Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 3576-3589Lee, I.-H., and Kim, K.-H. (2023). “Effect of physical properties of softwoods on embedment strength performance of self-tapping screws,” BioResources 18(2), 3576-3589.AbstractArticlePDF
The embedment strength performance of the self-tapping screw (STS) connector, used as a cross-laminated timber fastener, was evaluated considering tree species’ density and load direction as parameters. The STS had a diameter of 8, 10, and 12 mm. Considering the characteristics of the STS, the embedment strength of the threaded area and the shank area were compared. A larger diameter of the STS resulted in a higher yield load in all directions of the respective wood. The effective embedment area can estimate a more accurate value for the embedment strength. The embedment strength of the longitudinal cross section as the embedment area was higher than that of the radial and tangential sections. For the loading direction, the ratio of the embedment strength parallel and perpendicular to the grain of the specimens was 0.40 to 0.58 by wood species. The embedment strength predicted based on the specific gravity and diameter of the fastener differed considerably by 38% to 56% from the actual embedment strength of STS using the effective embedment area. This paper provides data for setting the adjustment factors predicting the embedment strength of STS connection.
- Researchpp 3590-3597Ruthes, H. C., dos Santos, H. F., De Araujo, V. A., Azambuja, M. A., Aquino, V. B. M., Chahud, E., Melgaço, L. A., Branco, N., Favarim, H. R., de Campos, C. I., Lahr, F. A. R., and Christoforo, A. L. (2023). “Estimation of toughness as a function of compression strength parallel to the grain of tropical woods,” BioResources 18(2), 3590-3597.AbstractArticlePDF
Tropical species are widely used in construction, and their physical and mechanical properties have been important characteristics with direct impact on the design of structures, especially the strength and stiffness of wood applied in them. Tests to obtain both parameters are conducted under ABNT NBR 7190 (1997) guidelines in Brazil, being rarely found in some research centers because of the higher costs of testing equipment. For instance, the toughness test depends on equipment with a pendulum, whose device requires accuracy and maintenance for reliable analyses. This paper aims to estimate toughness through another property more easily found, given by the compression strength parallel to the grain. For this, 20 tropical wood species of the South American region were used to obtain initial values of these properties. The characteristic values of the compression strength parallel to the grain as well as linear and quadratic regression models were obtained. Statistical analysis was performed and confirmed that a linear model gave better predictions than a quadratic model.
- Researchpp 3598-3607Zhang, K., Chu, C., Li, M., Li, W., Li, J.,Guo, X., and Ding, Y. (2023). “Transparent wood developed by impregnating poplar with epoxy resin assisted by silane coupling agent,” BioResources 18(2), 3598-3607.AbstractArticlePDF
Biodegradable transparent wood was fabricated by introducing epoxy resin E51 modified with the silane coupling agent (KH550) into bleached poplar veneer. The light transmittance of transparent wood was modulated by KH550 content. The silane coupling agent KH550 was able to change the compatibility of epoxy resin and wood substrate, thereby affecting the performance of transparent wood. In this study, the effect of KH550 on the properties of transparent wood and its mechanism were investigated. The light transmittance, tensile strength, and elongation at break of transparent wood showed an increasing and then decreasing trend with increased KH550 dosage. When the mass ratio of the coupling agent KH550 to the epoxy resin was 1:20, the transparent wood made by impregnating wood substrate with epoxy resin modified by KH550 had the best performance, with the fast degradation starting temperature of 338 °C, 81.07% light transmittance at λ = 780 nm, 59.92 MPa tensile strength, and 3.47% elongation at break. This work provides a new way for preparing high performance transparent wood.
- Researchpp 3608-3619Liao, W. C., Huang, J.-P., and Huang, W.-Y. (2023). “Chemical composition analysis and biofunctionality of Polygonatum sibiricum and Polygonatum odoratum extracts,” BioResources 18(2), 3608-3619.AbstractArticlePDF
Polygonatum sibiricum (P. sibiricum) and Polygonatum odoratum (P. odoratum) are commonly known Chinese herbal medicine sources. Although they had similar medical effects, the difference between these varieties was verified in this study. Liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) was used to determine their chemical composition. P. sibiricum has seven chemical components, whereas P. odoratum has only five. Based on the DPPH radical scavenging activity analysis results, half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of P. sibiricum and P. odoratum were 4.23 and 18.3 mg/mL, respectively. The results of ABTS+ radical scavenging activity analysis showed that the IC50 values of P. sibiricum and P. odoratum were 4.77 and 19.3 mg/mL, respectively. Moreover, P. sibiricum had higher total phenolic content (10.0 mg of gallic acid / g of extract), and better reducing ability than P. odoratum. Again, P. sibiricum showed better tyrosinase inhibition ability than P. odoratum, and the IC50 values were 9.68 and 15.4 mg/mL, respectively. P. sibiricum was concluded to have better biofunctionality than P. odoratum.
- Researchpp 3620-3641Jiang, D., Zhang, Y., and Chen, J. (2023). “Non-destructive testing of mechanical properties of solid wood panel based on partial least squares structural equation modeling transfer method,” BioResources 18(2), 3620-3641.AbstractArticlePDF
Calibration transfer between near infrared (NIR) spectrometers is a subtle issue in the chemometrics and process industry. Similar instruments may generate strongly different spectral responses, and regression models developed on a first NIR system can rarely be used with spectra collected by a second apparatus. In this work, two novel methods based on Structural Equation Modeling (SEM), called Enhanced Feature Extraction Approaches for factor analysis (EFEA-FA) and Enhanced Feature Extraction Approaches for spectral space transformation (EFEA-SST), were proposed to perform calibration transfer between NIR spectrometers. They were applied to a NIR nondestructive testing model for solid wood panels mechanical properties. Four different standardization algorithms were evaluated for transferring solid wood panels quality databases between a portable NIRS (InGaAs)-array spectrometer (NIRquest512) and a HSI Camera (SPECIM FX17). The results showed that EFEA-SST yielded the best model evaluation metrics (R2 and Root Mean Square Error of Prediction (RMSEP)) values for tensile strength (RMSEP=11.309, R2=0.865) parameters, while EFEA-FA gave the best fit for flexural strength (RMSEP=10.653, R2=0. 912). These results suggest the potential of two novel quality parameters prediction methods based on spectral databases transferred between diverse NIRS spectrometers.
- Researchpp 3642-3653Sjöstrand, B. (2023). “Progression of vacuum level in successive vacuum suction boxes in a paper machine – Impact on dewatering efficiency and energy demand – A laboratory study,” BioResources 18(2), 3642-3653.AbstractArticlePDF
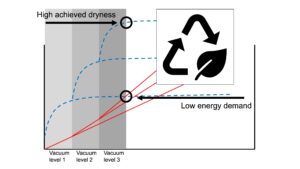
Producing tissue paper is an energy-demanding process; a significant amount of energy is expended when removing water by vacuum, mechanical pressing, and thermal drying. Because the water is most energy-demanding to remove in drying, making the preceding step of vacuum dewatering more efficient would benefit the whole process. This article focuses on developing a laboratory-scale method for verifying the nature of diminishing returns of water removal and investigating efficiency strategies of the vacuum dewatering. The theoretical concept of successive vacuum suction boxes with progressing vacuum levels was tested at the laboratory scale in order to show quantifiable results of the previously solely theoretical concept. The results confirmed that vacuum dewatering can be improved by adding progressively higher vacuum levels and that such a practice can benefit both outgoing dryness levels and expended vacuum pump energy. To truly examine the power of progression of vacuum levels, rewetting can be included in the calculations, by using an approximate value collected from pilot or full-scale measurements. For any new fiber mix, pulp type, vacuum level setup, basis weight, etc. the vacuum levels, rewetting, and dwell times need to be tuned to that specific case.
- Researchpp 3654-3665Yamada, T., Matsumoto, Y., Nge, T. T., and Yamada, T. (2023). “Acid-catalyzed solvolysis of softwood using polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether to produce functional lignin derivatives,” BioResources 18(2), 3654-3665.AbstractArticlePDF
Glycol lignins (GLs) produced through acid-catalyzed solvolysis of softwood meal using glycols, such as polyethylene glycol (PEG), have been used for the development of functional materials. In this study, GLs with various physical and chemical properties were synthesized via solvolysis with monomethyl ethers of polyethylene glycol (MPEG), such as MPEG-n4 and MPEG-n8. The effects of the reaction time and temperature on the yield, molecular weight, and thermal properties of MPEG-lignin were studied. The yield of MPEG-lignin increased with the solvolysis time. Acid-catalyzed solvolysis using MPEG-n4 occurred faster than that using MPEG-n8. Higher reaction temperature resulted in a higher yield of MPEG-lignin with a higher glass transition temperature (Tg) and viscous thermal flow temperature (Tf). The Tg and Tf of MPEG-lignins increased with the solvolysis time. The MPEG-lignins synthesized at higher reaction temperatures showed a relatively strong carbonyl absorbance band in the infrared spectra, which was ascribed to decomposed sugar derivatives.
- Researchpp 3666-3680Guo, H., Yi, B., Xu, H., Dong, L., Guo, G., and Gong, L. (2023). “Numerical simulation on influencing factors of co-firing of municipal solid waste and leather,” BioResources 18(2), 3666-3680.AbstractArticlePDF
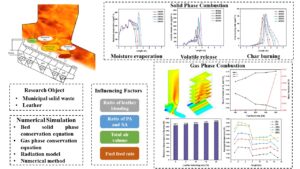
Incineration is an important method of recycling municipal solid waste (MSW). As an industrial waste, leather has a higher calorific value and more combustible components than MSW. The blending of leather can make up for the high moisture content and insufficient calorific value of MSW, providing a good solution to reduce the capacity of MSW and industrial waste. This study predicts the effect of blending combustion by means of numerical simulation; the effects of leather blending ratio, the ratio of primary air and secondary air, total air volume, and fuel feed rate were analyzed. The results showed that the appropriate increase of blending ratio improves the furnace chamber temperature, and the best blending amount of leather is approximately 10%. The best primary and second air ratio is 0.72:0.28. Insufficient airflow caused inadequate combustion, and excessive airflow reduced the furnace temperature. The feed volume in the range of 500 to 550 t/d had a good burning effect.
- Researchpp 3681-3693Liu, W., Zhang, X., Ren, H., Hu, X., Yang, X., and Liu, H. (2023). “Synthesis of biomass-based adsorbent from rice husk ash for copper ions adsorption,” BioResources 18(2), 3681-3693.AbstractArticlePDF
To solve the problems of low utilization of agricultural waste rice husk and heavy metal pollution, this investigation prepared a cheap copper ion adsorbent using rice husk ash (RA). The maximum Cu2+ adsorption capacity was 19.8 mg/g. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and surface area and porosity analyses were used to characterize the composition and structure of the material of silica-depleted rice husk ash (SDRA). The thermodynamics and kinetics of Cu2+ adsorption by SDRA were studied for their relevance to the adsorption mechanism. The adsorption of copper ions by SDRA was in accordance with the Langmuir model and the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. Furthermore, the increases in specific surface area and oxygen-containing functional groups following silica removal were primarily responsible for SDRA’s enhanced adsorption ability. And this is the first time that Cu2+ adsorbent has been prepared from the by-product of the synthesis of silane from rice husk ash. So, its synthesis cost is very low. Moreover, the preparation technique of SDRA is a revolutionary method of adsorbent creation that is both economical and environmentally benign.
- Researchpp 3694-3708Xiao, F., Li, D., Zhang, L., Du, Y., Xue, Y., Gong, P., Song, Y., Zhang, K., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, J., and Cui, Y. (2023). “Effect of seaweed extracts from different sources combined with urease and nitrification inhibitors,” BioResources 18(2), 3694-3708.AbstractArticlePDF
Urease inhibitors (UIs) and nitrification inhibitors (NIs) still have limitations in increasing crop yield. Therefore, to improve the application effect of inhibitors, the combination of seaweed extracts (SE) from different sources and inhibitors was added to urea to provide a theoretical basis for the development of a new generation of efficient stabilized urea fertilizer with both biostimulant and inhibitor technologies. The combinations were tested in outdoor pots with no N- fertilizer (CK), application of urea alone (U) as control, and kelp polysaccharide (KP), margin polysaccharide (MP), N−(n−propyl) thiophosphoric triamide (NPPT), dicyandiamide (DCD), and combinations of SE with inhibitor were added to urea to make eight fertilizer prototypes. Compared with KP, MP showed better application effect, with significantly higher grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) (P < 0.05). Compared with the addition of inhibitor alone, the combinations of NPPT with KP and MP, respectively, had opposite effects on urea−N transformation, meanwhile NPPT+KP had a positive effect. However, NPPT+MP significantly decreased yield, plant nitrogen uptake, and NUE (P < 0.05); DCD+MP decreased plant N uptake and NUE to some extent. Therefore, the addition of NPPT with KP and DCD with KP to urea significantly improved yield when planting maize in black soil.
