Volume 17 Issue 2
Latest articles
- Researchpp 3042-3056Al-Rajhi, A. M. H., Yahya, R., Alawlaqi, M. M., Fareid, M. A., Amin, B. H., and Abdelghany, T. M. (2022). "Copper oxide nanoparticles as fungistat to inhibit mycotoxins and hydrolytic enzyme production by Fusarium incarnatum isolated from garlic biomass," BioResources 17(2), 3042-3056.AbstractArticlePDF

Garlic (Allium sativum L.) being infected by mycotoxigenic fungi is one of the primary factors limiting its nutritional and medical value. Therefore, there is an urgent need to repress mycotoxigenic fungi utilizing safer treatments, possibly involving nanoparticles. Fusarium incarnatum was isolated from garlic (A. sativum L.) that showed fungal contamination and their identification was confirmed using amplified and sequenced internal transcribed spacer nuclear ribosomal DNA regions, which confirmed the isolation of F. incarnatum from all cultivars. Copper oxide nanoparticles (CuONPs) at different concentrations showed inhibitory activity against F. incarnatum growth and mycotoxins, particularly at 400 ppm. The production of F. incarnatum mycotoxins, i.e., beauvericins, fusarins, moniliformin, and enniatins, was inhibited to 62.8%, 45.4%, 58.1%, and 55.0%, respectively at 400 ppm of CuONPs compared to the control. Shrinkage of the F. incarnatum cell membrane and collapsing of the cell walls were recorded via transmission electron microscopy at 400 ppm, but negligible distortion appeared at 100 ppm of CuONPs. CuONPs at 100 ppm encouraged the activity of CMC-ase, zylanase, and amylase, while 200 and 400 ppm promoted less enzyme activity. The current findings suggest that CuONPs have a fungistatic effect on F. incarnatum and their mycotoxins.
- Researchpp 3057-3066Nazir, S., Asad, M. J., Saqlan Naqvi, S. M., Zainab, T., Malik, S. I., Mehmood, R. T., Khan, J., Sultana, T., Nasir, N., and Hassan, A. (2022). "An engineered Aspergillus fumigatus GH3 β-glucosidase with higher glucose tolerance," BioResources, 17(2), 3057-3066.AbstractArticlePDF
β-glucosidases (3.2.1.21) are present in all domains of living organisms, and their importance in a number of essential biological processes and industrial applications has been highlighted. They are interesting for biomass conversion because b-glucans are the world’s largest source of biomass. For this reason, several fungal β-glucosidases have been investigated. The β-glucosidase gene of Aspergillus fumigatus, as well as its mutants D262E and W263F, were cloned and expressed in Pichia pastoris in this study. Their optimum temperature, pH, glucose tolerance, metal ion effect, and Vmax, km, and kcat were determined. The optimal temperature for recombinant β-glucosidase was 65 °C. For mutant D262E, there is an improvement in pH stability ranging from 4 to 6. As compared to the D262E mutant and recombinant β-glucosidase, mutant W263F showed a higher glucose tolerance and kcat.
- Researchpp 3067-3081Zhu, X., Xin, S., Ding, H., Yang, Y., Chen, Y., Li, X., Shi, H., Tan, Z., Zhou, J., and Liu, P. (2022). "Functional characterization of a noncatalytic protein, Athe_0181, from Caldicellulosiruptor bescii in promoting lignocellulose hydrolysis," BioResources 17(2), 3067-3081.AbstractArticlePDF
Caldicellulosiruptor bescii is a cellulolytic bacterium that secretes multifunctional glycoside hydrolases for efficient hydrolysis of lignocellulose into fermentable sugars. Additionally, some abundant noncatalytic proteins accompanying multifunctional glycoside hydrolases are also secreted by C. bescii, but its function has not yet been demonstrated. In this study, noncatalytic protein Athe_0181 and multifunctional glycoside hydrolases CbMan5C/Cel5A were expressed and purified from Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). Effective binding capacity of Athe_0181 to lignocellulose was displayed, and it showed preferential affinity to rice straw. Athe_0181 was shown to be a cellulase synergistic protein. It exhibited high synergistic activity of 523% in the presence of 25 μg/mL of CbMan5C/Cel5A with microcrystalline cellulose as the substrate. The structure-modifying activity of Athe_0181 to microcrystalline cellulose was demonstrated by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction analysis. These characteristics demonstrated that Athe_0181 played a role in the synergism of glycoside hydrolases from C. bescii for efficient hydrolysis of lignocellulose.
- Researchpp 3082-3094Dygas, D., Janicka, P., Berlowsla, J., and Kregiel, D. (2022). "Conventional and unconventional yeasts able to grow on rapeseed meal hydrolysates," BioResources 17(2), 3082-3094.AbstractArticlePDF
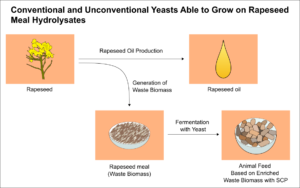
Yeast strains and appropriate hydrolysis conditions were selected for efficient single cell protein (SCP) production from waste rapeseed meal. High potential for effective biomass production was observed for Yarrowia lipolytica LOCK0264 with 10 g of rapeseed meal at 4.9 × 108 ± 1.5 × 108 (2.91 logarithmic units). The highest yeast multiplication rate was obtained for Metschnikowia pulcherrima NCYC747 with 12.5 g of rapeseed meal and with 15 g of rapeseed meal at 1.6 × 108 ± 3.8 × 107 and 4.5 × 108 ± 4.0 × 107 (2.75 and 2.86 logarithmic units, respectively).
- Researchpp 3095-3106Su, Z., Fan, S., Gong, C., Ni, J., Zhang, Y., Yang, B., Peng, F., and Mahmoud, M. S. (2022). "Incineration properties and kinetic studies of sludge from old newsprint fiber line," BioResources 17(2), 3095-3106.AbstractArticlePDF
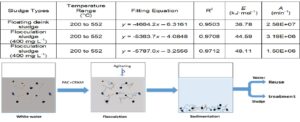
The basic incineration properties of flotation deinking sludge and two kinds of flocculating sludge from old newsprint fiber line were studied. Coats-Redfern was used for incineration process analysis, and based on the kinetic parameters of the three types of studied sludge at a heating rate of 10 °C·min-1, the reaction orders were confirmed in the organic incineration region. The activation energy of the three sludge types were 38.78, 44.59, and 48.11 kJ·mol-1, and their frequency factors were 2.58 E+07 min-1, 3.19 E+06 min-1, and 1.50 E+06 min-1, respectively. Organics incineration in the flocculation sludge was more difficult than the incineration of the deinking sludge; as the flocculate dosage increased, the incineration difficulty increased. However, the amount of flocculating sludge generated from the flocculation treatment of the deinking white water accounted for less than 10% of the flotation deinking sludge, and their elemental content and calorific value related to combustion were also similar to each other; therefore, it could be predicted that the flocculating sludge would not greatly impact the sludge treatment system. Therefore, it could be incorporated into existing sludge incineration systems for reduction and thermal energy recovery.
- Researchpp 3107-3129Geng, L., Shen, W., and Xu, Z. (2022). "Embodied carbon and influencing factors of China's paper industry's export trade to the United States," BioResources 17(2), 3107-3129.AbstractArticlePDF
The paper industry is a high-carbon emission and energy-intensive industry. From the perspective of low-carbon trade and carbon neutrality, its energy conservation and emission reduction are worthy of attention. This study used the input-output model to calculate the embodied carbon emissions of China’s paper industry’s export trade to the United States from 2006 to 2020 and used the logarithmic mean division index (LMDI) method to analyze influencing factors of the change of embodied carbon emissions. The study found that the embodied carbon emissions of China’s paper industry’s export trade to the United States generally shows a stable downward trend after reaching the peak with the increase of export trade scale; scale effect is the main factor that causes the embodied carbon emissions, while technological progress, policy support, and environmental regulations are important driving forces to promote carbon emission reduction. The research results of this paper not only can test and guide China’s paper industry trade policies and industrial policies, but they can also provide decision-making reference for China and the United States to promote the carbon emission reduction of the paper industry.
- Researchpp 3130-3147Llovera, L., and Benjelloun-Mlayah, B. (2022). "Silica extraction from organosolv pretreated wheat straw," BioResources 17(2), 3130-3147.AbstractArticlePDF
The silica contained in biomass is generally recovered from the ashes after combustion. In this study, the main objective was the recovery of silica from wheat straw, without degrading the other biomass components. To achieve this goal, the wheat straw was first pre-treated by an acidic organosolv process to separate it into its three major components: cellulose, lignin, and hemicelluloses. The silica, due to the pre-treatment conditions, was in the cellulose fraction, from which it was extracted, under alkaline conditions. The goal was to recover pure silica with suitable particle size and BET surface area, enabling its use in various industrial applications. The extraction and precipitation steps of silica recovery were studied. After optimization, the silica extraction conditions were set at pH 9 to 10 and 85 °C and the precipitation at pH 5 to 5.5. In these conditions, up to 82% of total silica in straw was extracted with high purity, an average particle size of 4 µm, and a BET surface area of 156 m2/g. In summary, silica can be extracted from lignocellulosic biomass, at high yield and purity, without affecting the biorefinery co-products’ yields and quality.
- Researchpp 3148-3162López-Gómez, Y. M., Barbero-López, A., González-Prieto, O., Venäläinen, M., and Haapala, A. (2022). "Tree species-based differences vs. decay performance and mechanical properties following chemical and thermal treatments," BioResources 17(2), 3148-3162.AbstractArticlePDF
Many thermal and chemical treatments are known to inhibit wood decay despite the wood grade processed, but their impact, e.g., chemicals’ leaching and decay resistance, may not be similar. The aim of this study was to test whether some model treatments retain their performance in different wood species. Additionally, the effects of thermal modification and linseed oil-based varnish treatments as means to mitigate water-soluble chemicals leaching were assessed. The mass loss caused by Trametes versicolor was measured after a 12-week exposure to analyze whether the different treatment approaches prevented the fungal decay after a standard leaching test. The mechanical properties before and after exposure were tested independently to determine whether the mechanical properties of different wood species were affected by the tested treatments and wood decay. The responses of the tested wood species were found to vary by treatments, but thermal and chemical fixation methods for water-soluble tannins were beneficial in all cases considering the mass loss and the degradation of modulus of rupture and modulus of elasticity of treated wood. Varnish was overall the most effective treatment against decay, but the results emphasize the need for testing potential preservation methods and chemicals on several species.
- Researchpp 3163-3177Kim, M. J., Park, H. J., Kang, P., Kim, I. C., Yim, J. H., and Han, S. J. (2022). "Purification and characterization of a new cold-active cellulolytic enzyme produced by Pseudoalteromonas sp. ArcC09 from the Arctic Beaufort Sea," BioResources 17(2), 3163-3177.AbstractArticlePDF
A cold-active endoglucanase-producing bacterium was isolated from the Beaufort Sea of the Arctic Ocean and identified as Pseudoalteromonas sp. ArcC09. Cellulolytic activity of ArcC09 reached a maximum of 60 U/mg when cultivated in ZoBell medium for 72 h at 15 °C. This purified endoglucanase, with a molecular mass of 28 kDa, exhibited maximum activity at pH 7.0 and 55 °C. The ArcC09 endoglucanase exhibited 10% and 36% of its maximal activity even at low temperatures of 5 °C and 15 °C, respectively. However, it showed lower thermal stability than a mesophilic cellulase, which is characteristic of a psychrophilic enzyme. The activity was inhibited by CuSO4, and linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS). These findings supplement the understanding of cold-active endoglucanases and may have commercial applications in enzymatic digestion of cellulosic biomass to fermentable sugars.
- Researchpp 3178-3201Li, Y., Zambrano, F., Wang, Y., and Marquez, R. (2022). "How China's foreign waste ban will reshape the U.S. recycling supply chain: Economic and environmental considerations towards a circular economy oriented paper recycling industry," BioResources 17(2), 3178-3201.AbstractArticlePDF
Until recently, China was the largest scrap and unsorted waste importer in the world. Chinese industries sorted the imported wastes and recovered plastic, paper, textiles, and metals, using them as raw materials for manufacturing processes. Since 2013, the Chinese government has imposed measures to ban the import of wastes, the latest one being the “National Sword” policy (fully deployed in January 2021), banning the import of unsorted and recycled wastes. As a result, collecting wastes and recyclables and sending them to China is no longer an option; this has drastically affected the recycling industry supply chain with considerable consequences. This study analyzed the development of Chinese foreign policies on the export of paper waste materials from the U.S. and their specific impact on the recovered paper recycling industry. The economic and environmental consequences of the policy on the U.S. paper recycling industry were analyzed using three scenarios: landfilling (as a baseline), incineration, and recycling. The CO2 emissions were estimated and then compared. It was found that recycling would result in the largest reduction in greenhouse gases. Although recycling was the best evaluated scenario, it has the greatest costs; therefore, possible solutions towards adding value to paper wastes were analyzed.
