Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 6086-6117Beaufils-Marquet, M., Blanchet, P., Hussain, A., and Landry, V. (2023). “Investigation of cellulose filaments as filler in rigid insulating polyurethane foam,” BioResources 18(3), 6086-6117.AbstractArticlePDF
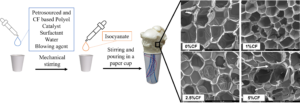
Cellulose is a biopolymer that has broad potential applications including in building insulation, and it was studied for its potential as a filler material. A closed-cell polyurethane foam insulation formulation was developed, and cellulose filaments (CFs) were introduced at varying percentages. The viscosity and morphology of the formulations were studied, as were different foam properties, such as water vapor permeability, reaction kinetics, density, porosity, thermal conductivity, and compressive strength foams as a function of cellulose filaments content. A commercial foam was also tested as a reference. The cellulose filaments impacted the formulations’ viscosity, and all the properties of the resulting insulating material. For example, samples containing 5% of cellulose filaments were found to perform differently than samples containing 0%, 1% and 2.5% mainly due to agglomerate formation, which impacted cell size (about 0.1 mm2 at 0%, 1% and 2.5% versus a mean of over 0.4 mm2 at 5%), and differential vapor sorption (with a mass change of 2%wt at 0 parts per hundred of polyol versus 2.5%wt at 5% from 0% to 95% relative humidity). However, the required performances by the standards of polyurethane foam insulation material were always fulfilled regardless of the amount of cellulose filaments present.
- Researchpp 6118-6131Shen, J., Zhu, X., and Chen, J. (2023). “Experimental and numerical study on shear properties of timber-to-timber joint using a dowel reinforced with a self-tapping screw,” BioResources 18(3), 6118-6131.AbstractArticlePDF
Herein, a beech wood dowel reinforced with a self-tapping screw (composite dowel in brief) is proposed. Composite dowels were welded into the predrilled holes by high speed rotation. Force-displacement curves were obtained using a single-shear and dual connection. A double-peaked pattern was found in the bearing process, indicating that the wooden dowel and the self-tapping screw had a synergistic bearing effect in the bearing process. Regarding the failure mode, the self-tapping screw and the wooden dowel were bent, whilst the default wooden dowel fractured. Further, the numerical simulation was carried out using the finite element analysis software ABAQUS, and the result differed from the test value by only 4.30%, showing a high prediction accuracy. The study of the bearing capacity of the composite dowels provides a theoretical basis for the practical application of wooden dowels reinforced by self-tapping screws.
- Researchpp 6132-6141Alamsyah, E. M., Darwis, A., Suhaya, Y., Sutrisno, Munawar, S. S., Malik, J., and Sumardi, I. (2023). “Modified grain orientation of laminated veneer lumber characteristics of three fast-growing tropical wood species,” BioResources 18(3), 6132-6141.AbstractArticlePDF
Laminated veneer lumber (LVL) and modified grain orientation of LVL (LVB) are composite products made from veneer that are predicted to replace construction timber. The purpose of this study was to determine the physical and mechanical properties of LVL and LVB of mahoni (Swietenia macrophylla), manglid (Manglietia glauca), and gmelina (Gmelina moluccana) and to compare their characteristics. The results showed that the physical and mechanical properties of LVL and LVB generally meet the standards for use in construction. Differences in the properties of LVL and LVB occurred in the properties of hardness and screw tests, while the other properties were similar. The parallel fiber direction was better in terms of adhesive strength, while the compaction density was slightly higher than LVL. The LVL flexural strength was better than LVB in flat and edge test directions. This difference correlates with the adhesive strength in the shear strength test due to the different orientation of the fiber directions.
- Researchpp 6142-6154Abada, E., Modafer, Y., Mashraqi A., Shater, A.-R. M., Al Abboud, M. A., Amin, M. A., Abdel Ghany, T. M., and Said, H. A. (2023). “Ameliorative effect of micro-algal and medicinal plants on some biochemical properties of bean plants under salinity stress,” BioResources 18(3), 6142-6154.AbstractArticlePDF
This study was conducted to examine the ameliorative effects of foliar application of some micro-algal (Chlorella vulgaris and Spirulina platensis) and some medicinal plant leaves (Salix alba, Psidium guajava, and Olea europaea) extracts on Phaseolus vulgaris (Bean) under salinity stress. On a loamy soil, a pots trial was carried out on bean plants grown under salinity stress. Growth characteristics, pigments, osmolytes, total phenol, and antioxidant enzyme contents were determined. S. platensis extract application showed the greatest improvement in shoot length and fresh weight of shoot, which rose 23.5% and 65.1%, respectively compared to the control. The utilized bio-stimulants, particularly S. platensis extracts, remarkably increased the chlorophyll content compared to the control under salinity stress. The photosynthetic pigment, soluble sugars, and soluble protein levels were strengthened by foliar application of bio-stimulant extract. Proline and antioxidant enzyme levels are significantly reduced using algal and plant extracts treatment. These findings support the treatment’s increased contribution to reducing salt stress and their detrimental effects on bean plants.The findings of this study indicate that the use of these biostimulants, especially S. alba, P. guajava, and O. europaea leaf extracts can be considered as an unconventional, ecofriendly, and novel tool in the mitigation of salinity stress.
- Researchpp 6155-6168Kuzugüdenli, E. (2023). “Relationships between black pine wood production (m3 per year) and some habitat factors in the East Mediterranean region,” BioResources 18(3), 6155-6168.AbstractArticlePDF
The present study aims to identify the relations between the wood production (m3 per year) of the black pine (Pinus nigra Arnold.) and its habitat characteristics in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. A total of 120 samplings with different aspects, site altitudes, and site classes were studied. In each sample area, at least 5 trees were designated, and soil samples were taken by excavating earth pits. Certain characteristics of the soil samples were identified in the laboratory environment. The relations between the dominant height values of the trees in the sample areas and soil, climate, and physiographic factors were analyzed using correlation analysis, multiple regression analysis, and artificial neural network methods. Significant relations between the wood production values of the trees in the sample areas and slope from physiographic habitat characteristics, average annual temperature from climate characteristics, and pH and total carbonate from soil characteristics were found. The wood production of black pine was explained by multiple regression analysis at a level of 22.4% and by artificial neural network method at 72%.
- Researchpp 6169-6182Lee, M., Kang, E.-C., Lee, S.-M., and Yoon, S.-M. (2023). “Mechanical properties of structural particleboard and termite and decay resistance,” BioResources 18(3), 6169-6182.AbstractArticlePDF
The mechanical properties and termite and decay resistance performance of wood-based panel used in wooden houses were evaluated. The physical and mechanical properties, along with the resistance levels, of commonly used wood-based panels, including oriented strand board, structural particleboard, and particleboard for use in interior, were compared. The structural particleboard complied with the physical, mechanical, and formaldehyde emission standards of the International Organization for Standardization and Japanese Industrial Standard, surpassing the requirements for oriented strand board. The structural particleboard exhibited excellent water resistance and a consistent performance. Decay tests classified the particleboard and structural particleboard as “Resistant,” with mass losses of 7.82 to 12.72% (white rot) and 14.69 to 16.55% (brown rot). Pine (Pinus densiflora) and oriented strand board exhibited no decay resistance, with mass losses exceeding 45%. The particleboard and structural particleboard demonstrated superior termite resistance, resulting in 100% termite mortality in three days without chemical treatment. The structural particleboard exhibited excellent water, decay, and termite resistance, which can be an advantage in wooden-house construction in terms of maintenance.
- Researchpp 6183-6193Erdem, R. (2023). “Change of Cr, Co, and V concentrations in forest trees by species, organ, and soil depth,” BioResources 18(3), 6183-6193.AbstractArticlePDF
Heavy metal pollution is one of the most important environmental problems threatening living organisms and environmental health. Thus, there is much research interest in monitoring and reducing heavy metal pollution. Plants’ potential to accumulate heavy metals in various organs differs greatly. Therefore, it is necessary to determine the most suitable species and organs first and acquire knowledge of the subjects such as the transfer of heavy metals within plants and their particular intake into plants. This study investigated Cr, Co, and V, which are among the most important and dangerous heavy metals, and are listed in the primary pollutant list of the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Their concentrations were studied at different depths of soils where Pinus nigra, Pinus sylvestris, Fagus orientalis, and Abies nordmanniana subsp. bornmüelleriana species are grown, in the leaves, cones, wood, bark, and roots. The results showed that the intake of these elements into plant bodies generally occurs through the soil. Additionally, the highest concentrations in both leaves and roots were generally obtained in Fagus orientalis and Abies nordmanniana subsp. bornmüelleriana species. It can be stated that those species are the most suitable species to monitor and reduce heavy metal pollution.
- Researchpp 6194-6203Ding, L., Ni, J., Hao, Y., Hai, B., and Ao, T. (2023). “Preparation, characterization, and catalytic properties of SO42-/SnO2-Hangjin2#Clay solid superacid catalyst,” BioResources 18(3), 6194-6203.AbstractArticlePDF
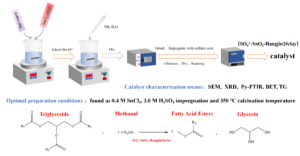
A new sulfate oxide solid acid catalyst SO42-/SnO2-Hangjin2# clay was compounded with Hangjin2#clay, activated by sulfuric acid, as a carrier. In the catalysis of Xanthoceras sorbifolium Bunge, using the yield of oil and methanol synthesis of biodiesel as an index, the effect of SO42-/SnO2-Hangjin2#clay and the preparation conditions on the activity of solid acid were investigated. The variables included in the optimization process were concentration of Sn, impregnation sulfuric acid concentration, and calcination temperature. The optimal conditions were found as 0.4 M SnCl4, 3.0 M H2SO4 impregnation, and 350 °C calcination temperature. The catalyst was examined by scanning electron microscope, X-ray diffraction meter, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, surface area, and thermal weight analysis. The results showed that the introduction of Hangjin2#clay in the SO42–-SnO2 solid acid catalyst improves its catalytic activity.
- Researchpp 6204-6220Nik Wee, N. N. A., Md Saleh, N., Devi, T., Samsuri, A., and Mat Salleh, M. Z. (2023). “Synthesis of silica from rice husk as coating material on magnetic nanoparticle for efficient adsorption of phenol from water samples,” BioResources 18(3), 6204-6220.AbstractArticlePDF
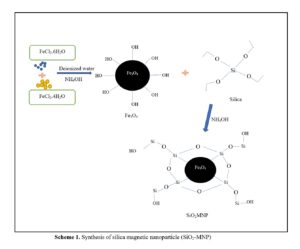
Silica (SiO2) from rice husk was coated with magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) as an adsorbent to adsorb phenol from river water. The structure of SiO2 and SiO2-MNPs were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) showed a rod shape, with a rough surface area in the range of 2 to 3 µm. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy (EDX) were used to examine the resulting spherical shape of the synthesized SiO2-MNP. The results showed a range of 1.3 to 1.5 nm for SiO2 and 4.2 to 6.4 nm for SiO2-MNP. Vibrating-sample magnetometer (VSM) showed an Fe value of 45.1% in SiO2-MNP (VSM); for MNP, SiO2, SiO2-MNP 104.12, 4.72, and 8.01 emu/g, respectively. Response surface methodology (RSM) was used to study the parameters and responses to obtain an optimized condition in SiO2-MNPs usage. The optimized parameters were extraction time selected at 5 min, pH 8, 8 mL acetonitrile as solvent and 15 min as sonication time. The application of SiO2-MNPs was applied to real water samples, with recovery of 84% of phenol. Thus, the synthesized adsorbent, SiO2-MNPs, was developed successfully for phenol removal from water samples.
- Researchpp 6221-6235Kopaczyk, J., Jelonek, T., and Szwed, T. (2023). “The impact of resin harvest history on properties of Scots pine wood tissue,” BioResources 18(3), 6221-6235.AbstractArticlePDF
This study was conducted in Central Europe (Poland) in pine forests that were subjected to the process of resin harvesting in the 1970s. Forty trees were designated for the study, which had one or two resin blazes. The objectives of the experiment were to determine the effect of resin tapping on the changes in annual growth, wood density, and mechanical strength of wood in the damaged trees. Resin tapping affected the development dynamics, especially in trees with a single resin blaze. In addition, bark cutting affected wood density over the cross-section. However, no significant variation was found in terms of the mechanical properties of wood, which may support the theory of adaptive tree growth and optimization of tree’s structure to its functions.
