Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 7530-7549Erken, K. (2021). "Investigation of vegetative properties and generative production of the potential ornamental and narrow endemic species Verbascum yurtkuranianum (Scrophulariaceae) for ex situ conservation," BioResources 16(4), 7530-7549.AbstractArticlePDF
Verbascum yurtkuranianum is a narrow endemic species occurring in a single location, the northern Bursa province (Turkey). It is an endangered and potentially ornamental plant. No conducted study on its life and biology, production, and aesthetic features is available. This study aimed to reveal its vegetative properties, seed characteristics, methods and requirements for seed germination, germination speed, and potential ornamental value so it can be conserved ex situ and produced. Verbascum yurtkuranianum has potential value as an ornamental plant regarding its aesthetic features as a flower. This study revealed that the total number of individuals in the species is 788. Without any treatment, 70.7% germination rate is achieved if the seeds are stored at 4 °C. The optimum germination temperature was from 15 to 20 °C (77.3% and 78.7%, respectively), and the photoperiod regulation for seed germination was 12/12 or 8/16 (light/dark) hours (74.7% and 76.0%, respectively). The most effective treatment to promote germination rate was found by implementation of 60 min ultrasonic waves (94.3%) or application of 120 min vacuum (95.3%). Germination occurred between 8 and 10 days. A parcel of ex situ conservation was constituted with the seedlings obtained from the germination studies.
- Researchpp 7550-7561Spulle, U., Meija, A., Kūliņš, L., Kopeika, E., Liepa, K. H., Šillers, H., and Zudrags, K. (2021). "Influence of hot pressing technological parameters on plywood bending properties," BioResources 16(4), 7550-7561.AbstractArticlePDF
Different types of wood are used to manufacture of various wood products. In direct production processes, additional resources such as energy, adhesives, labor, etc. are also used. In line with sustainable environmental policies, all resources must be used more rationally, while simultaneously increasing the efficiency of the direct production processes. This research examined whether it is possible to reduce energy and labor resources in the technological process of hot pressing of birch plywood (nominal thickness 9 mm), by varying the holding time under pressure, pressure, and adhesive consumption. The Box-Behnken experimental design for a multifactor experiment was used to investigate the influence of technological parameters of plywood pressing. The highest strength in static bending both parallel and perpendicular to the plywood grain was achieved by pressing plywood with the following gluing parameters: highest pressing pressure, 3.2 MPa; minimal holding time under pressure, 9 minutes; and average phenol-formaldehyde adhesive consumption 150 grams per square meter.
- Researchpp 7562-7577Cao, S., Cai, J., Wu, M., Zhou, N., Huang, Z., Cai, L., and Zhang, Y. (2021). "Surface properties of poplar wood after heat treatment, resin impregnation, or both modifications," BioResources 16(4), 7562-7577.AbstractArticlePDF
To investigate the surface properties of different modified poplar (Populus tomentosa Carr.) wood samples, the color, surface roughness, and wettability of untreated poplar wood (control) and poplar modified via heat treatment, resin impregnation, and impregnation combined heat treatment were analyzed and compared in this study. The impregnant used in the test was a modified urea-formaldehyde resin with a low molecular weight and low viscosity. The results showed that the lightness of the samples was sorted in order as follows: the control was lighter than the resin impregnated sample, which was lighter than the impregnation combined heat treatment sample, which was lighter than the heat treatment sample. The surface of the control samples was relatively smooth, while after the impregnation, heat, and impregnation combined heat treatments, the Ra and Rz values increased, which indicated increased surface roughness due to the modifications. Among them, the heat-treated samples had the roughest surface, and the surface roughness of the impregnation combined heat treated samples at 160 °C had no major difference from the resin impregnated sample. The wettability of the samples decreased after heat treatment and increased after impregnation combined heat treatment. It was concluded that after the modification treatments, the color of the wood became darker, and the surface roughness and hydrophobicity increased.
- Researchpp 7578-7591Wang, X., Liu, S., Zhang, D., Bi, D., Wang, L., Zhang, J., and Yi, W. (2021). "Selective preparation of furfural via the pyrolysis of cellulose catalyzed with nitrided HZSM-5," BioResources 16(4), 7578-7591.AbstractArticlePDF
Furfural is a high-value compound that can be prepared by catalytic pyrolysis of biomass. In order to improve the selectivity of furfural in the process of cellulose catalytic pyrolysis, the ammonia-modified HZSM-5 (N-HZSM-5) was used as the catalyst for experimental research on a horizontal fixed bed. The effects of different nitriding temperatures and times on N-HZSM-5, and the effects of different catalyst to cellulose (CA to CL) ratios on furfural selectivity were evaluated. The results showed that N-HZSM-5 can effectively improve the selectivity for furfural. At the optimal conditions (nitriding temperature: 800 °C, nitriding time: 6 h, CA to CL ratio: 4), the selectivity of furfural was up to 24%, which was much higher than those of noncatalytic pyrolysis (1.2%) and HZSM-5 catalytic pyrolysis (3.6%). In order to better evaluate the performance of the catalyst, a series of characterizations were carried out on the N-HZSM-5. The results showed that compared with HZSM-5, N-HZSM-5 had an increased pore size, it was less acidic, and it had more uniform surface acidity. It was conducive to the selective formation of furfural. Therefore, the ammonia-modification can effectively control the structure and acidity of HZSM-5, and N-HZSM-5 exhibits a non-negligible potential in catalyzing the pyrolysis of cellulose for furfural.
- Researchpp 7592-7607Liu, Y., Wang, F., and Sun, Y. (2021). "Esterification of cellulose with betaine using p-toluenesulfonyl chloride for the in-situ activation of betaine," BioResources 16(4), 7592-7607.AbstractArticlePDF
A novel synthesis method was developed for betaine-modified cellulose ester using a mixed N,N-dimethylacetamide/lithium chloride solvent system; p-toluenesulfonyl chloride was used for the in-situ activation of the betaine. The influence of the reaction temperature and time, as well as the anhydroglucose unit to p-toluenesulfonyl chloride to betaine mass ratio on the degree of substitution of the product was evaluated. Increasing the proportion of betaine and p-toluenesulfonyl chloride was beneficial to the esterification reaction. The degree of substitution was 1.68 at 90 °C for 32 h with an anhydroglucose unit to p-toluenesulfonyl chloride to betaine molar ratio of 1 to 2 to 3. The physicochemical properties of the betaine-modified cellulose were closely related to the degree of substitution. Major changes in the morphologies, crystallinity, thermal properties, porosity, and the average degree of polymerization resulted from the modification. The introduction of betaine made cellulose esters thermally less stable than neat cellulose but more difficult to completely degrade. The crystalline structure of the cellulose esters was destroyed, and the products exhibited a porous nature. Dye sorption studies demonstrated that the betaine-modified cellulose holds the potential of adsorbing anionic substances, which is the premise of its application.
- Researchpp 7608-7622Hu, G., Hu, J., Chen, H., Song, S., and Chu, F. (2021). "Influence of pH and ionic strength on the aggregation behaviors of xylan rich hemicelluloses with alkaline lignins," BioResources 16(4), 7608-7622.AbstractArticlePDF
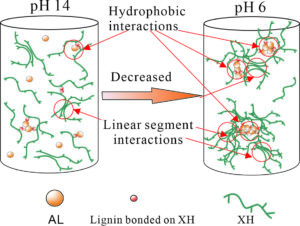
The evolution of xylan-rich hemicelluloses (XH) aggregation behaviors in the presence of alkaline lignins (AL) under a wide range of pH values and NaCl concentration were investigated via dynamic light scattering and turbidity measurements. XH isolated from wheat straw contain a xylose backbone with arabinose side chains and a small amount of phenol groups. XH tend to aggregate in solution due to their low ratio of arabinose to xylose and hydrophobic phenol groups. AL interact with XH through the phenol groups bonded to the hemicellulose main chain to form an AL-XH complex. As the pH value decreases, the particle size and turbidity of AL, XH and their bonded complex all increase. The size of the AL-XH complex agglomerate is greater than the size of a XH at the same pH value, which indicates that the self-assembly of lignin molecules initiate the aggregation of XH. The particle size and turbidity of XH and AL-XH complexes increase as the XH concentration increase. At low pH values, e.g., 6.0, the particle size of the AL-XH complex more obviously increases compared to the XH particles. The size and turbidity of the AL, XH, and AL-XH complex agglomerates increased as the NaCl concentration increased.
- Researchpp 7623-763Marques, J. P. R., Aferri, G., Montanha, G. S., Guedes, F. T. P., Soares, M. M., Muniz, L. F., Tomazello-Filho, M., Xavier, M. A., and de Carvalho, H. W. P. (2021). "Sugarcane as a forage plant: Structural and chemical traits that affect fiber quality," BioResources 16(4), 7623-7634.AbstractArticlePDF
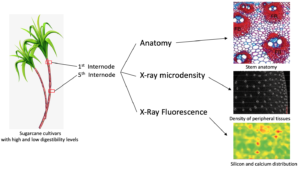
Sugarcane is widely used as feed for cattle, buffalo, goats, and sheep, primarily during drought periods. Some sugarcane cultivars contain low digestibility fibers, which compromises animal performance. Thus, the present study reports on anatomical, chemical, and elemental analysis along stem internodes of two sugarcane cultivars to better understand the structure-digestibility relationship of industrial cultivar cv. IACSP95-5000 compared to a forage cultivar (cv. IAC86-2480). X-ray microdensitometry assays revealed that the peripheral tissues of IACSP95-5000 were denser than IAC86-2480. In the first internode, cv. IACSP95-5000 has more vascular bundles and occupy a larger area. In addition, it had more fibers surrounding the vascular bundles compared to cv. IAC86-2480. However, fibers are prominent at the fifth internode in both cultivars but are more evident in cv. IACSP95-5000. The microprobe X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy analysis showed that silicon and calcium elemental distribution were similar for both cultivars. The structural features of the forage sugarcane presented herein are able to explain the digestibility differences between cultivars.
- Researchpp 7635-7647Vaysi, R., and Ebadi, S. E. (2021). "Thermal yellowing of hornbeam chemi-mechanical pulps bleached with hydrogen peroxide and sodium dithionite," BioResources 16(4), 7635-7647.AbstractArticlePDF
The thermal yellowing of hornbeam chemi-mechanical pulps (CMP) after bleaching with hydrogen peroxide and sodium dithionite was investigated. The hornbeam chips were randomly chosen from Mazandaran wood and paper industries. The CMP pulps prepared with 85% yield were separately bleached with diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA), without DTPA, and hydrogen peroxide. Some pulps were bleached with sodium dithionite. The optical properties of prepared hand-sheets of 60 g/m2 after spraying with 0.5% DTPA were measured using TAPPI standard methods. All prepared papers were thermally aged separately in an oven at 105 °C for 0, 10, 20, 30, and 40 h. The optical properties, such as brightness, yellowness, coefficient of absorption, k/s ratio, post color (PC) number, and a* factor, before and after thermal aging were measured. The results showed that from 0 to 40 h, the optical properties of paper increased except brightness and greenness. This increase was more extensive up to 15 h. Additionally, among the various treatments, DTPA treatment in long-term thermal aging and the use of sodium dithionite and hydrogen peroxide in the short-term aging had noticeable effects on brightness durability and decrease in the color reversion. Thus, there was an increase in the durability of the paper against thermal deterioration.
- Researchpp 7648-7670He, Z., Lu, W., Hua, G., and Wang, J. (2021). "Factors affecting enterprise level green innovation efficiency in the digital economy era – Evidence from listed paper enterprises in China," BioResources 16(4), 7648-7670.AbstractArticlePDF
The Guidelines on Building a Market-Oriented Green Technology Innovation System, which was released by China in 2019, has become a powerful signal to guide the development of green technology innovation (GTI). In the current digital strategy of China, the public media has become a key factor for promoting the transparency of enterprise environmental information. This paper measures the GTI efficiency of the listed paper enterprises in China as well as incorporating media attention into the research framework to explore the influencing factors of GTI of the listed paper enterprises in China during the digital economy era. The results showed that a positive media report had a positive impact on GTI and has become a new driving factor in promoting sustainable production in the digital era. Government support and openness also have a positive impact on GTI. However, negative media reports, environmental regulations, and technological innovation abilities have an inhibitory effect on the GTI efficiency of paper making enterprises.
- Researchpp 7671-7683Nlandu, H. M., Chorfa, N., Bekacemi, K., and Hamoudi, S. (2021). "Potato starch nanocrystal preparation via supercritical carbon dioxide pretreatment combined with enzymatic hydrolysis," BioResources 16(4), 7671-7683.AbstractArticlePDF

In this work, starch nanocrystals were successfully produced from downgraded potatoes using enzymatic hydrolysis combined with a supercritical carbon dioxide pretreatment to improve the accessibility of the enzyme to the starches. Enzymatic hydrolysis was carried out using the pullulanase enzyme at a temperature of 60 °C and a pH of 4. Following hydrolysis, the starch nanoparticles were recovered via precipitation and recrystallization. Comparative characterization of the native, supercritical carbon dioxide-pretreated, and hydrolyzed-recrystallized starch materials was conducted via transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction. The scanning electron microscopy images revealed alterations, e.g., layered strips, on the surface of the potato starch granules after the supercritical carbon dioxide pretreatment. The transmission electron microscopy images revealed that spherical nanostructures from 80 nm to 150 nm were successfully produced. The Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy spectra displayed several absorption bands corresponding to the molecular structure of starches. The X-ray diffractograms exhibited a typical B-type scattering pattern for all the samples. In addition, it was found that the crystallinity of the potato starch nanoparticles was considerably increased compared with native starch.
