Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 2404-2416Villalba, M. E., Olson, J. A., and Martinez, D. M. (2024). “Understanding the limits of a screening operation. Part 1: Characterization of screen plugging,” BioResources 19(2), 2404-2416.AbstractArticlePDF
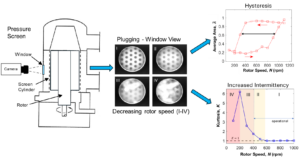
Pressure screening is a critical step in the production of high-quality paper. In efforts to meet sustainable market demands, mill operators are forced to push the limits of screening operation to the point where plugging becomes a recurrent issue. This two-part study provides insights into the limits of screening operations. In the first part, some published imaging data was analyzed to delve into the plugging mechanisms. The observed hysteresis and intermittency were measured by image processing techniques, which revealed that an intermittent behavior of plug-and-release events is intensified as permanent, stable plugs start to form. The intermittency was characterized as changes in the distribution of open area fluctuation peaks. Thus, the kurtosis of the fluctuation peak distribution is proposed as a metric for a plugging soft-sensor. In part 2 of this investigation, the limits of screening operation were characterized by performing a series of screening trials. The utility of the soft-sensor metric for plugging was assessed with the pressure fluctuation data.
- Researchpp 2417-2435Wu, J., Zhao, L., and Song, G. (2024). “Carbon dots prepared from waste wood and residual adhesive and their use as catalysts for hydrogen production,” BioResources 19(2), 2417-2435.AbstractArticlePDF
Large quantities of waste wood with residual resin adhesives are not recycled efficiently. To address this issue, waste wood with residual resin adhesives was synthesized into carbon dots (CDs) via a facile hydrothermal self-assembly method to enhance the H2 evolution performance of graphite C3N4 (g-C3N4), a metal-free photocatalyst. Among all samples, the most significant enhanced sample was MCN-UF-3.5, which has an H2 evolution of 22.1 mmol·g-1·h-1, which is 3.91 times that of unmodified g-C3N4. The band gap and recombination of photogenerated charges were both improved by the doping of CDs. Meanwhile, the DFT calculation showed that adding CDs, especially with the -NH2 group, can significantly deform the structure and destroy the symmetry. This consequence implies an enhancement in the activity of the hydrogen evolution reaction, confirming the feasibility of the modification.
- Researchpp 2436-2451Zhuang, X.-W., Feng, Y.-S., Qiao, H., Yu, H.-X., Yang, W.-M., and Pan, X. (2024). “Glucose conversion process to methyl lactate catalyzed by SnCl4-based homogeneous catalysis,” BioResources 19(2), 2436-2451.AbstractArticlePDF
Biomass is a renewable alternative to fossil fuels and a valuable source of chemicals. In this study, a facile and efficient method was established to improve the selectivity of methyl lactate (MLA) for the homogeneous Lewis acid catalyzed chemical conversion of glucose and methanol. The effects of catalyst dosage, reaction temperature, and reaction time were systematically investigated, with an emphasis on the variation trends of MLA and other by-products. Through process optimization, the best catalyst molar ratio was 0.075 to 0.1, the reaction temperature was 170 to 180 °C, and the reaction time was 3 h. Under these conditions, the conversion of glucose in methanol exceeded 98%, and the yield of MLA was greater than 40%.
- Researchpp 2452-2465Vikman, M., Mikkelson, A., and Rautkoski, H. (2024). “The impact of lignin content on the biodegradation of virgin paper pulps in soil and marine environment,” BioResources 19(2), 2452-2465.AbstractArticlePDF
Paper pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material used in the industrial production of paper and board products. In addition to cellulose and hemicellulose, paper pulp contains 1 to 20% lignin, depending on the raw materials and pulping process used. Lignin is a heterogenous aromatic polymer that is hydrophobic and more resistant to microbial degradation compared to the easily biodegradable cellulose and hemicellulose. In this study, the biodegradation of paper pulps containing varying amounts of lignin was examined in soil and marine environments using ISO testing methods. Lignin significantly reduced the mineralization of paper pulps to CO2 in both environmental conditions, and a strong inverse correlation between lignin content and the mineralization to CO2 was observed. A similar impact was observed with natural materials containing lignin, such as birch sawdust. Since the calculation of biodegradability in most ISO and EN standards is based solely on the concept of mineralization to CO2, materials containing lignin can receive poor values in these tests. The implications of this for standardized requirements of biodegradability and possible options to overcome testing deficiencies are discussed.
- Researchpp 2466-2479Jo, J. I., Purusatama, B. D., Qi, Y., and Kim, N. H. (2024). “Qualitative and quantitative anatomical characteristics and radial variation of major cell components in Paulownia tomentosa wood grown in Korea,” BioResources 19(2), 2466-2479.AbstractArticlePDF
Qualitative and quantitative anatomical characteristics and radial variations of the major cell components in Paulownia tomentosa wood were examined using optical microscopy and X-ray diffraction to aid in wood identification and as quality indices. The vessel arrangement on the transverse surface was either ring-porous or semi-ring-porous. Most vessels had solitary pores, while some vessels had multiple radial pores. The axial parenchyma was generally confluent and partially of aliform type. Tyloses with high frequency in the vessel lumen and multiseriate rays (2 to 5 cells) were typical. The vessel diameter of earlywood and latewood was approximately 240 and 107 μm, respectively, with a range of 165 to 289 μm in earlywood and 55 to 149 μm in latewood. Ray height and fiber length were approximately 178 and 740 μm, respectively. The vessel diameter in both earlywood and latewood and the fiber length increased gradually with an increasing number of growth rings. Ray height was constant from the pith to the middle section and decreased toward the bark. The anatomical characteristics and radial variation of major components of P. tomentosa can be used as wood identification keys and quality indices.
- Researchpp 2480-2502Hua, D., Yuan, S., Zhao, Y., Xu, H., Chen, L., Jin, F., and Li, Y. (2024). “Effects of different acidification-resisting strategies on anaerobic digestion of kitchen waste: Methanogenic properties and microbial community shift,” BioResources 19(2), 2480-2502.AbstractArticlePDF
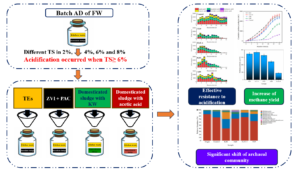
Anaerobic digestion (AD) has been widely used as a promising technology for the treatment of kitchen waste (KW). The effects of several acidification-resisting methods were compared, which included the supplementation of trace elements (TEs) and zero-valent iron (ZVI) / powdered activated carbon (PAC), and the application of the sludge domesticated by acetic acid (HAc) and KW as inoculum. The results showed that the supplementation of TEs and ZVI/PAC at total solid (TS) content of 6% and optimal addition doses resulted in an increase in methane yield to 346 and 366 mL/g VS, respectively. In addition, the methane yields of 327 and 241 mL/g VS were obtained by applying the sludge domesticated with KW and HAc as inoculum, while the methane yield of the control was only 89.2 mL/g VS, representing a relative increase of 288%, 311%, 267%, and 170%. The acidification could be alleviated by applying these methods, and also the methanogenic profile was improved. Furthermore, microbial community analysis revealed that the enrichment of Methanosarcina, which enhanced the substrate utilization capacity and subsequently increased methane production, was achieved through the addition of TEs and ZVI/PAC, along with the application of sludge domesticated by KW.
- Researchpp 2503-2523Dursun, N. (2024). “Estimation of pruning wastes and biochar production potential of Turkey,” BioResources 19(2), 2503-2523.AbstractArticlePDF
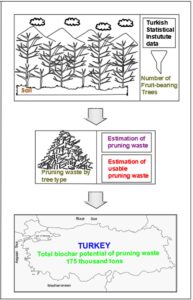
In agriculture-producing countries, pruning waste is obtained from fruit-bearing trees during the fruit-growing process. The present study aims to determine the potential of biochar of pruning wastes, obtained as a result of agricultural activities that have economic value. To the best of the author’s knowledge, no study has been conducted in Turkey to make a regional estimation of the biochar potential of pruning wastes. Biochar produced from waste provides the advantage of use in various fields, such as soil remediation and water and wastewater treatment. In this study, data on the number of trees bearing fruit (almond, apple, apricot, cherry, peach, pear, plum, and sour cherry) from the Turkish Statistical Institute were used based on the equations specified. First, the amount of pruning waste, then the usable pruning waste, and finally their biochar potential were calculated. It was estimated that the apple tree had the highest total biochar potential (41.5 thousand tons/year). Regarding the regions, the highest biochar potential was in the Central Anatolia Region for the apple tree (19.3 thousand tons), followed by the Eastern Anatolia Region for the apricot tree (13.6 thousand tons). The total biochar potential of pruning wastes from fruit-bearing trees in Turkey was estimated at 175 thousand tons for the year 2021.
- Researchpp 2524-2545Ratnasingam, J., Othman, K., Amir, M. A., Jegatheswaran, N., Ab Latib, H., and Liat, L. C. (2024). “Elucidating the challenges to Bumiputera entrepreneurs’ participation in the domestic furniture and wood products market in Malaysia,” BioResources 19(2), 2524-2545.AbstractArticlePDF
The limited market share and growth of Bumiputera entrepreneurs in domestic furniture and wood product industry in Malaysia remains a long-standing challenge. Therefore, a study to examine the market factors that contribute to the failure to thrive among Bumiputera entrepreneurs, registered with the Malaysian Timber Industry Board, was conducted. The results revealed that most of the respondents were micro- and small-sized enterprises, with sales focused on the domestic and contract markets. They were mostly producing sofa and kitchen cabinets, made to order, and sold in domestic markets within the vicinity. The respondents also indicated that the major challenges that impeded their ability to penetrate and capture market share include the limited production volume, lack of product diversity, limited government contract, and inter-ethnicity business collaboration. The Chi-square and Pearson Product Moment Correlation tests found that the significant challenges were only the limited production volume due to small company size, lack of product diversity, and the limited inter-ethnicity business collaboration among Bumiputera entrepreneurs. Therefore, policymakers should take heed that despite the many years of targeted and affirmative assistance to expand the domestic market share of Bumiputera entrepreneurs, the results remain poor, and inevitably, a new approach to Bumiputera entrepreneurs’ development must be adopted.
- Researchpp 2546-2561Arabi, M., Hazrati, M., and Rostampour-Haftkhani, A. (2024). “Performance of laminated veneer lumber panels from fast-growing species with different layering arrangements,” BioResources 19(2), 2546-2561.AbstractArticlePDF
This study investigated the effect of various layer arrangements and their impact on the properties of laminated veneer lumber (LVL). Seven different layer arrangements (CCCCCCC, DDDDDDD, PPPPPPP, CDDDDDC, CPPPPPC, CDDCDDC, CPPCPPC, CDCDCDC, CPCPCPC, CCDDDCC, CCPPPCC, CCDCDCC, and CCPCPCC) were used in the manufacturing of the LVL, with each arrangement represented by a combination of the three wood species: hornbeam (C), paulownia (P), and poplar (D). The veneers were bonded with a polyurethane adhesive and pressed under 1 MPa pressure. The physical and mechanical properties of the laminated veneer lumber, including modulus of rupture, modulus of elasticity, block shear, delamination, and swelling, were measured under both dry and cyclic conditions (boil and dry). The modulus of rupture and modulus of elasticity of the LVLs increased when the proportion of hornbeam in the lamination increased. In the cyclic boil-dry condition, the laminated veneer lumbers with the configurations CPCPCPC and CDCDCDC showed the best structural performance. Furthermore, the study found that when one or two upper layers of poplar and paulownia were replaced with hornbeam layers, cracks were observed in the laminated veneer lumber samples. However, when the layers of poplar and paulownia were replaced with hornbeam alternately, no cracks were observed after saturating the laminated veneer lumber with water. The utilization of an alternating arrangement of poplar and paulownia layers with hornbeam in LVL can be used as an effective and cost-efficient approach for enhancing and reinforcing the LVL performance.
- Researchpp 2562-2574James, R. M. S., Tahir, P. M., Yusof, N. M., Al-Edrus, S. S. O., Abidin, Z. Z., Palle, I., Uyup, M. K. A., and Lee, S. H. (2024). “Effects of bleaching treatment on the properties of bio-polyurethane films from liquefied bamboo,” BioResources 19(2), 2562-2574.AbstractArticlePDF
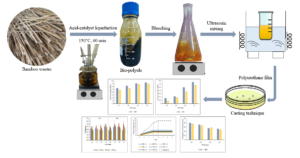
Malaysian bamboo residues were subjected to a liquefaction process. Bleaching of the liquefied product was carried out to reduce its coloration. Polyurethane (PU) films were then manufactured as a coating material by reacting the -OH groups in the bamboo material with isocyanate (-NCO). The study’s objective was to investigate the effects of bleaching on the properties of resulting polyurethane films and to elucidate its behavior as affected by the NCO/OH ratios. Bamboo residues, in powder form, were liquefied with polyethylene glycol (PEG 400) and glycerol (Gly) as reactive co-solvent, and sulphuric acid as catalyst. The obtained liquefied bamboo was then bleached with hydrogen peroxide. Bleached and unbleached liquefied bamboo were used to produce PU film by reacting isocyanate at NCO/OH ratios of 1.6, 1.8, 2.0, and 2.2. The results revealed that the NCO/OH ratios improved the mechanical performance of the PU films. Bleaching treatment slightly reduced the thermal stability and mechanical strength of the PU films. However, bleached PU films displayed lower water absorption and lower biodegradation than unbleached PU films. Nevertheless, the performance of the bleached PU films was still acceptable, indicating that the bleaching treatment using hydrogen peroxide is feasible to obtain semi-transparent film.
