Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 3414-3439Sismanoglu, S., Akalin, M. K., Akalin, G. O., and Topak, F. (2023). “Effective removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions by using black cumin (Nigella sativa) seed pulp and biochar,” BioResources 18(2), 3414-3439.AbstractArticlePDF
Black cumin seed pulp (C), as well as biochar (CC) produced via pyrolysis of black cumin seed pulp were used to remove methylene violet 2B (MV) and basic yellow 28 (BY28) from aqueous solution. Adsorption isotherms and kinetics were applied at 10, 25, and 35 °C. The adsorption of methylene violet 2B and basic yellow 28 on the black cumin seed pulp and biochar surface was exothermic; the heat of adsorption values were lower than 0. The adsorption capacities of BY28-C, BY28-CC, MV-C, and MV-CC were 212.8, 625, 164, and 909 mg g-1 at 25 °C, respectively. The adsorption of black cumin seed pulp and biochar data were examined with the Freundlich, Langmuir, Temkin, Dubinin-Radushkevich (D-R), and Flory-Huggins (F-H) isotherm models. The kinetics of the adsorption were fitted to the pseudo first-order and pseudo second order equations. The pseudo second order equation gave a better fit than the pseudo first-order equation.
- Researchpp 3440-3451Lima, L. V. L., de Castro, V. R., Surdi, P. G., Zanuncio, A. J. V., Zanuncio, J. C., Carneiro, A. C. O., Gominho, J., and Araújo, S. O. (2023). “Properties of Pinus sp. pellets prepared after in-line pre-compaction with torrefaction,” BioResources 18(2), 3440-3451.AbstractArticlePDF
Pelletizing and torrefaction increase biomass energy density, generating a more homogeneous fuel with lower moisture, enabling it to burn in equipment with high energy efficiency. This work evaluated the quality of pellets made from wood particles that had been densified and torrefied in an extruder-type system. Particles of the Pinus sp. wood were torrefied at 200, 250, and 300 °C for six minutes and then compacted to produce pellets. The physical, chemical, and mechanical properties of these pellets were evaluated and compared with standard ones. Torrefaction modified the pellets properties by increasing ash, fixed carbon, higher heating value, and the energy density, while reducing the volatile matter and equilibrium moisture content. The mechanical durability of the pellets was lower than that defined by the European, German, and American standards. The torrefaction pre-compaction route with torrefied particles at a temperature of 300 °C was the most efficient for energetic use, compared to the in natura biomass. The latter has negative aspects such as great variation in size (length and diameter) and density besides high moisture content.
- Researchpp 3452-3470Wasinarom, K., Sungworagarn, S., Sathitruangsak, P., Singmai, W., and Onthong, K. (2023). “Thermal behavior of biomass under thermochemical treatment at different air fluxes in an updraft reactor,” BioResources 18(2), 3452-3470.AbstractArticlePDF
Thermochemical treatment was investigated experimentally at different air fluxes in an updraft reactor. The test rig was equipped with a special attached door that will open at a specific time step. This unique feature allows investigators to obtain information on the packed bed color variation along the different heights of the reactor that evolves at different points in time. The analysis focused on the temperature dynamics obtained from installed thermocouples with the packed bed color variation at each time step. The investigation was conducted for three different supply air mass fluxes, which were 670, 480, and 190 kg/m2h. The general thermal behavior is addressed in the first part of the paper because it is similar for all different input air mass fluxes. Next, the distinctive operation parameters among different air mass fluxes are discussed; these included the hot spot zone, fuel conversion characteristic, temperature distribution, heat transfer, and kinetic activities along the height of the reactor.
- Researchpp 3471-3478Cao, Y., Li, X., Liu, L., Xie, G., Lai, M., and Gao, J. (2023). “Increased dimensional stability of Eucalyptus grandis × Eucalyptus urophylla ‘GLGU9’ wood through palm oil thermal treatment,” BioResources 18(2), 3471-3478.AbstractArticlePDF
Eucalyptus grandis × Eucalyptus urophylla ‘GLGU9’ is one of the most commonly planted tree species in South China. It is a new variety created by Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Forestry Research Institute. As a fast-growing species, the poor dimensional stability is one of its main drawbacks, which restricts its applications. Thermal treatment is one of the effective methods to improve the dimensional stability of wood. GLGU9 wood was treated using thermal modification with palm oil. The oil was used as a heating medium and a shielding material at temperatures of 150, 170, 190, 200, and 210 °C, at various treatment durations of 1.5, 3, 4.5 and 6 h. To investigate the effect of palm oil thermal treatment on dimensional stability, the anti-shrink efficiency (ASE1) and anti-swelling efficiency (ASE2) were examined. The results indicated that the ASE1 and ASE2 were increased by 62.8% and 56.6% at 210 °C for 6 h treatment, respectively.
- Researchpp 3479-3495Margavi, M. R. A., Talaeipour, M., Hemmasi, A., Bazyar, B., and Ghasemi, I. (2023). “Fabrication of novel biocomposite made of chemically treated sludge fibers and various molecular weight polypropylene,” BioResources 18(2), 3479-3495.AbstractArticlePDF
The effect of the chemical treatment of paper mill sludge fibers and polypropylene molecular weight were studied relative to the physical, mechanical, and morphological properties of a novel cellulosic biocomposite. Paper mill sludge fibers were treated with acetic anhydride, and succinic anhydride was mixed with maleic anhydride polypropylene (MAPP) and coupling agent (0 and 3%). The ratio of fibers and polymer materials was considered 30 to 70, which was manufactured by the hot-pressing method at 180 °C. Water absorption, volume swelling, and contact angle were examined on each specimen according to ASTM standards, while Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) explored the efficiency of chemical modification of fibers and the morphology of biocomposites, respectively. The results showed that chemical treatment of fibers reduced the water absorption and volumetric swelling. Both tensile and flexural strength were increased with chemical treatment using the coupling agent. Comparison of fibers treated with succinic acid and acetic acid showed that the succinic acid enhanced the mechanical properties better than the acetic acid treatment. Finally, FTIR analysis showed that the hydroxyl groups decreased, and SEM images indicated the interface between fibers and polypropylene improved via chemical treatment of sludge fibers.
- Researchpp 3496-3508Tandoğan, M., Özel, H. B., Gözet, F. T., and Şevik, H. (2023). “Determining the taxol contents of yew tree populations in western Black Sea and Marmara regions and analyzing some forest stand characteristics,” BioResources 18(2), 3496-3508.AbstractArticlePDF
Yew tree (Taxus baccata L.) is mainly populated in Türkiye, Europe, and Caucasia regions. It has natural anticancer compounds and is a source of raw materials used in modern medicine. The present study aimed to examine the taxol contents of yew trees naturally grown in Marmara and Western Black Sea regions by subjecting needle samples taken from 17 yew populations to extraction and liquid chromatography tandem mass / mass spectrometer system (LC-MS/MS) analysis. It was also examined whether a relationship exists between some stand characteristics and taxoid contents of the needles. From these analyses, the highest taxol contents were found in Bartın-Gölderesi, Yığılca-Kurtkayası, İnebolu-Karagöl, and Yenice-Kızılkaya populations. The statistical analyses showed that there were significant relationships between compound contents and slope, humus content, total nitrogen content (%), and potassium (K). It is recommended to use these derivatives obtained from natural forests in sapling nursing and tissue culture studies, to produce pharmaceutical materials from leaves and protect and improve the current gene sources.
- Researchpp 3509-3521Dal, A. E. B., Ozdemir, A. D., Gucus, M. O., Herouini, A., and Kemassi, A. (2023). “Phytochemical analysis and insecticidal activities of seed extracts from Oenanthe pimpinelloides L. treated paper samples vs. Tribolium castaneum,” BioResources 18(2), 3509-3521.AbstractArticlePDF
The utilization of plant extraction products from Oeneanthe pimpinelloides (Apiaceae family) seeds were investigated in terms of their use as an insecticide control of packaging materials. The aim was to investigate their insecticidal effects against the flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. The Oeneanthe pimpinelloides seeds were extracted with methanol. By using the liquid-liquid extraction method, the hexane extract (II) was separated from the methanol extract (I) and hexane and methanol were evaporated. Then, the chemical composition of each sample was determined via gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. The methanol extract predominantly contained tetrahydrofuran, 1-methoxy-2-propanol, 1-methoxy, 2-butoxyethanol, 1-phenylethanone, cyclohexene carboxylate derivative, (3-phenyl-2-propynylidene) cyclopropane, diphenyldiazene, and dihydroxypropyl ester components, while the hexane fraction contained nonane, 1-octanol, decane, undecane, tridecane, alkyl benzene, benzene sulfonic acid, benzoxazine, and hexadecanoic acid components, as well as some derivatives of them. Each fraction was dissolved in DMSO for impregnation on filter paper. The insecticide effects of the paper samples were determined against Tribolium castneum. According to the results, the mortality started after 3 d for each fraction. After 4 d, the hexane fraction indicated total mortality in comparison with the methanol fraction, which showed partial mortality (3/5).
- Researchpp 3522-3539de Lima, D. M., Lima Júnior, H. C., and Medeiros, I. S. (2023). “Physical and mechanical properties of glued laminated bamboo,” BioResources 18(2), 3522-3539.AbstractArticlePDF
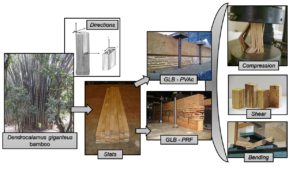
Certain bamboo species have mechanical properties that are compatible with construction material. Despite this, their low shear strength, the presence of nodes in their culms, and their circular geometry inhibit the expansion of the use of this material as construction material. One technique that can solve these problems is glued laminated bamboo (GLB). Based on such findings, this paper aims to evaluate the physical and mechanical properties of glued laminated bamboo of the Dendrocalamus giganteus species. Two glues were used: resorcinol-formaldehyde (PRF) and polyvinyl acetate (PVAc). The following physical and mechanical characterization tests were performed on glued laminated bamboo: water absorption, density, compression parallel to fiber direction, tension parallel to fiber direction, shear parallel to the glue layer, shear parallel to fiber direction, and bending. The results, analyzed using statistical models, showed that the GLB has physical and mechanical properties comparable to those of hardwoods.
- Researchpp 3540-3559Chuda, A., Otlewska, A., and Ziemiński, K. (2023). “Insights into the microbial community structure in the biodegradation process of high-strength ammonia digestate liquid fraction in conventional activated sludge system,” BioResources 18(2), 3540-3559.AbstractArticlePDF

Biodegradation of digestate liquid fraction was performed in the activated sludge system with acetic acid, flume water, and molasses as external carbon sources. High-throughput sequencing was used to gain in-depth insight into the activated sludge microbial community. The type and amount of carbon source in influent (COD/TN ratio) significantly influenced microbial community structure, especially at the genus level, and thus the biodegradation performance of digestate liquid fraction. The highest total nitrogen and chemical oxygen demand removal efficiencies averaging 85.3% and 88.3%, respectively, were achieved in series with acetic acid and flume water and COD/TN ratio of 10.7 and 11.2, respectively. The microbial diversity in these series averaged at 3.08 and 3.65. The dominant bacteria at the phylum level in series with acetic acid were Proteobacteria and Bacteroidota, and at the genus level Azospira, while in series with flume water they were Bacteroidota and Firmicutes, and Macellibacteroides, respectively.
- Researchpp 3560-3575Wang, Y., Sun, Y., and Wu, K. (2023). “Investigation of the mechanical properties in the production process of biomass fuel pellets,” BioResources 18(2), 3560-3575.AbstractArticlePDF
The compacting force in the biomass pelletizing process has remarkable effects on energy consumption, equipment life, and pellet quality. This paper presents an experimental study on the mechanical behavior for the pelletizing process of rice straw, wheat straw, and wood shavings, under different levels of technological parameters, including moisture content, compacting velocity, and particle size. Effects of these parameters on the constant coefficients in the three equations were analyzed. The relationship between the coefficients and the pelletizing process was considered. Results showed that Peiyun Huang equation was more suitable for the whole compacting process compared with the other two equations, which meant it was feasible to estimate the required input of the pelletizing system by measuring the product density based on the Peiyun Huang equation. No specific relationships between the coefficients and pellet quality and energy consumption were observed. It is infeasible to predict the pellet quality and energy consumption only by the mechanical properties of the biomass in densification process.
