Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 7180-7204Hassan, R. R. A., Mahmoud, S. M. A., Karam, Y. A., Salah, S. M., Ebrahim, S. Y., Abdelwahab, M. A., Ahmed, A. M. H., Ali, H. M., Böhm, M., and Salem, M. Z. M. (2021). "Application of frankincense and rice starch as eco-friendly substances for the resizing of paper as a conservation practice," BioResources 16(4), 7180-7204.AbstractArticlePDF
Smart, environmentally friendly alternatives, i.e., frankincense and rice starch, are recommended for usage in modern paper conservation processes during the re-sizing process treatments. Different concentrations of frankincense and rice starch were applied to paper samples before and after ageing. Multiple analysis methods were performed to ensure the effectiveness of these materials. Promising results were found, but at varying degrees according to the type and concentration of the materials. Scanning electron microscopy illustrated that the frankincense particles were completely absorbed into the cell walls after ageing. Results indicated that there was no considerable change in pH before and after treatment or ageing; the best results for decreasing the acidity utilized a treatment with a mixture of frankincense and rice starch in a 2 to 1 ratio (F2S1). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy illustrated an increased CH2 region and decreased OH stretching as a result of the bonds formed from the starch and crystals formed by frankincense, which agreed with the increased coating and strength of the paper fibers. The total color change values of all the treated samples after ageing were less than 4.5. Frankincense was found to provide strength in supporting wood fibers.
- Researchpp 7205-7219Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Sun, X., Wang, Y., and Liu, Z. (2021). "Separation and characterization of biomass components (cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin) from corn stalk," BioResources 16(4), 7205-7219.AbstractArticlePDF
Representative hemicellulose, milled wood lignin (MWL), and cellulose were directly separated from corn stalk, and their main chemical content was determined using NREL methods. The chemical elements, chemical groups, and molecular structure of corn stalk biomass components (hemicellulose, MWL, and cellulose) were analyzed by elemental analysis, Fourier transform infrared, and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy analyses.The results showed that the purity of the biomass components separated from corn stalk was high, the degree of damage was relatively small, and their own structural characteristics were relatively intact. The hemicellulose that was separated from corn stalk was mainly composed of L-arabino-β-(1→4)-D-glucuronoxylan units. There were also sugar residues attached to the main chain in the form of side chains, such as D-glucopyranose, galactose, glucuronic acid, and galacturonic acid. The isolated cellulose consisted of glucosyl linked by β-(1→4)-glucosidic bond. The MWL separated from corn stalk has a GSH-type of β-O-4 structure, and the contents were as follows, in order of more to less: guaiacyl (G), p-hydroxyphenyl (H), and syringyl (S) units. Biomass components with high purity were separated from corn stalk, and their respective structure and composition were understood, which provides a foundation for the subsequent high-value utilization of corn stalk.
- Researchpp 7220-7233Chen, J., Lu, X., Pang, Z., Li, B., and Dong, C. (2021). "Carbon nanospheres derived from crop residues by acidic lithium bromide hydrate treatment," BioResources 16(4), 7220-7233.AbstractArticlePDF
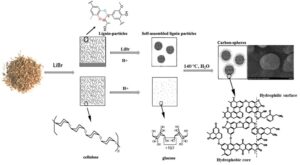
Exploring an efficient technique for carbon sphere preparation has attracted extensive attention. Herein, acidic lithium bromide hydrate (ALBH) was used in the hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) process to overcome the recalcitrance of lignocellulose, such that nano-carbon spheres were prepared at mild condition: 140 °C for 150 min with 0.8 M of HCl from 20-40 meshed corn stover. That carbon spheres showed decent morphology properties and abundant functional groups, which was better than that from pine and poplar wood. The corn stover derived carbon nanospheres could efficiently adsorb both heavy ions and methyl orange in wastewater. Meanwhile, the ALBH after reaction could be recovered and reused. Specifically, the morphologies and adsorption capability of the prepared carbon nanospheres using recovered ALBH were negligibly affected even after 5 cycles. These results verified the practical production of carbon nanospheres from lignocellulose at mild conditions, which provided more potential for the synthesis of novel biomass-based materials for comprehensive applications.
- Researchpp 7234-7248Wang, Y.-C., Lien, T.-S., Chen, N.-Y., and Hsu, T.-H. (2021). "Purification and characterization of β-N-acetylglucos-aminidase from Grifola frondosa," BioResources 16(4), 7234-7248.AbstractArticlePDF
Using commercial API-ZYM screening kits, highly active α-glucosidase, β-glucosidase, and β-N-acetylglucosaminidase were found in Grifola frondosa, having potential for carbohydrate utilization. Of these, β-N-acetylglucosaminidase, which converts chitin to N-acetylglucosamine, was purified and characterized. The recovery was 24.5%, and the purified enzyme had a specific activity 0.67 U/mg protein. Chitinase activity was confirmed by zymogram analysis. The enzyme was also shown to be β-N-acetylglucosaminidase, as N-acetylglucosamine was the main hydrolysis product from colloidal chitin. Thus, the molecule was named NAG38, to indicate β-N-acetylglucosaminidase activity and a molecular weight of 38 kDa, as determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Enzymatic activity was optimal at pH 7.0 and 50 °C, with Km and Vmax values of 0.112 mM and 0.570 μmol/min/mg protein against p-nitrophenyl N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide. The bioactivity was inhibited by Hg2+, Ag+, Mg2+, Zn2+, Ca2+, and Mn2+, with residual enzyme bioactivity only 11.1% after incubation in Hg2+, but was not substantially inhibited by Ba2+, K+, and Na+.
- Researchpp 7249-7262Olejnik, K., Stanisławska, A., and Bloch, J.-F. (2021). "Effect of uniaxial stress on bursting energy absorption of paper," BioResources 16(4), 7249-7262.AbstractArticlePDF
The overall usefulness of the bursting energy absorption (BEA) was studied for a better analysis of paper strength properties. Additionally, the changes of the BEA during more complex deformations of paper products, e.g., preliminary or simultaneous tensile and burst, were determined. For the purpose of the research, an experimental setup was designed. The results showed that the correlation between BEA and bursting strength was linear, but the proportionality strongly depended on paper grade. Thus, a more accurate method to characterize the bursting resistance (BR) of paper was proposed. The BR parameter is described by the three following parameters: average bursting strength, average bursting energy absorption, and the slope of the fitted linear regression curve (relationship between the bursting energy absorption and the bursting strength). This method revealed new mechanical behaviors of papers related to their preloading.
- Researchpp 7263-7282Hamed, O., Qaisi, M., Abushqair, I., Berisha, A., Dagdag, O., Janem, A., Azzaoui, K., Al-Kerm, R., Al-Kerm, R., and Hammouti, B. (2021). "Cellulose powder functionalized with phenyl biguanide: Synthesis, cross-linking, metal adsorption, and molecular docking," BioResources 16(4), 7263-7282.AbstractArticlePDF
A cellulose polymer functionalized with an amine chelating agent was designed and synthesized in a three-step process that involved oxidizing cellulose powder into dialdehyde cellulose, reacting cellulose dialdehyde with phenyl biguanide to create an imine linkage between the two reactants, and reducing the imine linkage to an amine. The cellulose amine polymer was cross-linked with glycerol digycidyl ether and evaluated as an adsorbent of toxic metal ions from wastewater. The adsorption efficiency of the cross-linked cellulose amine polymer toward Pb(II) and Cu(II) was evaluated as a function of the adsorbent dose, pH, time, temperature, and initial ion concentration. The cross-linked cellulose amine polymer showed an excellent efficiency toward over 15 metal ions present in a real sample of sewage. Thermodynamic analysis showed a spontaneous adsorption of metal ions on the polymer at room temperature. Monte Carlo and Molecular Dynamic simulations showed that the Cu(II) and Pb(II) ions adsorbed onto the cellulose amine polymer surface in a considerable amount, which agreed with the experimental and thermodynamic data. The negative free energy value confirmed the spontaneity of the adsorption process. As such, cross-linked cellulose amine polymers could be a promising alternative to current commercial adsorbents.
- Researchpp 7283-7299Cid, A., Blanchet, P., Robichaud, F., and Kinuani, N. (2021). "Estimating wooden prefabricated building export potential from the Province of Quebec to the northeastern United States," BioResources 16(4), 7283-7299.AbstractArticlePDF
The import activity of wooden prefabricated buildings in the Northeastern US region was over CAD 41.8 million during 2019, according to the US Census Bureau. This amount was growing at a 12.5% annual rate on average since 2017. There is evidence of a continued shortfall in supply for the construction market to be overcome in the region. The objective of this study was to estimate the export potential of wooden prefabricated buildings from the Province of Quebec to the Northeastern US region for the next decade in relation to the export activity and production capacity of the industry. The value of annual production of wooden prefabricated buildings in Quebec was up to CAD 578 million in 2019, according to iCRIQ. Export activities from Quebec are mainly directed to the Northeastern US, and were of CAD 18.8 million in 2019, or 81% of Quebec’s wooden prefabricated building exports. Results suggest that potential for wooden prefabricated building exports from the Province of Quebec to the US Northeastern region is important in terms of market share. The study also suggests that by drastically increasing the production capacity of the industry there is no chance that supply will overcome demand.
- Researchpp 7300-7336Ren, H., Wang, L., Li, M., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., Li, X., Zheng, Y., and Li, J. (2021). "Investigation of co-ensiling for the storage of grain stillage and Jerusalem artichoke residue from inulin extraction," BioResources 16(4), 7300-7336.AbstractArticlePDF
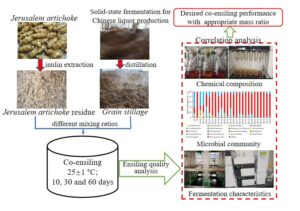
Jerusalem artichoke residue (JR) was co-ensiled with grain stillage (GS) at various weight mixing ratios (JR only, 4 to 1, 2 to 1, 1.2 to 1, 1 to 1.5, 1 to 2.7, 1 to 7, and GS only) for 10, 30, and 60 d for agricultural biomass storage. Results showed that the middle level of GS to JR ratios, e.g., 1.2 to 1 and 1 to 1.5, achieved the best co-ensiling performance among all studied ratios. The water-soluble carbohydrate (WSC) contents were significantly higher than those of the other treatments (p < 0.05), and the lignocellulose contents were significantly lower than those of other treatments (p < 0.05). The silages ensiled at the above-mentioned ratios had a higher feed value and biodegradation potential than other ratios. Lactobacillus was the dominant bacterial species during the ensiling process, and its relative abundance was significantly correlated with the content of different components, e.g., WSC, crude protein, and starch, as well as fermentation characteristics. Fungal species, e.g., Kluyveromyces and Monascus were also observed, and the relative abundance of which was positively correlated with different nutritional components. In conclusion, GS and JR can be successfully stored via co-ensiling.
- Researchpp 7337-7354An, Q., Liu, Z.-Y., Wang, C.-R., Yang, J., Chen, S.-Y., Chen, X., Zhang, Y.-J., Bian, L., and Han, M.-L. (2021). "Laccase activity from Pleurotus ostreatus and Flammulina velutipes strains grown on agro- and forestry residues by solid-state fermentation," BioResources 16(4), 7337-7354.AbstractArticlePDF
Laccase activity from Pleurotus ostreatus and Flammulina velutipes strains was investigated with various agro- and forestry residues by solid-state fermentation. Different species or strains belonging to the same species had the unique capacity of secreting laccase on solid-state fermentation with various agro- and forestry residues. Overall, the capacity of secreting laccase for P. ostreatus strains was superior to F. velutipes strains due to the value of maximum activity on various agro- and forestry residues, except on the stalk of straw. Compared with Populus beijingensis, corncob, and stalk of straw, the presence of cottonseed hull was helpful to improve laccase activity for P. ostreatus strains because the maximum laccase activity from cottonseed hull was higher than that from the other three agro- and forestry residues. The presence of stalk of straw was more helpful to improve laccase activity for F. velutipes strains because of the maximum laccase activity from stalk of straw was higher that from Populus beijingensis, corncob, and cottonseed hull. These results indicated the importance of selecting suitable agro- and forestry residues for fungi producing laccase. These findings contributed to the selection of suitable strains to obtain an integrated application of low-cost laccase in the factory.
- Researchpp 7355-7366Ayrilmis, N., Akkuş, M., and Yılmaz, S. N. (2021). "Effect of thermal modification on the surface quality of a coating applied to wood via the electrostatic spray deposition technique," BioResources 16(4), 7355-7366.AbstractArticlePDF
The surface properties of thermally modified ash wood with a powder coating were investigated, and the results were compared to the unmodified wood. The wood specimens were sanded with 80 grit sandpaper and then pre-heated at 80 °C for 5 min in an infrared oven. The surface of the unmodified and the modified wood specimens were coated with an epoxy/polyester (1 to 1 ratio) hybrid coating using an electrostatic corona spray gun at the pilot plant established in the laboratory. The coatings on the wood specimens were cured at different curing conditions in an infrared oven, i.e., 120 °C/15 min, 140 °C/10 min, and 160 °C/10 min. The results showed that the thermal modification (TM) of the wood caused a slight decrease in the mechanical performance of the surface system (wood substrate and coating film). For example, the scratch and abrasion resistance of the unmodified specimens at the curing temperature of 120 °C were 3.33 N and 135 revolutions but were 3.12 N and 120 revolutions after the TM. However, the average surface roughness (1.26 mu) and contact angle (60.8°) of the distilled water on the cured coatings on the modified wood were lower than those on the unmodified wood (1.86 mu and 80.8°, respectively).
