1, and 83.8%. This reduction increased to 81.3, 82.8, 86.9, and 90.7% via 200 U/mL of lipase, respectively. Protease was less effective than lipase in the degradation of aflatoxin B1, B2, G1, and G2 with reduction levels of 35.8, 54.9, 66.5, and 70.2%, respectively, at 25 U/mL of protease. This investigation offers new concepts for the quick screening of aflatoxin-degrading enzymes and offers a theoretical basis for the degradation of aflatoxins. Interactions between aflatoxin B1 (considered as a ligand) and proteins that were taken as receptors (Structure of Lipase PDB ID: 1DT3 and Protease PDB ID: 2PRO) were elucidated. The molecular modeling results of utilized compound showed a notable binding score and best Root Mean Square (RMS) define value, indicating efficient binding mode and appropriate interactions with amino acids of selected proteins.
- Researchpp 2714-2723Yao, Z., Liang, Y., Zhan, P., Shao, L., and Wu, Z. (2024). “Effect of surfactant on pseudo-lignin formation,” BioResources 19(2), 2714-2723.AbstractArticlePDF
In this study, a nonionic surfactant (JFC-M) was used as an additive for hydrothermal pretreatment of crushed poplar wood. The pseudo-lignin extracted from holocellulose after hydrothermal pretreatment was characterized, and the composition of liquid and solid fractions obtained after pretreatment at different experimental conditions was analyzed. The results showed that the addition of JFC-M surfactant accelerated the dissolution of biomass cellulose and effectively inhibited the production of pseudo-lignin in hydrothermal processes, under the same hydrothermal pretreatment conditions. The pseudo-lignin yield for the control group was 14.2% (no JFC surfactant added), whereas when the JFC-M concentration was 2%, the pseudo-lignin yield was 9.8%.
- Researchpp 2724-2735Cebi Kilicoglu, M. (2024). “Effects of heavy metal contamination on fungal diversity in Pinus brutia shoots,” BioResources 19(2), 2724-2735.AbstractArticlePDF
The effects of heavy metal pollution have become a significant global issue in recent years. The primary objective of the present study was to compare the heavy metal concentrations in Pinus brutia shoots grown in an organized industrial zone (OIZ) and a forested area (Adalar) and to examine how these heavy metals affect fungal microbiota. The results achieved here showed that Ni and V concentrations were lower than the detectable limits in both the Adalar and the OIZ region, whereas Se and Cu concentrations were lower than the detectable limits in the shoots collected from the Adalar. Concentrations determined in samples collected from the OIZ were approximately 6 times higher for Cr and 16 times higher for Zn in comparison to the samples collected from the Adalar. Metagenomic analysis revealed that the most common fungal genera were Aureobasidium, Gibberella, Hazslinszkyomyces, Alternaria, Cladosporium, Buckleyzyma, Lasiodiplodia, and Hormonema for the OIZ area and Hormonema, Aureobasidium, Alternaria, Cladosporium, Arthrinium, Fonsecazyma, and Truncatella for the Adalar region. In the future, this study may serve as a reference for the development of innovative strategies for the remediation of heavy metal pollution for a sustainable and clean environment using biological sources.
- Researchpp 2736-2748Zhang, H., Wang, A., Zhao, R., and Hu, J. (2024). “Cation-mediated acid-base pairs for mild oxidative cleavage of lignocellulosic β-1,4-glycosidic bonds,” BioResources 19(2), 2736-2748.AbstractArticlePDF
Solar-driven lignocellulosic biomass photoreforming holds significant promise for the production of value-added chemicals and fuels. The cleavage of the β-1,4-glycosidic bond is crucial for the effective conversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Polymeric carbon nitride (PCN) with acid-base pairs (M-C sites) is developed through heteroatomic carbon incorporation and cation insertion. It can be used for the gentle oxidation of cellobiose to monosaccharides, bypassing the formation of organic acids such as gluconic acid and glucaric acid. A series of different alkaline/alkaline-earth cation for regulation of acid-base pairs exhibited a negative correlation between β-1,4-glycosidic bond cleavage and cation radii. In particular, the introduction of short-radius cations (such as Li) into PCN enabled the formation of acid-base (M-C) pairs characterized by strong acidity. It also enhanced electron delocalization around M-C sites, potentially promoting the generation of reactive radicals in the reaction. Electron paramagnetic resonance analysis confirmed the presence of •OH radicals. The mild oxidative species, are the primary reactive radicals responsible for β-1,4-glycosidic bond cleavage in cellobiose. This study provides insightful evidence for the rational regulation of acid-base sites in facilitating β-1,4-glycosidic bond cleavage. It sheds light on the oxidative cleavage mechanisms integral to lignocellulosic biomass photoreforming, offering insights for advancing sustainable biomass conversion technologies.
