Volume 18 Issue 1
Latest articles
- Researchpp 1836-1847Kukwa, R. E., Kukwa, D. T., Nande, W. U., and Tse, M. T. (2023). "Conversion of waste products derived from rice processing industry into bioethanol," BioResources 18(1), 1836-1847.AbstractArticlePDF
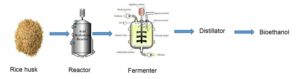
The effects of acid and alkali hydrolysis, as well as rice husk varieties (pure and mixed), on bioethanol production using saccharification and fermentation, were investigated in this study. Microbes such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae are currently used for fermenting agricultural wastes to bioethanol, an environmentally friendly alternative to petroleum energy sources. Rice husks were ground to a fine powder, then hydrolyzed with acid and alkali, and incubated for five days. A refractometer was used to perform a sugar reduction test, which determined the presence of fermentable sugar in the media. The parameters revealed that the variety of rice husk used did not affect the ethanol percent yield, which was 14.8 ± 0.5% and 15.0 ± 0.5% for the pure and mixed varieties, respectively; however, there was a substantial difference in the percentage yield in the method of pre-treatment. The percentage yield of ethanol in the acid pre-treated sample was higher (14.8 ± 0.5% and 15.0 ± 0.5%) than that of the alkali (6.1 ± 0.5% and 4.8 ± 0.5%). The presence of alcohol in the sample was confirmed by FTIR analysis, while GC-MS identified the specific compounds and their percentage composition – ethanol (9.67%). This suggests that using H2SO4 in the hydrolysis of rice husk is a promising and effective method for producing bioethanol.
- Researchpp 1848-1866Venera, M., Chuvaeva, A., and Fedorov, V. (2023). "Wood industry clusters and their optimal location for the efficient use of forest raw materials," BioResources 18(1), 1848-1866.AbstractArticlePDF
World experience in the creating of clusters in different industries has shown their effectiveness. This paper investigated the resource potential for creating a cluster designed for wood processing and to process wood waste from the timber industry of the Krasnoyarsk Territory of Russia. Static indicators were assessed, representing a quantitative characteristic of forest raw material resources: total and operational reserves of wood available in the region. While studying the state and use of forest resources, significant reserves of forest resources and secondary raw materials were revealed. Main indicators of the forest industry of the region over recent years were analyzed. The main systemic issues hindering the development of the timber industry were exposed. It was concluded that the region has raw material potential and industrial infrastructure necessary for the formation and sustainable development of a cluster for processing waste from the timber industry. Analysis of the producers and harvesters of forest products’ locations revealed potential wood industry clusters, and areas suitable for cluster economic development were proposed. The average figures of the nearest neighbor were used and analyzed to examine the spatial distribution of raw material harvesters and enterprises that produce finished products with respect to transport infrastructure, staffing, and raw material availability.
- Researchpp 1867-1881Zhu, X., Wang, X., Wang, B., Zhang, M., An, Z., and Han, W. (2023). "Periodic hygrothermal properties of Salix liquefaction products / isocyanate rigid foam materials," BioResources 18(1), 1867-1881.AbstractArticlePDF
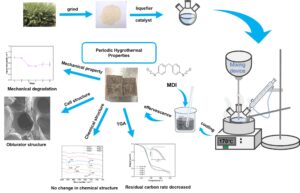
Under specific circumstances, the liquefaction product of biomass polyol can be converted into hard polyurethane foam. In this study, the rigid foam material (RPUF) was created by reacting the liquefaction product of Salix psammophila with isocyanate. The mechanical properties, chemical structure, cell structure, and thermal stability of RPUF were characterized by mechanical properties tests, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The impact strength, compressive strength, and flexural strength of RPUF after hygrothermal treatment showed a downward trend. FTIR showed that the change of temperature and humidity did not affect the chemical structure of RPUF. SEM showed that the destruction of cell structure of RPUF was increased with the extension of time. TGA showed that the initial decomposition temperature of RPUF was reduced by periodic hydrothermal treatment, and the residual carbon rate decreased with the extension of treatment time.
- Researchpp 1882-1900Li, Y., Xu, Z., Zhang, Q., Di, J., Yang, R., Gai, X., Wang, H., and Zhang, T. (2023). "Mesoporous biochar derived from bamboo waste: Template/hydrothermal preparation and highly efficient pharmaceutical adsorption," BioResources 18(1), 1882-1900.AbstractArticlePDF
In order to explore the feasibility of using template/hydrothermal method to produce mesoporous biochars from real biomass directly for adsorptive removal of pharmaceuticals, six mesoporous biochar samples were produced from bamboo waste through this method and characterized, and their adsorption capabilities for berberine hydrochloride and matrine from water were evaluated. Characterization results confirmed the mesoporous structures of the biochar samples, and the biochars had BET surface areas in the range of 180 to 880 m2/g. Pore properties of the biochars mainly depended on the synthesis compositions and were related to their adsorption capabilities. The bamboo derived mesoporous biochars provided effective adsorption with the highest uptake amounts of 645 and 496 mg/g for berberine hydrochloride and matrine at 0.1 mg/mL and 298 K, respectively. The adsorption equilibrium could be reached in 90 min for berberine hydrochloride and 60 min for matrine on the selected mesoporous biochar. This study provides an effective strategy to produce biomass derived mesoporous biochars as efficient adsorbents in water treatment and pharmaceutical purification.
- Researchpp 1901-1915Norazli, N., Mohammad Rawi, N. F., Abdulwahab Taiwo, O. F., Mohamad Kassim, M. H., and Jawaid, M. (2023). "Delignification’s effect on microcrystalline cellulose obtained from oil palm empty fruit bunch fibres," BioResources 18(1), 1901-1915.AbstractArticlePDF
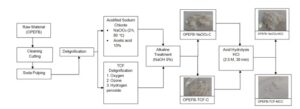
The effects of acidified chlorite (NaClO2) and totally chlorine free (TCF) bleaching were evaluated relative to the properties of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) fabricated from oil palm empty fruit bunch fibres (OPEFB). The MCC properties were analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) methods, and they were compared with commercial MCC. The results revealed that all MCC belongs to cellulose type 1 and OPEFB-NaClO2-MCC showed a higher crystallinity index than OPEFB-TCF-MCC. The TGA indicated that all MCC samples showed a higher decomposition temperature compared to pure cellulose. However, OPEFB-NaClO2-MCC showed better thermal stability than OPEFB-TCF-MCC. It was clear from SEM images that the different MCC particles had rough surfaces and micro-sized particles. Overall, results confirmed that the obtained MCC samples displayed comparable properties with those of commercial MCC. The MCC produced from OPEFB using NaClO2 is a promising material to prepare high value-added products compared to MCC produced using TCF delignification treatment.
- Researchpp 1916-1932Li, P., Qin, Y., Xu, Q., and Jiang, G. (2023). "Biodegradable composites based on well-characterized cellulose and poly (butyleneadipate-co-terephthalate)," BioResources 18(1), 1916-1932.AbstractArticlePDF
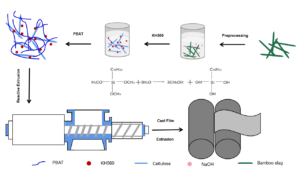
As a biodegradable and flexible copolymer, poly(butyleneadipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) is used for packaging. However, high cost and limited properties restrict its applications. Because of the hydrophobic nature of PBAT, low mechanical properties are observed when PBAT and cellulosic fibers, which are hydrophilic, are used in blends. To increase the interfacial adhesion between cellulose and PBAT, γ-(2,3-epoxypropoxy) propytrimethoxysilane (KH560) was used as a reactive compatibilizer to modify cellulose. A one-step method was demonstrated for compounding and subsequent extrusion blowing, which is a simple and environmentally friendly approach to fabricate a series of K-Cellulose/PBAT (KH560-Cellulose/PBAT) composites. The morphology and structure of the cellulose were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Fourier transform infrared spectrophotometry. Meanwhile, thermal analysis of the hybrids showed an improvement of the thermal stability of the composites with increased silanized cellulose content. In addition, the barrier properties of films are measured by water vapor permeability (WVP) and oxygen permeability (OP). Finally, after addition of reactive compatibilizer KH560, there was considerable improvement with increased the cellulose content, as shown through mechanical properties testing. Therefore, the composites prepared with these enhanced properties have great potential as substitutes for traditional commodity polymers.
- Researchpp 1933-1947Johst, P., Kaeppeler, U., Seibert, D., Kucher, M., and Böhm, R. (2023). "Investigation of different cardboard materials under impact loads," BioResources 18(1), 1933-1947.AbstractArticlePDF
Packaging materials, such as cardboard, must endure vigorous loads during handling and transport, which could lead to damage to the packaged goods. To ensure that the transported goods reach the consumer safely, a profound knowledge of the behavior of packaging materials under impact loads is required. This study experimentally investigated the behavior of two different cardboard materials under impact loads. Different kinetic energy levels were obtained using a specially developed test rig. First, the resulting damage of the specimens was qualitatively characterized based on digital analysis. Second, the damage was quantitatively analyzed using the imprint diameter after impact as the characteristic parameter. It was found that three different damage phenomena occurred on both investigated materials: imprint, cracking, and breakthrough. Different imprint diameters were detected with increasing kinetic energy of the impactor. The impact load resistance of the material with the higher grammage was higher than that of the material with the lower grammage.
- Researchpp 1948-1970Yang, C., Guan, B., Zhang, Z., Zhang, J., Xue, B., and Tian, X. (2023). "The establishment and numerical calculation of a heat transfer model of a graphene heating energy storage floor," BioResources 18(1), 1948-1970.AbstractArticlePDF
A new type of graphene electric heating solid wood composite floor and its heat transfer model were designed to enable users to have a higher-quality and safe living experience. A heat transfer mathematical model was developed. The structural entity of the composite graphene heating floor was drawn using Solidworks software. The floor structure was abstracted as a two-dimensional model using MATLAB software to obtain the temperature rise curves and corresponding time of each group. Then, six groups of the best data were selected from the experimental data to simulate the heat storage capacity of graphene floors. The optimal group of the model was verified via experiments. According to the simulation, the comprehensive performance was optimal when the overall thickness of the floor was 18 mm, the thickness of the floor surface was 4 mm, and the thickness of the heat-accumulating layer was 2 mm. The experimental results showed a maximum difference between the measured and calculated data of only 3.2%, which shows the scientific validity, accuracy, and advancement of the model. The composite graphene electric heating energy storage floor designed in this study can be regarded as safe, reliable, environmentally friendly, and healthy.
- Researchpp 1971-1998Khierallah, A. H. I., Bouazza, A. H., and Montplaisir, D. (2023). "Nanofibrous material of n-succinyl chitosan/ polyethylene oxide in the removal of emerging pharmaceuticals from aqueous solution by adsorption/desorption method," BioResources 18(1), 1971-1998.AbstractArticlePDF
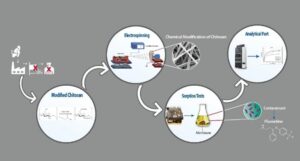
Pharmaceutical metabolites and their residues have been identified as major environmental pollutants in aquatic ecosystems. N-succinyl chitosan (NSCS) was studied as a potential adsorbent for a pharmaceutical residue, fluoxetine, from aqueous media. NSCS was investigated using Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and 1H-nuclear magnetic residence (NMR) spectroscopies. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to investigate the formation of nanofibers by electrospinning of these green biomaterial polymer membranes. The mechanisms of FLX adsorption, as well as the effects of pH value in the original solution on adsorption capacities, were investigated using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC-UV DAD) under identical adsorption conditions. It was found that NSCS/PEO nanofibers with a diameter of 183 ± 38 nm were more effective to remove pharmaceutical residues from aqueous media than other commercial and modified adsorbents such as activated carbon (AC). FLX adsorption on NSCS/PEO nanofibers was favoured at pH 8.0. Pseudo-first order model was the more adequate to represent the kinetic data, being the maximum adsorption capacities of FLX on NSCS/PEO reached up to 70%. A study of the desorption potential and reusability of the mat was also conducted. According to the results, electrospun NSCS/PEO mats can be desorption and reused up to 4 times without significant loss in adsorption capability.
- Researchpp 1999-2010Cui, H., Li, T., Chen, T., Wu, L., Li, H., Liu, C., Xin, M., and Song, Y. (2023). "Parameter calibration for simulation of Gentiana seedling substrate based on discrete element method," BioResources 18(1), 1999-2010.AbstractArticlePDF
The physical and mechanical parameters of the rotten rice straw (RRS), rice husk biochar (RHB), and the mixture of the two materials (the substrate) were calibrated by Plackett-Burman and Box-Behnken experiments to obtain the parameters for simulation of the forming of the Gentiana seedling substrate mat (GSSM). The particle contact parameters were calibrated, and the repose angle was taken as the response value based on the Hertz-Mindlin approach with the JKR contact model of discrete element method (DEM). A quadratic regression model was established and optimized using Design-Expert software. The parameters that most affected the substrate repose angle were the restitution coefficient of RRS of 0.20, the rolling friction coefficient of RRS of 0.04, the surface energy of RRS for JKR of 0.53, and the surface energy of RHB-RRS for JKR of 2.11. The simulated repose angle of the substrate and the bending strength of GSSM were compared with that of the verified experimental values respectively based on the optimal parameters. The relative errors of repose angles and bending strengths between the values of the simulation and the measurement were 0.71% and 1.39% respectively, indicating that the parameters obtained in this study can provide a reliable reference for the forming of GSSM.
