Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 5319-5334Tan, H. (2022). "Crushed mussel shell powder and optional borax in surface char layers to protect four wood species against fire," BioResources 17(3), 5319-5334.AbstractArticlePDF
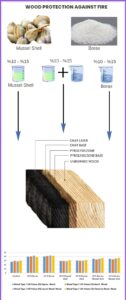
The goal is to protect semi-finished/finished wood components from burning/fires in a variety of settings (wooden buildings, historical sites, restoration, etc.). Natural (organic) sea mussel shells (Chamelea gallina) were crushed and prepared with water in various solution concentrations (10%, 15%) after the pyrolysis process, either alone or together with boron compounds (borax). The limiting oxygen index value (LOI) was determined by making retention calculations. Coatings were applied to the wood as a double treatment, with boron compounds (borax) used for comparison purposes. Eastern spruce (Picea orientalis (L.) Link.), Anatolian chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.), eastern beech (Fagus orientalis Lipsky), and locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) were chosen for this research. When the pyrolysis-treated impregnated samples were compared to the pyrolysis-treated control sample, the limiting oxygen index value (LOI) was found to be significantly higher in the impregnated samples. After impregnation, 15% borax (0.89%) in acacia wood had the highest retention value, whereas 10 percent mussel shell (0.22%) in spruce wood had the lowest. The maximum limiting oxygen index value (LOI) was found in acacia wood (42.8%), while the lowest value was found in acacia wood (28.9%) impregnated with 10% mussel shell powder after the pyrolysis process.
- Researchpp 5335-5348Hamdan, S., Rahman, M. R., Mohamad Said, K. A., Zainal Abidin, A. S., and Musib, A. F. (2022). "Sompoton: Sabah bamboo mouth organ," BioResources 17(3), 5335-5348.AbstractArticlePDF
This study considered the Sabah traditional bamboo musical instrument, sompoton. The fast Fourier transform (FFT) of sompoton was determined via a Pico oscilloscope. All three sompotons displayed almost similar fundamental frequencies. The individual tubes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8 (except tube 7) of sompoton I, II, and III produced the fundamental frequency (in hertz) as 924, 758, 655, 589, 449, 407, 537, as 954, 779, 655, 614, 469, 387, 552, and as 944, 820, 655, 635, 407, 407, and 552, respectively. The averaged frequency obtained from the three sompotons (with the diatonic frequency and note in bracket) was 940.6 (932.3-A5# tube 1), 785.6 (783.9-G5 tube 2), 655 (659.2-E5 tube 3), 612.6 (622.2-D5# tube 4), 547 (554.3-C5# tube 8), 441.6 (440-A4 tube 5), and 400.3 (392-G4 tube 6). The tunings were remarkably similar in the tonal relationships. The pitch of the drone tube (tube 6) repeated an octave higher at tube 2, the intervals of perfect 4th higher at tube 8, and the intervals of perfect 5th higher at tube 4 were always found. The standard deviations of the fundamental pitch from the three sompotons for tube 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8 were 15.3, 31.5, 0.0, 9.2, 31.6, 11.5, and 8.7, respectively.
- Researchpp 5349-5371Świderski, B., Antoniuk, I., Kurek, J., Bukowski, M., Górski, J., and Jegorowa, A. (2022). "Tool condition monitoring for the chipboard drilling process using automatic, signal-based tool state evaluation," BioResources 17(3), 5349-5371.AbstractArticlePDF
An automatic approach to tool condition monitoring is presented, with the best solution achieving overall accuracy of 94.33% and 9 misclassification errors. In the wood industry, cutting tools need to be evaluated periodically. This is especially the case when drills are concerned; since when dulled, the resulting poor-quality product may generate loss for the manufacturing company, due to the need to discard it during quality control. Each tool can be classified either as useful or useless, and the second type should be exchanged as fast as possible. Manual evaluation of tools is time consuming, which results in production downtime. This problem requires a faster, automated, and precise solution for the work environment. In response to this issue, an ensemble algorithm was developed. Different signals were collected for the input data, including feed force, cutting torque, noise, vibrations, and acoustic emission. Based on those signals, a set of 152 initial features was generated, while after feature selection 19 of them were used by the classifiers. Different algorithms were tested and evaluated in terms of overall accuracy and number of errors. The best classifiers were used to prepare ensemble solution, which was able to classify the tools accurately, with very few errors between recognized classes.
- Researchpp 5372-5392Su, Y., Zou, J., and Lu, W. (2022). "Evaluating the ultimate bearing capacity of glued laminated bamboo hollow columns under eccentric compression," BioResources 17(3), 5372-5392.AbstractArticlePDF
To improve the utilization rate of bamboo, glued laminated bamboo hollow column (GLBHC) was examined under eccentric compression to study the effects of different slenderness ratios, eccentric distances, and wall thicknesses on its ultimate bearing capacity. The nonlinear deformation of the material and the P-delta effect of the column occur under eccentric compression, which can affect its ultimate bearing capacity, so it is very important to analyze the elastic-plastic buckling of the column. Moreover, the discontinuity of the hollow column section aggravates the nonlinear deformation. To accurately estimate the ultimate bearing capacity of GLBHC, considering the difference in tensile and compression elastic modulus, two eccentric compression models were established. A formula for ultimate bearing capacity of the GLBHC under eccentric compression was proposed, and the calculated results were in good agreement with the test results.
- Researchpp 5393-5419Ren, J., and Xiong, X. (2022). "Digital design process and part family division of solid wood custom cabinet door based on multi-attribute overlapping clustering technology," BioResources 17(3), 5393-5419.AbstractArticlePDF
The flexible production of solid wood custom furniture is needed to meet the individual needs of the market. Based on M Company, this study developed a digital design platform and its key technologies (data extraction and integration, part family division, coding technology, model base construction, information interaction, and connection) and proposed a multi-attribute overlapping clustering technology (MOCT) method for the division of a family of cabinet door parts. The results indicated that the platform and technologies based on M company provides a reference for the digital transformation of solid wood furniture. The part family division method based on MOCT displayed excellent grouping performance and adjustability, and it could be extensively applied to the group processing of solid wood furniture parts.
- Researchpp 5568-5577Yang, M., Fang, C., Su, J., Cheng, Y., Zhang, Q., and Liu, M. (2022). "Synthesis mechanism of carbon microsphere from waste office paper via hydrothermal method," BioResources 17(4), 5568-5577.AbstractArticlePDF
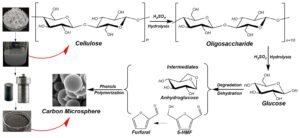
Carbon microsphere was successfully synthesized from waste office paper via hydrothermal method and high temperature treatment in nitrogen atmosphere. The process of carbon microsphere synthesis from waste office paper fiber using concentrated sulfuric acid was studied, and the influence of H2SO4 concentration and reaction time on the hydrolysis reaction was considered. To investigate the mechanism of conversion of waste office paper to carbon microsphere, Fourier transform infrared spectrometry was used to analyze the chemical composition of the supernatant liquid product and the non-carbonized carbon microsphere. The weight loss of the non-carbonized carbon microsphere was assessed through thermogravimetry. Scanning electron microscopy was used to analyze the morphology. The hydrolysis reaction of waste office paper fiber and synthesis mechanism of carbon microsphere under different conditions were evaluated. The results showed that when the reaction time reached 24 h, the product had uniform particle size and was well dispersed, and the more sulfuric acid present led to the waste office paper fiber being more thoroughly hydrolyzed.
- Researchpp 5578-5599Parveen, H., Tewari, L., Pradhan, D., and Chaudhary, P. (2022). "Comparative study of diverse pretreatment approaches to degrade lignin from Bambusa balcooa," BioResources 17(4), 5578-5599.AbstractArticlePDF
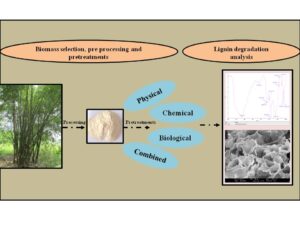
Bamboo biomass is a potential source of monomeric sugars containing a high cellulose content with a low amount of lignin. However, for efficient hydrolysis, an effective biomass pretreatment technique is required to minimize the lignin content and other barrier components. In the present study, bamboo biomass was treated with different physical, chemical, biological, and combined treatments to reduce the lignin content. Among all the pretreatments, the maximum lignin removal amount (14.5%) was obtained with the combined chemical and biological treatment under 2% NaOH + 1% H2O2 + WDP2 fungal culture (5 plugs) conditions. In addition, the ligninolytic fungus and NaOH pretreatment was primarily effective in removing lignins, whereas the H2O2 pretreatment efficiently minimized cellulose crystallinity. Scanning electron microscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy was utilized to analyze the structural changes of the raw and treated biomass. The structural analysis indicated that all the treatments caused disruption in the biomass structure and reduced the compactness of the biomass, which facilitated the biomass conversion during the hydrolysis process. The findings of the present study indicated effective pretreatment methods in overcoming the recalcitrancy of potential lignocellulosic biomass for maximum hydrolysis.
- Researchpp 5600-5611Park, C.-W., Han, S.-Y., Park, J.-S., Lee, E.-A., Bandi, R., Dadigala, R., Kim, J.-K., Kwon, G.-J., Kim, N.-H., and Lee, S.-H. (2022). "Deep eutectic-like solvent-assisted isolation of lignin from Pinus densiflora and its characteristics," BioResources 17(4), 5600-5611.AbstractArticlePDF
Lignin, the most abundant aromatic biopolymer on Earth, has great potential to replace petrochemical-based polymers in the production of value-added products. However, lignin is difficult to extract from lignocellulose because of the recalcitrance of the latter. Herein, the extraction of lignin from lignocellulose using deep eutectic-like solvents (DESs) as green solvents was investigated. Three types of DESs were used, and the effects of treatment temperature (100, 110, and 130 °C) and time (6, 12, and 24 h) on lignin yield and its characteristics were studied. For each DES, the yield of DES-lignin increased with reaction temperature and time. At the same time, the lignin yield obtained using different DESs decreased in the order of choline chloride/lactic acid > betaine/lactic acid > K2CO3/glycerol. At higher temperatures and longer reaction times, lignin with a high molecular weight was produced, which was attributed to the recondensation of lignin fragments. Furthermore, the methoxyl and hydroxyl group contents decreased with increasing reaction temperature and time. Thermal stability studies revealed that the increased molecular weight of DES-lignin enhanced its thermal resistance.
- Researchpp 5612-5621Chanlert, P., Jintara, A., and Manoma, W. (2022). "Comparison of the sound absorption properties of acoustic absorbers made from used copy paper and corrugated board," BioResources 17(4), 5612-5621.AbstractArticlePDF
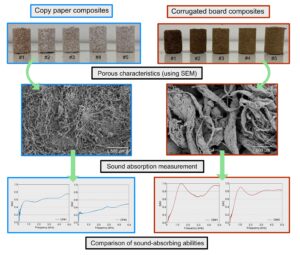
Due to the increasing demand for eco-friendly, inexpensive sound absorbers, this study investigated composites made from recycled paper pulp and urea-formaldehyde adhesive. By varying the pulp contents, five samples from used copy paper and five samples from used corrugated board were fabricated. For the same type of porous absorber, one with a lower bulk density has a higher total porosity, resulting in a higher sound absorption coefficient (SAC) spectrum. Sound-absorbing performance of copy paper composites with bulk densities below 442.4 kg/m3 and corrugated board composites with densities of less than 474.8 kg/m3 can be alternatives to commercial polyurethane foam of the same thickness. The noise reduction coefficient (NRC), as well as the average SAC of all corrugated board composites at medium (αM) and high (αH) frequencies were greater than those of copy paper composites. However, the average SAC at low frequency (αL) was not explicitly different for copy paper and corrugated board composites. In conclusion, corrugated board composites are a better candidate as sound absorbers than copy paper composites with the same pulp content.
- Researchpp 5622-5631Gao, R., Li, J., Xia, J., Lin, Q., and Wang, L. (2022). "Influence of polyethylene oxide (PEO) on the performance of Chinese lacquer films," BioResources 17(4), 5622-5631.AbstractArticlePDF
The Chinese lacquer composite films were prepared by modifying raw lacquer with polyethylene oxide. The film was characterized via Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, and scanning electron microscopy. The infrared spectra confirmed the interaction between the polyethylene oxide and urushiol. The heat-resistance of the film was found to have decreased due to the presence of polyethylene oxide via thermogravimetric analysis. Additional pores and wrinkles were observed in the scanning electron microscopy image of polyethylene oxide modified lacquer films. The mechanical properties were tested according to the national standard. The results indicated that the gloss and flexibility of the modified film was enhanced by the presence of polyethylene oxide. When the ratio of polyethylene oxide was 3%, the gloss was increased from 59.8 to 81.6 and the flexibility changed from 15 mm to 1 mm. The alkaline-resistance, hardness, and adhesion were also increased via the modification of polyethylene oxide.
