Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 8309-8319Van Duong, D., and Hasegawa, M. (2021). "Predicting mechanical properties of clear wood from Acacia mangium provenances using ultrasound," BioResources 16(4), 8309-8319.AbstractArticlePDF
Ultrasound was considered as a means for determining mechanical properties of clear wood in six different Acacia mangium provenances from a trial forest planted in Vietnam. A total of 30 trees (5 trees from each provenance) with no major defects were selected, and a 50-cm-long log was obtained at 1.3 m above the ground from each tree for the assessment of mechanical properties. The measured average ultrasound velocities for provenances tested in the longitudinal direction ranged from 4094 m/s to 4271 m/s. The predicted average dynamic modulus of elasticity (Ed) values varied from 7.42 GPa to 8.70 GPa among provenances. The Ed indicated significant positive correlation coefficients with modulus of elasticity (0.64 to 0.96), modulus of rupture (0.44 to 0.87), and compression strength (0.54 to 0.92) for provenances examined in this study. The results indicated that the use of ultrasound was feasible to determine the mechanical properties of A. mangium provenances planted in Vietnam.
- Researchpp 8320-8337Nandika, D., Darmawan, W., Karlinasari, L., Hadi, Y., Abdillah, I., and Putri, J. (2021). "Physical-mechanical properties and durability enhancement of glued laminated lumber made from inner part of Gewang (Corypha utan Lam.) trunk: The effect of lamina densification and lumber smoking," BioResources 16(4), 8320-8337.AbstractArticlePDF
The inner part of gewang (Corypha utan Lam.) trunk has significantly lower physical-mechanical properties as well as biodeterioration resistance, compared to outer parts. This study investigated a method for improving the physical-mechanical properties and biodeterioration resistance of glued laminated lumber made from the inner part of gewang trunk (GLIT). The effects of pretreating the lamina with densification and exposing the GLIT to smoking process were investigated. The seven layers of GLIT samples were bonded with isocyanate adhesive at a glue spread of 280 g/m2, then smoked for 15 days. Solid lumber pieces made from the inner part as well as the outer part of GLIT were also prepared for comparative purposes. Physical and mechanical properties of the lumber samples were tested according to Japanese agricultural standards. Meanwhile, dry-wood termite and wood decaying fungi resistances of the lumber samples were determined according to Indonesian standard. Results showed that overall physical-mechanical properties as well as dry-wood termite and decay resistances of densified-smoked GLIT were enhanced significantly. Pretreating of lamina and post-production smoking can be considered as a potential method to improve physical-mechanical properties and biodeterioration resistance of the GLIT.
- Researchpp 8338-8352Dömény, J., Brabec, M., Rousek, R., Rautkari, L., and Čermák, P. (2021). "Effect of microwave and steam treatment on the thermo-hygro-plasticity of beech wood," BioResources 16(4), 8338-8352.AbstractArticlePDF
The effects of microwave and steam treatment were analyzed relative to the immediate (thermo-hygro-plasticity) and post-assessed (permanent changes) properties of wood. The study was conducted using European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) standard and 1.5 times up-scaled (only for microwave-heated and reference samples) bending specimens tested in a static three-point loading mode. The specimens were plasticized by heat and moisture (1) separately and (2) simultaneously by heating moist specimens using (i) various microwave regimes in continuous mode, and (ii) heated saturated steam in discontinuous mode. Oven-dried specimens tested at 20 °C served as references. The thermo-hygro-plasticity was studied immediately after treatment, whereas the permanent changes were assessed after oven-drying of plasticized specimens to 0% moisture content. Permanent structural changes were analyzed using scanning electron microscopy. Microwave treatment increased the plasticity of wood (decreasing the modulus of elasticity by 70%) comparably to steam treatment, when the output moisture content was 30% or higher. A similar degree of plasticity was found in up-scaled specimens heated by microwaves. Further analyses confirmed that microwave treatment did not cause any permanent damage to wood structure or reduce mechanical performance. The results showed that microwave treatment is an efficient alternative to steaming when plasticizing moist wood.
- Researchpp 8353-8365Bian, H., Yang, Y., and Tu, P. (2021). "Crystalline structure analysis of all-cellulose nanocomposite films based on corn and wheat straws," BioResources 16(4), 8353-8365.AbstractArticlePDF
Cellulose solution and nanocellulose were prepared from corn straw and wheat straw and then used to fabricate an all-cellulose nanocomposites film (ANF). The crystal structure (CS) of ANFs was analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectrometry (FTIR). Cellulose-I and cellulose-II were found to coexist within regenerated cellulose films (RCF) and ANFs. With the change of nanocellulose content, the proportions of cellulose-I and cellulose-II changed. Cellulose transformation was found to depend on the raw material and the preparation method. When cellulose solution was prepared from corn straw that had been extracted, the cellulose type tended to be transformed from cellulose-I to cellulose-II; the proportion of cellulose-I showed a tendency to increase when nanocellulose content exceeded 1.5%. When the dissolved cellulose had been treated by an acid-alkali method, the results did not follow a clear pattern. However, when cellulose solution was prepared from wheat straw, under extraction method, the cellulose type tended to transform from cellulose-I to cellulose-II; under acid-alkali method, cellulose-I did not follow a clear pattern with nanocellulose content. Though the small amount of nanocellulose can’t dominate the content of cellulose-I, it could cause an increase in disorder of the cellulose matrix.
- Researchpp 8366-8378Bakri, M. M. (2021). "Evaluating the effects of cellulolytic enzymes and Lactobacillus bulgaricus on mycotoxins production and the quality of maize silage," BioResources 16(4), 8366-8378.AbstractArticlePDF
Fungal spoilage and mycotoxin contamination are two of the greatest hazards of silage. The present work was carried out to evaluate the impact of Lactobacillus bulgaricus and cellulolytic enzymes on the maize silage (MS) quality. Fungal analysis of different MS samples showed different mycotoxigenic fungi. The highest frequency (62.8%) was associated with Fusarium spp. Four species with different relative densities were found: F. graminearum (71.1%), F. culmorum (15.2%), F. proliferatum (11.2%), and F. oxysporum (2.50 %). High-performance liquid chromatography analysis showed the presence of trichothecene, nivalenol, zearalenone, and fumonisins mycotoxins in MS inoculated by F. graminearum. The inhibition % of trichothecene, nivalenol, and zearalenone synthesis was 50.2%, 47.5%, and 23.5%, respectively, in MS inoculated by Lactobacillus bulgaricus after a 30 d incubation period. Trichoderma harzianum succeeded in producing cellulolytic enzymes, i.e., carboxymethyl cellulase, manganase peroxidase, and laccase, with a maximum production of 350 µg/mL, 5.47 µg/mL, and 16.0 µg/mL, respectively, after 21 d using MS as the substrate. Treatment by the extracted cellulolytic enzyme with L. bulgaricus enhanced unfavorable conditions for MS fungal contamination, i.e., the production of lactic acid, a lowered pH, and increased L. bulgaricus colony-forming units, compared to the addition of enzyme extract or L. bulgaricus alone.
- Researchpp 7-20Majka, J., Sydor, M., Pędzik, M., Antov, P., Krišťák, Ľ., Kminiak, R., Kučerka, M., and Rogoziński, T. (2022). "Quantifying the finest particles in dust fractions created during the sanding of untreated and thermally modified beech wood," BioResources 17(1), 7-20.AbstractArticlePDF
This article deals with the fractionation of wood dust by sieve after sanding. Dust from untreated beechwood was compared to dust from thermally modified beechwood (at 200 °C for 3 h). The authors hypothesized that the thermal modification changes the particle size distributions of the dust sieve fractions and that all the dust sieve fractions contain the finest particles, which are suspendable in the air and are potentially respirable. To obtain dust for testing, both wood materials were sanded with P120 paper at a belt speed of 14.5 m/s and a pressure of 0.65 N/cm2. A set of sieves with aperture sizes of 25, 80, and 250 µm were used to separate the dust into sieve fractions with grain sizes less than 25 µm, 25 to 80 µm, 80 to 250 µm, and greater than 250 µm. The content of the finest particles in the fractions was measured via a laser particle sizer. Both dusts had similar particle size distributions. In addition, each investigated fraction of both dusts contained the finest particles, i.e., less than 10 µm. It follows that the laser analysis method may be necessary to correctly assess the occupational risk at a sanding.
- Researchpp 21-36Tokdemir, V., and Altun, S. (2022). "A case study of wood thermoplastic composite filament for 3D printing," BioResources 17(1), 21-36.AbstractArticlePDF
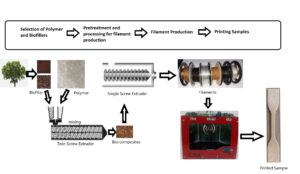
The 3D printing technology is a method of converting proposed complex geometric shapes into solid models. One of these methods is the FDM (fused deposition modeling) printing technology as a considerably affordable and the most commonly used method in the world. The purpose of this study is to obtain FDM 3D printer filaments that are as natural as possible, resembling wood and evoking the sensation of wood upon touching through deployment of bio-based plastics and additives. Polylactic acid (PLA) and bio thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) were used as matrices, and lignin and Arboform, a lignin-based biomaterial, were used as additives. The characteristics of composites achieved through addition of 10% lignin and Arboform to matrices were identified by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and the tensile test. The effects of some printing parameters on the mechanical characteristics were also determined. Lignin induced a decrease in mechanical characteristics for both PLA and TPU. Arboform, on the other hand, demonstrated good bonding with TPU and increased tensile strength. Production of flexible and sufficiently durable parts by means of 10% Arboform-containing TPU filaments was demonstrated.
- Researchpp 37-51Saengwong-ngam, R., Matan, N., and Matan, N. (2022). "Effects of a plant-cushioning material containing tangerine oil on bruising and mould growth of banana (Kluai Hom Thong) and its potential reuse," BioResources 17(1), 37-51.AbstractArticlePDF
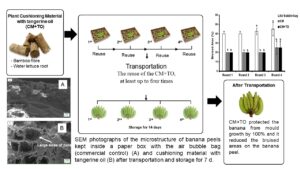
The objectives of this study were to investigate the effects of a plant-cushioning material containing tangerine oil in conserving the quality of a Kluai Hom Thong banana during transportation and storage. In addition, the reuse of the plant-cushioning material with and without tangerine oil for two, three, or four transportation and storage cycles was investigated. The results demonstrated that the plant-cushioning material with tangerine oil protected the Kluai Hom Thong banana from mould growth by 100% and it reduced the bruised areas on the banana peel by 80%. The tangerine oil vapour released from the plant-cushioning material might also affect the ripening of the banana, since the colour changed from green to yellow more quickly in the fruit that had been treated with tangerine oil compared to the control fruit. In addition, this intelligent cushioning material containing tangerine oil has great potential in reducing bruised areas, inhibiting mould and extending the quality of the banana during transportation and storage (14 days) for at least one time compared to the control (5 to 7 days). The reuse of the plant-cushioning material, at least up to four times with and without tangerine oil for the protection of the banana, showed great potential.
- Researchpp 52-63Wang, X., Le, X., Peng, W., Ye, P., An, J., Zhang, G., Wang, P., and Xie, Y. (2022). "Effect of pH on the formation of benzyl ester bonds between glucuronic acid and dehydrogenation polymer," BioResources 17(1), 52-63.AbstractArticlePDF
The effect of pH on the addition reaction of glucuronic acid to quinone methides generated in the synthesis of dehydrogenation polymer (DHP or artificial lignin) was investigated. The DHP-glucuronic acid complexes were formed during DHP polymerization catalyzed by a mixture of laccase, β-glucosidase, and O2 within the pH range 7 to 4 in the presence of coniferin as a precursor. The structure of the product and the content of benzyl ester bonds were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, solid-state cross-polarization magic angle spinning carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, ion chromatography, high performance liquid chromatography, and elemental analysis. The results showed that the pH of the reaction system had an important role in the formation of the benzyl ester bonds. Acidic conditions favored the reaction of quinone methide intermediates with carboxyl groups of glucuronic acid in the biosynthesis of DHP. However, weakly acidic conditions (pH 6) enhanced the reaction of quinone methide intermediates with glucose. In neutral conditions, the DHP-protein complex can be efficiently synthesized by the addition reaction of quinone methide intermediates with amino acids in protein.
- Researchpp 64-74Alvarez-Vera, M., Vázquez, J., Fernández, D., and Reinoso, R. (2022). "Poultry feathers and offal treatment by using beneficial microorganisms," BioResources 17(1), 64-74.AbstractArticlePDF
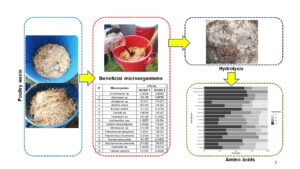
Poultry waste can be hydrolyzed using microorganisms to obtain useful amino acids for agriculture processes. This research treated poultry waste by applying beneficial microbial consortia. Microorganisms were obtained from Brassica oleracea (commonly known as cabbage) and Jungia rugosa (widely known as matico de puna) plants. Each sample was sent to the laboratory for gender, species, and concentration identification. Poultry waste (feathers, offal, blood) and a liquid solution made up of water, molasses, and microorganisms were placed inside plastic tanks. Four treatments were established (T1, T2, T3, and T4). T1 and T3 were composed of 80% water, 10% molasses, and 10% microorganisms; T2 and T4 were composed of 70% water, 20% molasses, and 10% microorganisms. The contents in each tank were periodically stirred for one month. Sixteen microorganisms were identified in each sample. In each treatment, nine essential and nine non-essential amino acids were found in different concentration levels. It is assumed that indigenous microbial consortia benefit the hydrolysis of poultry waste. Furthermore, the type and content of amino acids are related to the microbial activity of each consortium.
