Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 5724-5749Deaconu, I., Porojan, M., Timar, M. C., Bedelean, B., and Campean, M. (2023). “Comparative research on the structure, chemistry, and physical properties of Turkey oak and sessile oak wood,” BioResources 18(3), 5724-5749.AbstractArticlePDF
The objective of this research was to establish comparatively some relevant features of Turkey oak and sessile oak wood, in order to better understand the drying behavior of these species. The analyzed samples were obtained from freshly harvested trees of the same age, originating from the Southern Sub-Carpathians. The microscopic analysis revealed that Turkey oak has larger earlywood pores than sessile oak. In heartwood, they are partly filled with tyloses for both species. The macroscopic analysis showed that Turkey oak wood has a much lower proportion of heartwood (only 50%) compared to sessile oak (90%). The comparative FTIR analysis of the two species showed similar qualitative chemical composition, but also some differences between sapwood and heartwood regarding the relative proportion of the main constituents, and very likely in the structure of lignin. High amounts of extractives were found in Turkey oak sapwood (5.34% in cold water, 7.77% in hot water, and 21.60% in NaOH 1%), close to the values obtained in sessile oak heartwood. The research also revealed that the Turkey oak sapwood and heartwood have statistically similar values of oven-dry density, shrinkage coefficient, fiber saturation point, while in sessile oak, the values are clearly higher in the heartwood.
- Researchpp 5750-5764Zhang, W., Zhou, C., Yu, M., Huang, T., and Kaner, J. (2023). “Interface design for the mobile terminal for furniture shopping in the post-epidemic era: An empirical evidence of user demand collection,” BioResources 18(3), 5750-5764.AbstractArticlePDF
The Internet economy is flourishing, and the form of consumption has shifted from offline brick-and-mortar shopping to online consumption. At the same time, COVID-19 led to many offline stores being constrained in many ways, accelerating the conversion of shopping. The purpose of the study is to enable users to effectively use mobile products and optimize their service experience during furniture consumption. This study compares the relevant theories and the current state of research. Through qualitative and quantitative methods, user needs are investigated and data analysis is conducted to summarize interface improvement suggestions. The high-fidelity prototype design was conducted, and the interactive prototype was delivered to users for testing to verify the effect and feasibility of interface optimization and to propose improvement suggestions for the mobile terminal of furnishings.
- Researchpp 5765-5776Wang, Y., Ma, J., Zheng, Q., Ma, Y., Jia, S., and Li, X. (2023). “Heterogeneous phosphotungstate catalyst mediated efficient alcoholysis of furfuryl alcohol into long-chain levulinates,” BioResources 18(3), 5765-5776.AbstractArticlePDF
The synthesis of alternative fuels from biomass has emerged to be a vital strategy to maintain sustainable development. Long-chain levulinate esters (LEs) are a class of good biofuel candidates because they have similar structures to biodiesels and superior heating values. The synthesis of long-chain LEs with effective heterogeneous catalysts has always been challenging. In this work, a few heterogeneous phosphotungstate catalysts were facilely prepared, among which the V3+ exchanged phosphotungstic acid catalyst (VPW) was the most active for the alcoholysis of furfuryl alcohol (FA) and 1-hexanol into 1-hexyl levulinate (HL). A maximum HL yield of 63% was achieved at 180 °C. The VPW catalyst could be reused without obvious decrement of activity. The system was also applicable to the alcoholysis of FA with other hexanols and 1-octanol into various long-chain LEs.
- Researchpp 5777-5797Chen, D., Yin, D., Liu, W., Lan, W., and Wang, Y. (2023). “Anaerobic co-digestion scheme of biogas engineering based on feedstock and temperature,” BioResources 18(3), 5777-5797.AbstractArticlePDF
This article investigates the current status and distribution of the feedstock of biogas engineering in China, evaluates the temperature conditions for anaerobic co-digestion (AcoD), and assesses the biogas production potential of feedstock in AcoD, including six feedstocks, namely, maize straw (M), wheat straw (W), rice straw (R), pig manure (P), cow manure (C), and sheep manure (S). The total amount of M, W, and R was 3.89 × 108, 2.10 × 108, and 1.50 × 108 tons, respectively, and that of P, C, and S was 8.46 × 108, 1.31 × 109, and 4.95 × 108 tons, respectively. However, the spatial distributions and amount of those resources were found to be uneven in China. Heilongjiang has abundant maize straw, and Henan has abundant wheat resources. Sichuan is rich in cow manure, while Inner Mongolia is rich in sheep manure. The analysis of total biogas production (TBP) by mono-digestion and co-digestion (using two feedstocks at ratio of 1:9, 3:7, 5:5, 7:3 and 9:1) showed that co-digestion outperforms mono-digestion under 15 and 25 °C. Thus, it is necessary to study anaerobic co-digestion scheme (AcoDS), which will provide a reference for biogas engineering in different regions to promote the biogas yield based on their actual situation.
- Researchpp 5798-5812Zhang, Z., and Zhou, H. (2023). “Dielectric characteristics of poplar powder under high-frequency electric field,” BioResources 18(3), 5798-5812.AbstractArticlePDF
Dielectric properties of poplar tree powder were measured at frequencies from 5 to 30 MHz. The effects of moisture content, frequency, and bulk density on the dielectric constant and dielectric loss factor were analyzed. The polar groups of wood powder were characterized by infrared spectroscopy to reveal the response mechanism of wood powder in the high-frequency electric field. The results showed that, in general, wood powder’s dielectric constant and dielectric loss factor increased with increasing bulk density and moisture content. In the moisture content range from 0 to 24%, the dielectric constant ε’ of wood powder decreased with the frequency increase with 5 MHz as the maximum value of ε’. When the moisture content was 0 ≤ w < 20%, wood powder’s dielectric loss factor ε” varied as a quadratic function with increasing frequency, corresponding to a maximum value of ε” at 13.4 to 17.7 MHz. When the moisture content was >20%, the dielectric loss factor ε” of wood powder decreased linearly with increasing frequency, and the maximum value of ε” was 5 MHz. The infrared spectrum showed that the polar groups in the wood powder were mainly -OH, C=O, C-O, and -CH, with the highest percentage of -OH.
- Researchpp 5813-5837Wang, Y., Zhang, P., Guo, J., Zhong, Z., Li, W., and Liu, X. (2023). “Aligned cellulose nanocrystal composite filament with high tensile strength enhanced by cationic polyacrylamide via flow focusing approach,” BioResources 18(3), 5813-5837.AbstractArticlePDF
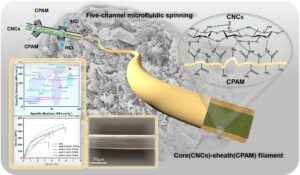
Unsatisfactory macroscopic strength is one of the important reasons that limit the application of cellulose composites. However, the mechanical properties of cellulose composites could be improved by the directional orientation of cellulose nanofibers. In this paper, a five-channel microfluidic chip was designed to fabricate core-sheath cellulose nanocrystal/ cationic polyacrylamide (CNC/CPAM) composite filament. The core spinning solution with high flow velocity promoted the extended arrangement of CPAM in sheath flow. CPAM with long chain structure could not only reduce the electrostatic repulsion between CNCs, but also ensures the fiber orientation by inhibiting the disorderly diffusion of CNCs, thus improving the toughness of the composite filament. The orientation of the composite fiber was studied by wide-angle X-ray scattering, showing an orientation index of 0.725. The mechanical properties of the composite fiber were tested by a universal material testing machine. The tensile strength was 510 ± 20 MPa, which was about 117% higher than that of pure CNC spun fiber, and the elongation at break was also increased by about 70%. The improvement in mechanical properties was attributed to the increase in the content of intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen bonds. In addition, the demonstrated spinning technology provided a new way for preparing high-performance composite fibers.
- Researchpp 5838-5858Gaudelas, A., Blanchet, P., Gosselin, L., and Cabral, M. R. (2023). “Physical characterization of biobased corrugated panels, an innovative material,” BioResources 18(3), 5838-5858.AbstractArticlePDF

Corrugated panels possess excellent thermomechanical properties, but, with presently no hygrothermal applications for building envelopes, their full potential still needs to be explored. This study characterized the physical properties of three biobased corrugated compositions to identify potential building applications. Flat samples of the same compositions were analyzed for certain properties to aid in understanding. As this characterization is groundbreaking, the testing was based on or inspired by established standards. Results suggest that the panels with two wood veneer cores and two kraft paper surfaces coated with polymers are the most promising, as such structures are less sensitive to water and possess a good moisture buffer value that should be advantageous for building construction. Corrugated panels are particularly interesting because their inner materials have properties comparable to those of conventional wood-based panels such as plywood. However, the apparent properties of corrugated panels become one to ten times smaller or larger, which opens up new design possibilities for building envelope applications.
- Researchpp 5859-5872Lee, M., Kang, E.-C., and Lee, S.-M. (2023). “Effects of different flame-retardant treatments on the sound absorption properties of low-density fiberboard,” BioResources 18(3), 5859-5872.AbstractArticlePDF
Internal finishing materials for large auditoriums or public facilities are regulated in South Korea to ensure their flame-retardant performance. Flame-retardant treatment of low-density fiberboard (LDF), an eco-friendly material, was performed to expand its use as a sound absorber by improving its fire safety. In this study, an LDF with a target density of 0.15 g/cm3 was prepared from radiata pine wood fibers and melamine–urea–formaldehyde resin, and recommended amounts of commercially available flame retardants (liquid type) were applied immediately after hot pressing. A powder-type flame retardant was blended with the resin used in LDF manufacture. The surface color and material changed partially depending on the flame-retardant type. The external application method slightly increased the moisture content and density, but it did not affect the physical properties of the LDF. The flame-retardant treatment reduced the emission of formaldehyde, as a scavenger. After treatment, the char area and char length of the LDFs decreased significantly to 9.42–23.64%, and 6.11–11.91%, respectively. The sound absorption performance of the flame-retardant-treated LDFs improved 4.08–9.11%, while their thermal-insulation performance remained unaffected. The flame-retardant-treated LDFs satisfy the regulation of flame retardancy, while maintaining sound absorption and thermal insulation functions.
- Researchpp 5873-5886Alipraja, I., Hernández, R. E., and Koubaa, A. (2023). “Effects of wood species on the energy requirements and size distribution of strands produced by a strander-canter,” BioResources 18(3), 5873-5886.AbstractArticlePDF
The effects of wood species on the performance of the strander-canting process were studied. Logs of balsam fir (Abies balsamea (L.) Mill.), black spruce (Picea mariana (Mill.) B.S.P.), and jack pine (Pinus banksiana Lamb) were processed under two temperature conditions (-13.3 °C and 22.3 °C). The cutting and feed speeds, rake angle, cutting width, and strand thickness were kept constant. The strander-canting process was evaluated by the strand dimensions and yield, as well as by the energy requirements. The results showed that wood species significantly affected the proportions of strands and fines, maximum power, mean energy consumption, and specific cutting energy when processing the logs under frozen conditions. In unfrozen conditions, wood species only affected the strand width and the maximum power. Unfrozen logs produced higher proportions of strands and a lower volume of pin chips and fines than frozen logs. The maximum power, mean energy consumption, and specific cutting energy were, on average, 2 to 4 times higher for the processing frozen logs than for unfrozen logs.
- Researchpp 5887-5907Mendez, O. E., Astete, C. E., Hermanová, S., Boldor, D., Orts, W., and Sabliov, C. M. (2023). “Biobased films from amphiphilic lignin-graft-PLGA copolymer,” BioResources 18(3), 5887-5907.AbstractArticlePDF

Amphiphilic copolymers were synthesized by grafting poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid with two lignin types: alkaline lignin and lignosulfonate. An interphase formation technique was used to produce films based on the copolymers. Films presented one side as being more hydrophobic (O-side) and smoother, and the second side more polar and with an uneven surface (W-side). Contact angle of water on the W-side was lower than the O-side corresponding to a higher lignin content and influenced by the lignin type (alkaline < lignosulfonate) and lignin: PLGA ratio. X-ray photoelectric spectroscopy analysis showed higher percentages of sulfur on the W-side, which supports a preferential partitioning of the lignin. Tensile testing demonstrated the significant impact of lignin type on the mechanical properties of the films. Alkaline films showed a higher maximum strength, a higher stiffness, and a higher tensile strength at the elastic limit compared to lignosulfonate films. However, for lignosulfonate films, ductility at break point was 4-fold higher than that of alkaline films.
