Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 5096-5106De, X., Zhang, B., Zhao, J., Guo, W., Zhang, J., Xue, R., and Yang, J. (2023). “Evaluation indexes of poplar sawdust and alfalfa grass forming pellets,” BioResources 18(3), 5096-5106.AbstractArticlePDF
An experimental study was conducted to obtain the degree and pattern of influence of the interaction of various test factors on the evaluation indexes of biomass-forming pellets and the optimal combination of test parameters. Poplar sawdust and alfalfa grass were crushed and compressed into pellets, which were used as test samples. The particle size and moisture contents of the biomass raw materials were selected as test factors, and the quality and performance evaluation indexes, such as relaxation density, Shore hardness, water resistance, crush resistance, longitudinal dimensional stability, forming rate, and productivity, were measured for each pellet group. The results showed that for the same biomass raw material, when the particle size range is zero to 1.5 mm and the moisture content is at 15%, the relaxation density, Shore hardness, and forming rate of the formed pellets are the greatest, and the crush resistance, water resistance, and longitudinal dimensional stability are the strongest. When the particle size range is about 4 to 5.5 mm and the moisture content is at 5%, the relaxation density, Shore hardness, and forming rate of the pellets are the smallest, and the crush resistance, water resistance, and longitudinal dimensional stability are the weakest. The best moisture content of the pellets is about 15%.
- Researchpp 5108-5119Luo, Z., Xu, W., and Wu, S. (2023). “Performances of green velvet material (PLON) used in upholstered furniture,” BioResources 18(3), 5108-5119.AbstractArticlePDF
Green Velvet Material (PLON), which is prepared from polyester slices, has been called a green material based on its ester composition, its ability to be degraded, and the possibility of recovering the value of used material by reprocessing. PLON is expected to be used as a material for the padding layer of upholstered furniture. This paper presented a comparative study of traditional flexible polyurethane foam and Green Velvet Material as the upholstered furniture’s padding layer. The compression mechanical properties of Green Velvet Material and flexible polyurethane foam, such as indentation force deflection, support performance, compression set, and resilience property, were analyzed. The results showed that Green Velvet Material had lower surface hardness and higher comfort compared to flexible polyurethane foam. In terms of resilience, both high-density and low-density Green Velvet Material performed better than the foam control group, but Green Velvet Material had a poorer ability to regain its shape after prolonged pressure. The 30 kg/m3 density Green Velvet Material was the closest to the compression and resilience properties of flexible polyurethane foam. The conclusions provide theoretical data for the effective and reasonable application of Green Velvet Material in upholstered furniture.
- Researchpp 5120-5132Said, K. A. M., Amin, M. A. M., Yakub, I., Rahman, M. R., Kueh, A. B. H., Hamdan, S., and Rahman, M. M. (2023). “Methylene blue adsorption mechanism onto palm kernel shell-derived activated carbon: From particle diffusion to site adsorption,” BioResources 18(3), 5120-5132.AbstractArticlePDF
The mechanism of methylene blue adsorption was investigated for palm kernel shell-derived activated carbon from the bulk solution to active sites. For different initial dye concentrations, 100 ppm methylene blue led to approximately 10 mg/g adsorption capacity while experiencing a decreasing trend at lower initial dye concentrations as follows: 50 ppm (approximately 5 mg/g) > 20 ppm (approximately 2 mg/g) > 5 ppm (approximately 0.5 mg/g). Based on the Boyd external diffusion model, the mechanism of methylene blue adsorption started with its diffusion from the bulk solution via the bounding film encapsulating the activated carbon. The adsorbed species occupied more than one class of active site with an adsorption rate of 0.54 mg/g.min, while the adsorption capacity accounted for 14.7 mg/g. The information about methylene blue offers useful insights into describing the steps of dye adsorption onto palm kernel shell-activated carbon.
- Researchpp 5133-5145Li, S., Zeng, S., Jiang, C., Xu, G., Zhang, Z., and Sun, Q. (2023). “Damage detection of wooden beams based on the modal strain energy change and evidence theory,” BioResources 18(3), 5133-5145.AbstractArticlePDF
A damage detection and localization method for wooden beams was proposed based on the modal strain energy (MSE) change and evidence fusion. The fused damage indicator was deduced using the first three mode shapes of the wooden beams before and after damage. The finite element modal analysis of the free-supported undamaged and damaged wooden beams with different damage severities at one or two locations was performed. The first three mode shapes were extracted from the corresponding modal analysis, with which the damage indicator based on the MSE change and the fused damage indicator of each damage case were computed. The simulation results show that the fused damage indicator accurately detected and located the damage with different severities at one or two locations. Finally, the modal test was completed using the same damage cases as the finite element simulation. The frequency functions of the whole beam were first obtained, with which the first three experimental mode shapes were then acquired, and the damage indicator based on the MSE change and the fused indicator were further computed. The test results verified the validity and reliability of the proposed damage indicator.
- Researchpp 5146-5164Percin, O., and Uzun, O. (2023). “Physical and mechanical properties of laminated wood made from heat-treated Scotch pine reinforced with carbon fiber,” BioResources 18(3), 5146-5164.AbstractArticlePDF
Laminated veneer lumber (LVL) and reinforced laminated veneer lumber (RLVL) with carbon fiber were produced from heat-treated Scotch pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) wood using phenol formaldehyde (PF), polyvinyl acetate (PVAc), and polyurethane (PU) resins. Wood veneers were subjected to heat treatments at 150 °C, 170 °C, or 190 °C for 2 h before lamination. The effects of the reinforcement, heat treatment temperatures, and resins on the properties of the LVL and RLVL were analyzed. Density, equilibrium moisture content (EMC), modulus of rupture (MOR), and modulus of elasticity (MOE) were evaluated. The results showed that MOR and MOE values of solid wood and LVL specimens decreased with increasing treatment temperature. However, reinforcement with carbon fiber increased both MOR and MOE. In addition, the density values of the all RLVL specimens improved, and the EMC altered significantly for all test specimens. Compared to solid samples, the highest MOR values increased by approximately 21% in PF-RLVL samples. Similarly, the highest MOE values increased by 31% in PF-RLVL samples. In conclusion, carbon fiber, one of the most used fabric types in composites, could be utilized in the manufacture of reinforced LVL with heat-treated veneers.
- Researchpp 5165-5181Jiang, J., Wang, S., Li, J., Cao, Y., Zhou, S., Gao, M., and Tang, B. (2023). “Hydrodeoxygenation of phenol as a model compound by Ni2P/HBeta-SBA-15,” BioResources 18(3), 5165-5181.AbstractArticlePDF
The stable silica sieve-based HBeta-SBA-15 catalyst-carrier was successfully prepared by a hydrothermal synthesis method, and then Ni2P/HBeta-SBA-15 new hydrodeoxygenation catalyst was successfully loaded by the equal volume impregnation method. It was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption-desorption, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and pyrolysis-infrared (Py-IR) methods. The results showed that SBA-15 was successfully immobilized on HBeta to form a microporous and mesoporous composite carrier. The introduction of SBA-15 not only increased the specific surface area of HBeta-SBA-15, but also reduced its acidity. After loading the active metal component Ni2P, the structure of the catalyst has not changed much. Hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) of phenol model compounds over Ni2P/HBeta-SBA-15 catalyst was studied in water. The response surface analysis showed that the conversion of phenol was 84.4% and the selectivity of cyclohexane was 94.2% at a lower temperature of 240 °C. The effect of reaction conditions on the yield of cyclohexane was as follows: the reaction temperature > the amount of hydrogen > the amount of catalyst > the reaction time. This study provides theoretical guidance for upgrading biomass pyrolysis oil to green fuel through hydrodeoxygenation.
- Researchpp 5182-5197Yavuz, H. (2023). “Evaluation of blue Cupressus Arizona cone in automotive brake pad biocomposite,” BioResources 18(3), 5182-5197.AbstractArticlePDF
Recently, new brake pads have been developed using sustainable materials that are not harmful to the environment. In this study, the effect of using blue-colored Cupressus arizonica cones was determined as a friction modifier in brake pad composites. Four different samples were prepared by grinding the cone material. The samples’ physical and chemical properties and performances were compared, and finally, their microscopic analyses were visualized by scanning electron microscopy. Maximum friction coefficient and minimum wear rate are required for brake pads. The maximum friction coefficient of 0.39 and the minimum wear rate of the samples containing Cupressus arizonica were obtained in the 0.124X10-7 cm3/Nm BCA3 sample. When the brake pads developed from lignocellulosic biomass were compared, it was determined that the BCA3 sample met the most reasonable performance values.
- Researchpp 5198-5208Luo, Y., and Xu, W. (2023). “Optimization of panel furniture plates rework based on intelligent manufacturing,” BioResources 18(3), 5198-5208.AbstractArticlePDF
Panel furniture uses an intelligent management system, combined with the production method of splitting orders by process, to achieve large quantities and large-scale manufacturing, but because of the insufficient and incomplete use of technology, capacity bottlenecks still exist. The problem of rework and replenishment is a long-term problem in furniture production. Under the constraints of existing production rules, the time difference of plates rework forces the original batch of plates to wait, which reduces the efficiency of warehousing. From the perspective of intelligent manufacturing for the optimization of the plates rework process, this study, through on-site observation records and data analysis of the production system, aimed to find short-term solutions and long-term solutions. In the short-term response, the time node for the completion of the replenishment is mainly according to the process regulations, and the plates are packaged into the warehouse after the replenishment is completed in batches. The long-term response strategy is mainly to achieve the interconnection of different production systems to achieve mutual information, and the paperless online operation of the plates rework process increases the subjective initiative of each process to improve the overall efficiency of the plates rework process.
- Researchpp 5209-5221Altun, B. (2023). “Effects of seasons and indole-3-buteric acid doses on the propagation of some native rhododendron species by air layering technique in their natural habitats,” BioResources 18(3), 5209-5221.AbstractArticlePDF
This research was conducted to determine to the effects of indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) doses and propagation season on rooting rates and some root parameters of Rhododendron species, R. ponticum L., R. luteum Sweet, R. ungernii Trautv, and R. caucasicum Pallas. Air layering technique and IBA doses (0, 500 ppm, and 1,500 ppm) were applied to each Rhododendron species in their natural habitat in autumn and spring. In the present investigation, dry root weight (mg), root length (cm), root volume (cm3), and root diameter (mm) were investigated as root quality parameters. The highest rooting efficiency (100%) was obtained from R. caucasicum and R. ungernii species. The rooting efficiencies of R. ponticum (between 6.67% to 66.67%) and R. luteum (between 0% to 53.33%) species were lower than the other two species. The heaviest dry root (266.10 mg), the largest root volume (1.49 cm3), and the thickest root diameter (0.05 cm) were obtained in autumn and 1,500 ppm IBA dose from R. caucasicum species. The longest roots, 349.21 cm, were formed in the R. ungernii species in the spring, during the air layering, in which 500 ppm IBA dose was applied.
- Researchpp 5222-5241Vera-Loor, A., Walger, E., Mortha, G., and Marlin, N. (2023). “Oxidation of fully bleached paper-grade kraft pulps with H2O2 activated by Cu(Phen) and the effect of the final pH,” BioResources 18(3), 5222-5241.AbstractArticlePDF
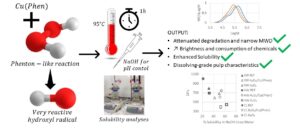
Hydrogen peroxide is an environmentally friendly bleaching chemical that is widely used in alkaline media in the pulp and paper industry. In this study, unconventional reaction conditions of the conventional bleaching P-stage were performed to evaluate its effect on cellulose. The objective was to “tailor” the cellulose degradation according to different applications, such as dissolving pulps. Different operating conditions were studied: pH variation (alkaline or acidic medium), as well as the addition of Cu(II) or the Cu(II)-phenanthroline complex. The hypotheses considered were (1) Using H2O2 in unconventional conditions will favor hemicelluloses removal after depolymerization and will lead to the desired cellulose degradation, and (2) H2O2 oxidation carried out under unconventional conditions will favor the dissolving ability of cellulose.
