Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 5919-5935Popović, J., Svrzić, S., Gajić, M., Maletić, S., Dodevski, V., Djiporović-Momčilović, M., Krstić, S., and Popović, M. (2022). "Light transmittance of mahogany wood treated with 20% hydrogen peroxide solution," BioResources 17(4), 5919-5935.AbstractArticlePDF
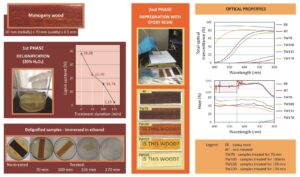
There is an increased research interest in methods for transparent wood production and its use. Wood transparency could be achieved by its delignification followed by an impregnation process with polymers having proper optical properties. However, delignification processes are mainly time consuming and not environmentally friendly. The possibility of treating mahogany wood (Swietenia macrophylla King) with 20% hydrogen peroxide for 70, 100, 135, and 170 min at 103 °C is presented in this research. According to the treatment duration, lignin content decreased 40 to 94% relative to its initial content in the control samples, whilst the cell structure remained intact. Due to the light scatter effect, caused mainly by wood tissue structure, the direct optical transmittance of treated samples in the visible light spectrum (400 to 800 nm) was less than 40%. Simultaneously, the total optical transmittance of samples treated for 100 and 135 min reached values between 70 to 80% with high values of the haze at approximately 30 and 60%. Optical transmittance in the visible spectrum area of the samples treated for 170 min was from 45 to 80% and the haze from 25 to 45%.
- Researchpp 5936-5957Li, X., Che, W., Piao, J., Li, X., Jin, F., Yao, T., Li, P., Wang, W., Tan, T., and Shao, X. (2022). "Peanut shell biochar’s effect on soil physicochemical properties and salt concentration in highly saline-sodic paddy fields in northeast China," BioResources 17(4), 5936-5957.AbstractArticlePDF
Soil salinization is a major ecological threat to crop growth and production. Biochar addition can alleviate the negative impacts of saline-sodic stress in crops. Here, a two-year field experiment was conducted in a highly saline-sodic paddy field to evaluate the response of soil physico-chemical properties, ionic concentration, and rice yield to biochar applications. The soil was amended with peanut shell biochar as follows: zero biochar (B0), 33.75 t ha−1 (B1), 67.5 t ha−1 (B2), and 101.25 t ha−1 (B3). Biochar significantly reduced soil bulk density (BD), while it markedly increased total porosity (TP) and saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ks). Furthermore, biochar markedly decreased the Na+ concentration, Na+/K+ ratio, Na+/Ca2+ ratio, HCO3-, and CO32- while it increased the concentrations of K+, Ca2+, and Mg2+. Biochar significantly decreased the electrical conductivity of soil saturation extract (ECe). The exchangeable sodium percentage (ESP) of B1, B2, and B3 were 53.6%, 62.3%, and 71.0% lower, respectively, than that of B0, and the corresponding decrease in sodium adsorption ratio (SARe) was 51.2%, 58.1%, and 60.5%. Biochar had no effect on the soil pH but significantly increased the soil cation exchange capacity (CEC). The rice biomass yield, grain yield, and harvest index significantly increased after biochar application.
- Researchpp 5958-5983Heo, J., An, L., Chen, J., Kim, M., Lee, S., and Kim, Y. (2022). "Application of three types of aminated lignins for efficient removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions in aqueous solution," BioResources 17(4), 5958-5983.AbstractArticlePDF
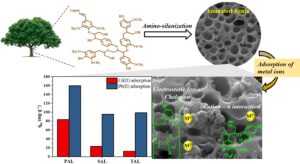
Lignin is a renewable natural aromatic polymer that is generated as a co-product during lignocellulosic biorefinery processes, and it has been applied widely as a functional biomaterial. In this study, the adsorption behavior of Cd(II) and Pb(II) metal ions was investigated via ion chelation using aminated lignins (ALs) with primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups. ALs exhibited optimal Cd(II) and Pb(II) adsorption capacities in solution under neutral conditions due to their chelating, electrostatic, and cationic–π interactions with metal ions. The AL with the primary amine group showed the highest adsorption capacities for both Cd(II) and Pb(II), reaching 83.2 and 159.7 mg·g-1, respectively, followed by the ALs with secondary and tertiary amine groups. The adsorption kinetics and isotherm analysis demonstrated that all adsorption behaviors followed the Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetics. Thermodynamic studies revealed that the adsorption processes of Cd(II) and Pb(II) using the ALs were spontaneous and endothermic. These results demonstrate that ALs are promising adsorbents for the removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) metal ions.
- Researchpp 5984-5998Lei, J., Wang, S., Lei, D., and Liu, Z. (2022). "Measurement and calibration of discrete element simulation parameters of crushed sugarcane tail leaves," BioResources 17(4), 5984-5998.AbstractArticlePDF
Discrete element simulation parameters of the tail stem and tail leaves of crushed sugarcane tail leaves (STL) were calibrated by a combination of physical experiments and simulation optimization design. First, the values or ranges of the basic physical parameters and contact parameters of crushed STL were measured using physical tests, and the results were used as the basis for the selection of the simulation parameters. Plackett-Burman testing was applied for the significance screening of the initial parameters. Then, the error values and significant parameters of stacking angle for the second-order regression models were obtained using the steepest ascent experiment and the Box-Behnken optimization test. An analysis of variance (ANOVA) was also performed. Finally, using 37.52° stacking angle of physical test as the validation target, the optimal combination of parameters was obtained: coefficient of static friction (COSF) for tail stem-tail stem of 0.45, COSF for tail leaf-tail leaf of 0.38, coefficient of rolling friction (CORF) for tail stem-tail stem of 0.14, and CORF for tail stem-tail leaf of 0.12. The error of stacking angle obtained from the simulation and the physical tests was 0.976%, which verifies the reliability of the optimal parameters.
- Researchpp 5999-6018Pang, S.-J., Ahn, K.-S., Kim, M.-J., Hwang, S.-W., Kang, S. G., Kwak, H. W., Yeo, H., and Oh, J.-K. (2022). "Effect of intumescent coating on the charring rate of nail-laminated timber," BioResources 17(4), 5999-6018.AbstractArticlePDF
Intumescent coating was studied relative to the fire performance of nail-laminated timber. Three NLT specimens were coated with three different intumescent coating thicknesses (1, 2, and 3 mm) in even-numbered laminae and compared to uncoated NLT specimens. As a result of the coating, the internal temperature of the coated specimen increased more slowly than that of the uncoated specimen. The average charring rate of the intumescent coating specimen was reduced by 12.8% (1-mm thickness), 14.1% (2-mm thickness), and 15.4% (3-mm thickness) compared with the uncoated specimen. However, statistical analysis showed there was no significance between 1-, 2-, and 3-mm coating thicknesses. The combustion of wide surfaces of timber laminae between the plywood was delayed due to the coated plywood, and the timber laminae became a one-dimensional charring rate problem. Therefore, if even laminae are coated with an intumescent, then the NLT can be designed with a one-dimensional charring rate condition.
- Researchpp 6019-6035Su, X., Chen, J., Liu, Y., Meng, G., and Wang, H. (2022). "Experimental study on flexural behavior of box floors with orthogonal rib beams made of poplar laminated veneer lumber," BioResources 17(4), 6019-6035.AbstractArticlePDF
This study examined the flexural behavior of the poplar laminated veneer lumber (LVL) box floor with orthogonal rib beams. Four 3.6 m × 4.8 m box floor samples made of poplar LVL orthogonal rib beams and oriented strand board (OSB) plates were tested under vertical uniform loading, from which the bearing capacity, stiffness, and failure characteristics were analyzed. There was no damage in all box floor samples at the normal service load of 2.5 kN/m2, and the maximum deflection was far less than the allowable value. When the maximum load was applied, the load-displacement curve of each floor sample exhibited a linear relationship without obvious failure. However, localized failure was manifested as the dislocation slip of the rib beams relative to the upper and lower floor slabs at the corner nodes and the joint expansion and staggered floors at the bottom plate, with obvious failure signs. The rib beam height had the most significant impact on the floor stiffness, followed by the spacing of short-side rib beams, whereas the OSB plate thickness had lest impact. The mid-span deflections of poplar LVL orthogonal ribbed box floor samples, which were calculated using the analog slab method, were in good agreement with the experimental results with an error being less than 10%.
- Researchpp 6036-6055Hashim, F., Surya, I., Rusli, A., and Ismail, H. (2022). "Microstructure-properties of dynamically vulcanized mengkuang leaf fibre/ethylene vinyl acetate/natural rubber thermoplastic elastomer composites," BioResources 17(4), 6036-6055.AbstractArticlePDF
Thermoplastic elastomer composites based on ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), natural rubber (NR), and Mengkuang leaf fibre were prepared using the sulfur and peroxide vulcanization systems. Different curing systems and fibre loadings affecting the processing torque, tensile, thermal, and morphology of the composites were investigated. Addition of Mengkuang leaf fibre resulted in poor fibre dispersion and agglomeration in the matrix, which may have affected the efficiency of stress transfer and thus could explain a decline in tensile and thermal properties. Composites with dynamic vulcanization showed a rougher surface that might be due to the presence of crosslinking, which requires more force to fail. The increase in stabilization torque for the composites with dynamic vulcanization was observed due to the addition of curing agents, which implies some changes at the molecular level due to crosslinking. Tensile properties of Mengkuang leaf fibre filled EVA/NR composites indicated that the tensile strength, elongation at break, and Young’s modulus of the peroxide cure system were higher than the sulfur cure system and unvulcanised composites. The sulphur cure system showed better resistance towards thermal degradation compared to the peroxide cure system. This was attributed to dicumyl peroxide (DCP), which degrades the polymer chain or the composites at high temperature.
- Researchpp 6056-6066Wang, Q., Liu, S., Chen, H., Liu, J., and Zhu, Q. (2022). "TEMPO-oxidized cellulose beads for cationic dye adsorption," BioResources 17(4), 6056-6066.AbstractArticlePDF
Toxic organic dyes present in wastewater should be removed before discharge. In this study, TEMPO-oxidized, regenerated cellulose beads were prepared using a simple falling ball technique for cationic methylene blue (MB) removal. The obtained cellulose beads were characterized using various analytical techniques. The results indicated that TEMPO-oxidized cellulose beads displayed porous structures with high content of carboxylic acid groups. Thus, the negatively charged cellulose beads can effectively adsorb cationic MB with an adsorption capacity of 495 mg/g at a starting concentration of 100 mg/L. This simple one-step adsorption process achieved near-complete MB removal at pH 7, indicating strong electrostatic interactions between cationic MB and negatively charged oxidized cellulose beads. The experimental data can be well described by the Langmuir isotherm model and the Pseudo-second-order model. The fabricated cellulose beads exhibit great potential for practical application in dye removal from wastewater.
- Researchpp 6067-6078Moon, B. G., Park, N. Y., Ko, Y. C., and Kim, H. J. (2022). "Characterization of paper surfaces by friction profilometry," BioResources 17(4), 6067-6078.AbstractArticlePDF
Friction profilometry is a powerful technique that is suitable for the surface characterization of paper products. In this technique, a stylus-type contact method that resembles papermaking processes is used for evaluating the quality attributes of products. The surface characterization requires both surface roughness and friction measurements. At present, however, few reports have been available regarding characterization of the friction by the surface profilometric method. The objective of this study was to provide guiding principles of a stylus-type contact surface profilometry for determining the friction properties of paper. Another objective was to introduce the concept of the mean absolute deviation (MAD) from the average coefficient of friction as a new friction parameter.
- Researchpp 6079-6093Vikman, M., Fearon, O., and Kalliola, A. (2022). "Biodegradation of alkali-O2 oxidized lignins used as dispersants," BioResources 17(4), 6079-6093.AbstractArticlePDF
Large quantities of lignin are produced as by-streams via chemical pulping and emerging biorefinery processes. These lignins are typically water-insoluble; however, they can be converted into a water-soluble form by chemical modifications. A novel LigniOx technology solubilizes lignin using alkali-O2 oxidation. The product can be used for bio-based dispersants. This study evaluated the biodegradability of alkali-O2 oxidized kraft, organosolv, and hydrolysis lignin. The oxidized lignins exhibited higher biodegradation in soil and in aquatic environments in comparison to a commercial kraft lignin and a commercial lignosulfonate. In soil, the biodegradabilities of oxidized lignins were 19 to 44%, whereas the reference lignins exhibited only 5 to 12% conversion to CO2. Biodegradation of the oxidized lignins and references in the aquatic environment increased in a similar order as in the soil environment, although the degradation in each sample was slightly smaller than in the soil. The improved biodegradability of the oxidized lignins was due to the altered chemical structure of lignin. Compared to the untreated lignin, the oxidized lignin contained structures formed in aromatic ring opening reactions, making the lignin more accessible to microbial degradation. In addition, the oxidized lignin contained carbon originating from small organic compounds, which are easily biodegradable.
