Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 2724-2735Cebi Kilicoglu, M. (2024). “Effects of heavy metal contamination on fungal diversity in Pinus brutia shoots,” BioResources 19(2), 2724-2735.AbstractArticlePDF
The effects of heavy metal pollution have become a significant global issue in recent years. The primary objective of the present study was to compare the heavy metal concentrations in Pinus brutia shoots grown in an organized industrial zone (OIZ) and a forested area (Adalar) and to examine how these heavy metals affect fungal microbiota. The results achieved here showed that Ni and V concentrations were lower than the detectable limits in both the Adalar and the OIZ region, whereas Se and Cu concentrations were lower than the detectable limits in the shoots collected from the Adalar. Concentrations determined in samples collected from the OIZ were approximately 6 times higher for Cr and 16 times higher for Zn in comparison to the samples collected from the Adalar. Metagenomic analysis revealed that the most common fungal genera were Aureobasidium, Gibberella, Hazslinszkyomyces, Alternaria, Cladosporium, Buckleyzyma, Lasiodiplodia, and Hormonema for the OIZ area and Hormonema, Aureobasidium, Alternaria, Cladosporium, Arthrinium, Fonsecazyma, and Truncatella for the Adalar region. In the future, this study may serve as a reference for the development of innovative strategies for the remediation of heavy metal pollution for a sustainable and clean environment using biological sources.
- Researchpp 2736-2748Zhang, H., Wang, A., Zhao, R., and Hu, J. (2024). “Cation-mediated acid-base pairs for mild oxidative cleavage of lignocellulosic β-1,4-glycosidic bonds,” BioResources 19(2), 2736-2748.AbstractArticlePDF
Solar-driven lignocellulosic biomass photoreforming holds significant promise for the production of value-added chemicals and fuels. The cleavage of the β-1,4-glycosidic bond is crucial for the effective conversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Polymeric carbon nitride (PCN) with acid-base pairs (M-C sites) is developed through heteroatomic carbon incorporation and cation insertion. It can be used for the gentle oxidation of cellobiose to monosaccharides, bypassing the formation of organic acids such as gluconic acid and glucaric acid. A series of different alkaline/alkaline-earth cation for regulation of acid-base pairs exhibited a negative correlation between β-1,4-glycosidic bond cleavage and cation radii. In particular, the introduction of short-radius cations (such as Li) into PCN enabled the formation of acid-base (M-C) pairs characterized by strong acidity. It also enhanced electron delocalization around M-C sites, potentially promoting the generation of reactive radicals in the reaction. Electron paramagnetic resonance analysis confirmed the presence of •OH radicals. The mild oxidative species, are the primary reactive radicals responsible for β-1,4-glycosidic bond cleavage in cellobiose. This study provides insightful evidence for the rational regulation of acid-base sites in facilitating β-1,4-glycosidic bond cleavage. It sheds light on the oxidative cleavage mechanisms integral to lignocellulosic biomass photoreforming, offering insights for advancing sustainable biomass conversion technologies.
- Researchpp 2749-2762Yuan, Y., Sun, X., Xu, D., He, J., Wang, X., Wu, D., and Li, S. (2024). “Enhanced dimensional stability of straw-based biocomposites modified with UV light-cured coatings,” BioResources 19(2), 2749-2762.AbstractArticlePDF
This study demonstrated an effective method to enhance the dimensional stability of straw-based biocomposites with modified lignosulfonate as a binder. The ultraviolet (UV) light-curable nanosol was prepared by adding 3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl methacrylate (MEMO) as sol–gel precursor into polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) solution. The MEMO/PVA coatings were generated using 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenylpropan-1-one (Darocur 1173) as radical photo-initiator and chitosan (CS) as additive, on straw-based biocomposites via UV-curing process. The effects of the crucial steps, such as the UV-curing process, hydrolysis time, Darocur 1173 dosage, and CS dosage on the dimensional stability of straw-based biocomposites, were evaluated. The optimum preparation parameters, obtained using the Box–Behnken design, were 31.9 min hydrolysis time, 4.5% Darocur 1173 dosage, and 2.7% CS dosage. Moisture resistance of minimum TS of CS-MEMO/PVA-coated straw-based biocomposites resulted in ~23.1% reduction in dimensional stability without significant decline in the mechanical properties when compared with those without UV curing. Moreover, the glossy spherical particles underwent arrangement in a fish-scale shape with scales closely linked with each other and no agglomeration occurred in CS-MEMO/PVA hybrid film. The CS promoted the cross-linking of MEMO/PVA coating on the biocomposite surface. The resulting biocomposites can be directly applied to public humid-environment applications such as bath furniture and bathroom partitions.
- Researchpp 2763-2781Tang, T., and Chen, Y. (2024). “Colour and furniture brand identity: Exploring the strategic value of brand’s iconic colour,” BioResources 19(2), 2763-2781.AbstractArticlePDF
This research explores the intersection of colour marketing and brand identity, focusing on the role of iconic colour in furniture branding. A comprehensive framework for crafting a furniture brand’s iconic colour was developed, and structural equation modeling was used to analyze data from three offline experiments with a total sample size of 111 subjects. The findings highlight the crucial influence of iconic colour on brand identity, revealing that both the referential meaning of hue and gender significantly impact brand perception. Contrary to conventional beliefs, variations in saturation and value are not solely detrimental; they can also enrich brand identity. The iconic colour serves as a cornerstone for ensuring consistency across internal and external brand dimensions, solidifying the brand’s core identifiers, and resonating with consumers’ minds. This research underscores the pivotal role of iconic colour in forging a coherent and distinct brand identity, offering valuable insights for marketers and brand strategists in the furniture industry and beyond.
- Researchpp 2782-2795Song, D.-B., Shim, K.-B, Lee, S.-J., Kim, K.-H., and Kim, C.-K. (2024). “Allowable bending properties of machine-graded Korean yellow poplar lumber,” BioResources 19(2), 2782-2795.AbstractArticlePDF
This study was conducted to investigate the feasibility of using yellow poplar as a structural member by determining allowable bending properties. Full-size lumber was classified by machine grading and the knot diameter ratio on the wide surface of lumber. The majority of machine grades of yellow poplar lumber with a cross-section of 38 × 89 mm2 were E8, E9, and E10. It was confirmed that the size of the knot diameter ratio tended to be smaller for higher machine grades. In the lowest grade, E8, of most machine grades, the allowable bending strength was lower than the corresponding design value in Korean standards. Application of 0.5 knot diameter ratio to the E8 grade lumber increased the bending strength to 3 MPa of the allowable value to suit the design value. All the allowable modulus of elasticities values of the majority of machine grades were higher than the design values. From the results of this study, it was expected that Korean yellow poplar could be utilized for structural bending members.
- Researchpp 2796-2810Karupaiah, V., Narayanan, V., Nagarajan, R., Ismail, S. O., Mohammad, F., Al-Lohedan, H. A., and Krishnan, K. (2024). “Performance evaluation of 3D-printed ABS and carbon fiber-reinforced ABS polymeric spur gears,” BioResources 19(2), 2796-2810.AbstractArticlePDF
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) polymer and carbon fiber reinforced acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (CF/ABS) spur gears were 3D-printed using fusion deposition modeling (FDM) with different fillet radii of 0.25, 0.50, and 0.75 mm. The performance of the fabricated gears was studied with the effect of fillet radius on varying load and speed conditions. The thermal properties of the gears were also investigated. The results indicated that 3D-printed CF/ABS spur gear exhibited better performance than the pure ABS. The 3D-printed CF/ABS gear with fillet radius of 0.25 mm recorded the highest wear and thermal stresses. However, the optimum performance was exhibited by the gear sample with highest fillet radius of 0.75 mm. Repeated gear tooth loading during service caused an increase in gear temperature due to the hysteresis and friction. Using optical microscopy, the tooth structures of both 3D-printed ABS and CF/ABS spur gears were analyzed before and after loading conditions to establish their failure mechanism. Evidently, various applications of the FDM 3D-printed spur gears depend on their different performances under loads and operating speeds. The methods and findings of this work can be regarded as helpful for future related work related to cellulosic reinforcing particles in a polymer matrix.
- Researchpp 2811-2825Yurtayeva, L. V., Alashkevich, Y. D., Kaplyov, E. V., Slizikova, E. A., and Marchenko, R. A. (2024). “Industrial hemp hurd processing for microcrystalline cellulose production and its usage as a filler in paper,” BioResources 19(2), 2811-2825.AbstractArticlePDF
This article substantiates the possibilities of replacing commercial wood with raw materials made from industrial hemp hurd (hemp-woody core) for the production of unbleached and bleached paper pulps. A comparative analysis of the mechanical characteristics of sheets of paper prepared in the Rapid-Köthen apparatus and obtained from pulp obtained from commercial wood and hemp-woody core (HWC) was undertaken. The objective of this study was to determine the effect of mechanical refining of a pulp on the production of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) from HWC. It was shown that an increase in the pulp refining degree from 15 °SR to 83 °SR led to a decrease in the degree of polymerisation of MCC from 272 to 75, the hydrochloric acid concentration from 73 to 45.63 g/L, and the hydrolysis time from 120 min to 60 min. With the addition of 5% MCC obtained from hemp-woody core, the mechanical properties of laboratory paper sheets from HWC were improved until they met ISO 12625-4-2017 (2017) requirements for NS-2. The results obtained support using hemp-woody core for the production of MCC.
- Researchpp 2826-2841Tuğba Üner, S., and Cesur Turgut, A. (2024). “Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens on volatile components and nutrient element contents of Mentha piperita L. grown under salt stress,” BioResources 19(2), 2826-2841.AbstractArticlePDF
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (Ba) was applied to Mentha piperita L. (peppermint) seedlings grown at various salt levels (0, 50, 75, and 100 mM) for 42 days (six weeks). The study was conducted in a total of eight groups, with 24 seedlings per group. At the end of the study, the seedlings were analyzed for plant nutrient elements and volatile compound contents. The negative effect of salt was observed in almost all parameters. When all groups were evaluated for plant nutrient elements, Ba had a positive effect on Zn, Mn, Cu, and Na values compared to the control, but it did not show any effect on B, Fe, K, P, Mg, and Ca. In volatile compounds, limonene was detected as the major component in all groups. As a result of the evaluation based on limonene, the highest rate was found in the control, and the lowest rate was found in 100 mM NaCl. The salt-dependent inhibition between the groups with the highest and lowest limonene was 73%. While the negative effects of salt were observed in almost all parameters, the promoter effects of Ba were not as pronounced.
- Researchpp 2842-2862Kaya, A. I., Yalçın, Ö. Ü., and Aydemir, D. (2024). “Effects of cellulose micro and nanocrystals on the mechanical, thermal, morphological, and structural properties of rigid polyurethanes,” BioResources 19(2), 2842-2862.AbstractArticlePDF
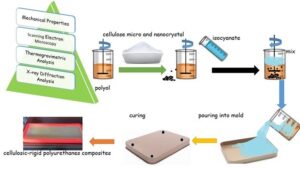
Effects of adding microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) and cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) were evaluated relative to the mechanical, thermal, morphological, and structural properties of rigid polyurethanes (rPUs). The composites were prepared with the blending of polyols/isocyanates and the cellulosic fillers at 0.25%, 0.5%, and 1% loadings. Scanning electron microscopic images showed that the samples had micro-scaled porosity, with cell sizes ranging from 250 to 800 nm. The fillers improved the mechanical strengths and modulus of neat rPUs due to the presence of the nano-sized cells in rPUs matrix. The addition of both fillers generally did not provide a positive effect on the thermal properties, and the weight loss generally increased while the loading rate of the fillers was increased from 0.25% to 1%. The samples had two small crystalline peaks at 18° and 19° according to the X-ray diffraction analysis. From the results, it can be said that the presence of both fillers generally improved all properties of the neat rPUs, and the effects of CNC on the properties were higher than MCC due to both lower particle size and the higher crystallinity of CNC.
- Researchpp 2863-2882Sulastiningsih, I. M., Trisatya, D. R., Indrawan, D. A., Supriadi, A., Aini, E. N., Santoso, A., Yuniarti, K., Prasetiyo, K. W., Syamani, F. A., Prabawa, S. B., Subiyanto, B., and Sumardi, I. (2024). “Properties of oriented strand boards made from two Indonesian bamboo species at different pressure levels and strand lengths,” BioResources 19(2), 2863-2882.AbstractArticlePDF
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of bamboo species, specific pressure, and strand length on the properties of oriented strand boards (OSBs). Laboratory scale OSBs were made from two Indonesian bamboo species [tali (Gigantochloa apus) and andong (Gigantochloa pseudoarundinacea)] with three different strand lengths (75, 100, and 150 mm). For each bamboo species and strand length, OSBs were fabricated by bonding bamboo strands with 7% phenol formaldehyde resin and 0.5% wax emulsion based on their oven-dry weight. The layer structure of the face, core, and back of the three-layer cross-oriented board were 25%, 50%, and 25%, respectively. A specific pressure of 25 or 30 kg/cm2 was applied for 6 min at 160 °C. The targeted OSB density was 0.75 g/cm3. The results showed that OSBs from andong bamboo had better dimensional stability and bending strength than those from tali bamboo. The bending strength of bamboo-based OSBs increased with increased bamboo strand length. A strong interaction was found between bamboo species, specific pressure, and strand length on the mechanical properties of OSBs. The properties of all bamboo-based OSBs produced in this study conform with the requirements of the Japanese Industrial Standard JIS A 5908 (2015) and British Standard BS EN 300 (2006).
