Review Articles
Latest articles
- Reviewpp 2327-2350Guo, W., and Huang, J. (2023). "Environmental applications of immobilized and bio-resourced redox mediators: A Review," BioResources 18(1), 2327-2350.AbstractArticlePDF
Redox mediators (RMs), also known as electron shuttles, have been widely reported to promote both biotic and abiotic reductions of oxidized pollutants in water, soil, biogeochemical cycles, and wastewater treatment systems. However, the continuous addition of dissolved RMs is unaffordable and the potential environmental risks remain unknown because most applied RMs are synthetic chemicals. Immobilization technology enables RMs to be attached on non-dissolved supports, avoiding wash-out from the treatment systems. This realizes the reuse of RMs in scaled-up engineering applications and the in-situ remediation. Moreover, renewable natural biomass and their derivatives, such as biochar, have also aroused increased interest because they provide an economical and feasible way to solve the shortcomings of applying soluble RMs. This review presents different RM immobilization methods, which include entrapment, adsorption, and surface modification, as well as the use of bio-resourced RMs. The immobilization procedures and reaction mechanisms of the immobilized RMs and bio-resourced RMs in environmental applications are critically compared and summarized.
- Reviewpp 2351-2385Islam, M., Saini, P., Das, R., Shekhar, S., Sinha, A., and Prasad, K. (2023). "Rice straw as a source of nanocellulose for sustainable food packaging materials: A Review," BioResources 18(1), 2351-2385.AbstractArticlePDF
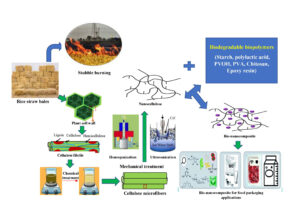
Asian countries, despite being the largest producers and yielding a significant proportion of the world’s rice, have poor disposal facilities for the harvested rice straw (stubble). Due to higher costs in their handling relative to their value, local farmers prefer the burning of stubble fields, thus creating environmental problems. Even though the government has taken initiatives, no effective solution has been discovered to handle this large agro-waste problem efficiently. In this regard, the utilization of rice straw to develop nanocellulose (NC) products is of interest. Renewability and biodegradability, along with suitable mechanical and thermal properties required for the packaging functions, are key advantages of NC. The bio-nanocomposites prepared using NC and other bio-based polymers are also being widely considered for sustainable food packaging applications due to the reinforcement provided by NC and alternative petroleum-based packaging materials. This review provides an overview of process utilization for preparing NC products using rice straw, pulping methods, and isolation to produce bio-nanocomposites for sustainable food packaging applications. The challenges and future aspects covering the utilization of rice straw for producing NC and eventually producing active packaging materials are also discussed.
- Reviewpp 2386-2407Ku Aizuddin, K. N. A., Lai, K.-S., Baharum, N. A., Thau Lym Yong, W., Ngi Hoon, L., Abdul Hamid, M. Z., Cheng, W. H., and Ong Abdullah, J. (2023). "Bamboo for biomass energy production," BioResources 18(1), 2386-2407.AbstractArticlePDF
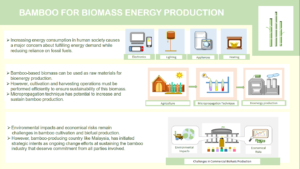
Energy consumption in human society has increased as more energy supplies are required to meet the needs of the world’s growing population. However, there is a major concern about fulfilling energy demand while reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Bamboo-based biomass has great potential for use as a raw material for the production of biofuels and bioenergy. Bamboo possesses excellent fuel qualities that can be converted into solid, liquid, and gaseous biofuels. Hence, the cultivation and harvesting operations must be performed efficiently to ensure that the availability of this biomass is sufficient to meet the demand for biofuel production. Several studies have shown that the micropropagation technique has increased bamboo production and that proper bamboo plantation management can benefit both the environment and society. Nevertheless, there are several challenges in bamboo cultivation and biofuel production, such as environmental impact from land management and economic risk from the industrial supply chain. Bamboo-producing countries, including Malaysia, have initiated several policies to propose strategies for sustaining the bamboo industry.
- Reviewpp 2408-2425Zuo, Z.-K., Xu, Z., Diao, G.-Y., Li, M., Ma, M.-G., and Shi, Z.-J. (2023). "Flexible functional composites for athlete health monitoring and auxiliary training applications," BioResources 18(1), 2408-2425.AbstractArticlePDF
The flexible functional composites have widely potential applications in the fields of athlete health monitoring and auxiliary training. Recently, there are a few reports on various functional composites such as graphene-based composites, MXene-based composites, and polymer-based composites, etc. However, the applications of flexible functional composites for athlete health monitoring and auxiliary training have not widely reviewed yet. This mini-review article summarizes these three types of functional composites for the applications of athlete health monitoring and auxiliary training. The synthetic methods, structures, and properties of functional composites are reviewed via some typical examples. We pay attention to the properties of composites sensor about health-monitoring. Moreover, the directions are suggested based on our knowledge. It demonstrates that these flexible functional composites will display excellent properties and promising applications potential in athlete health monitoring and auxiliary training.
- Reviewpp 2426-2439Gao, F., Yue, X., Yang, H., Yang, Y., Lam, S., Peng, W., and Chen, X. (2023). "Health damage and repair mechanism related to formaldehyde released from wood-based panels," BioResources 18(1), 2426-2439.AbstractArticlePDF
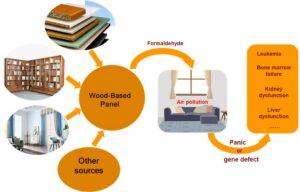
Wood-based panels, which contain wood raw materials along with urea-formaldehyde (UF) or phenol-formaldehyde (PF) resins, can increase the indoor air concentration of formaldehyde. Formaldehyde can stimulate the upper respiratory mucosa and cross-linking reaction with cell proteins and DNA, and this can result in degeneration and necrosis of respiratory cells and damaged cell proliferation. Formaldehyde can induce health hazards such as nasal cancer, leukemia, and destruction of the reproductive system. Acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 5 (ADH5) in the body cooperates with Fanconi anaemia complementation group D2 (FANCD2) to quickly metabolize formaldehyde into formate and maintain the balance of endogenous formaldehyde. However, when both ADH5 and FANCD2 proteins have defects or mutations, damaged DNA repair failure and cell proliferation induce a variety of health diseases. The damage has been found in the upper respiratory area, not on distal body tissues such as liver, kidney, and bone marrow. Meanwhile epidemiological survey has not shown a positive correlation between formaldehyde and health hazards. It is recommended that the use of wood formaldehyde-based products should be reduced, and pathogenesis genes and damage repair mechanism should be studied systematically and deeply to develop gene drugs to remove excess formaldehyde and activate the damage gene repair mechanism in the future.
- Reviewpp 2440-2519Owens, L. P., and Hubbe, M. A. (2023). "Performance factors for filtration of air using cellulosic fiber-based media: A review," BioResources 18(1), 2440-2519.AbstractArticlePDF
The filtration of air has attracted increasing attention during recent waves of viral infection. This review considers published literature regarding the usage of cellulose-based materials in air filtration devices, including face masks. Theoretical aspects are reviewed, leading to models that can be used to predict the relationship between structural features of air filter media and the collection efficiency for different particle size classes of airborne particulates. Collection of particles can be understood in terms of an interception mechanism, which is especially important for particles smaller than about 300 nm, and a set of deterministic mechanisms, which become important for larger particles. The effective usage of cellulosic material in air filtration requires the application of technologies including pulp refining and chemical treatments with such additives as wet-strength agents and hydrophobic sizing agents. By utilization of high levels of refining, in combination with freeze drying and related approaches, there are opportunities to achieve high levels of interception of fine particles. A bulky layer incorporating nanofibrillated cellulose can be used in combination with a coarser ply to achieve needed strength in a filter medium. Results of recent research show a wide range of development opportunities for diverse air filter devices containing cellulose.
- Reviewpp 4212-4230Dong, Z., Liang, C., and Zhao, J. (2023). “Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D) as a way to study adsorption and adsorbed layer characteristics of hemicelluloses and other macromolecules on thin cellulose films: A Review,” BioResources 18(2), 4212-4230.AbstractArticlePDF
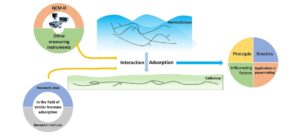
Cellulose and hemicellulose are abundant renewable resources. Thus, studying the adsorption mechanism of hemicellulose adsorption onto cellulose will contribute to further understanding of the fiber network, promote the development of new materials, and improve the utilization rate of resources. Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipative (QCM-D) is a research tool that can monitor quality changes at nanograms level; it is often used in the field of adsorption. Starting from the interaction between cellulose and hemicellulose, this paper outlines research on the principle, influencing factors, and kinetics of hemicellulose adsorption onto cellulose by QCM-D and expounds the research methods and means in the field of adsorption of similar biomass that can be used for reference. It provides a reference for further study of adsorption mechanism.
- Reviewpp 4231-4261Du, X., Wu, S., and Li, P. (2023). “Catalytic hydrogenolysis lignin to obtain phenols: A review of selective cleavage of ether bonds,” BioResources 18(2), 4231-4261.AbstractArticlePDF
Lignin depolymerized phenolic compounds and biofuel precursors are ideal value-added products for lignin residues generated in biorefineries and modern paper pulp facilities. Hydrogenolysis of lignin is an efficient depolymerization method for the production of carbon-neutral sustainable fuels and platform chemicals. Lignin is underutilized due to its complex structure, mainly because of its complex interunit linkage crosslinks such as α-O-4, β-O-4, 4-O-5, and β-5. This paper centers on the hydrolysis reaction of three major ether bonds (α-O-4, β-O-4, 4-O-5) in lignin and lignin model compounds based on different catalysts for hydrogenative degradation and catalytic systems. The methods and strategies to inhibit the condensation reactions are summarized. In particular, density functional theory calculation of the reaction pathways are combined with isotopically labeled reaction pathways to deeply analyze the hydrogenation degradation mechanism of biomass and further improve the yield of monophenols during the hydrogenation degradation of lignin. Finally, a brief summary of the challenges and prospects of lignin hydrogenation degradation is proposed.
- Reviewpp 4262-4331Hubbe, M. A., Trovagunta, R., Zambrano, F., Tiller, P., and Jardim, J. (2023). “Self-assembly fundamentals in the reconstruction of lignocellulosic materials: A review,” BioResources 18(2), 4262-4331.AbstractArticlePDF
This review article considers processes by which the main components of wood have been reported to arrange themselves into various kinds of organized structures, at least to a partial extent. The biosynthesis of wood provides the clearest examples of such self-organization. For example, even before a cellulose macromolecule has been completely synthesized in a plant organism, the leading parts of the polymer chains already will have assembled themselves into organized crystals, i.e., nano-fibrils. This review then considers a challenge that faces industrial engineers: how to emulate the great success of natural systems when attempting to achieve favorable materials properties, process efficiency, and environmental friendliness when developing new engineered wood structures, barrier films, and other desired products composed of lignocellulosic materials. Based on the reviewed literature, it appears that the main chemical components of wood, even after they have been isolated from each other, still have a remnant of their initial tendencies to come back together in a somewhat non-random fashion, following mechanisms that can be favorable for the production of engineered materials having potentially useful functions.
- Reviewpp 4332-4372Augustina, S., Dwianto, W., Wahyudi, I., Syafii, W., Gérardin, P., and Marbun, S. D. (2023). “Wood impregnation in relation to its mechanisms and properties enhancement,” BioResources 18(2), 4332-4372.AbstractArticlePDF
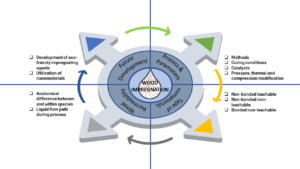
The principle of wood impregnation entails treating wood with a monomer/impregnating agent that diffuses into the cell walls, often followed by polymerization to change desired properties. Numerous studies related to this matter have been reported and continue to attract more interest, as wood impregnation can significantly improve wood properties. These processes can be grouped into two approaches: active modification involves the chemical alteration of wood structure by cross-linking, and passive modification features filling of cell cavities and/or cell walls with impregnating agents without any chemical reaction taking place. Wood impregnations could have resulted in an increase in its weight gain due to impregnating agents filling its cavities. It will diminish the utilization of wood as an engineering material in selected application fields. Owing to the extensive literature available, this article summarizes the representative achievements of wood impregnation. The mechanisms, benefits, and drawbacks of various impregnating agents on wood properties, along with grouping the impregnating agents that cause greater or lesser weight gain of wood were analyzed, compared, and evaluated. Thus, according to the application state of wood impregnations, the problems existing in those processes and the developmental trends in the future are also discussed in this review.
