Volume 18 Issue 2
Latest articles
- Researchpp 4116-4131Silva, G. A. O., Curvo, K. R., Oliveira, A. C., Neto, P. N. M., Vasconcelos, L. G., Carvalho, A. M. M. L., Silva, M. J., Natalino, R., and Pereira, B. L. C. (2023). “Effect of age on heartwood proportion, color, chemical composition, and biological resistance of teakwood,” BioResources 18(2), 4116-4131.AbstractArticlePDF
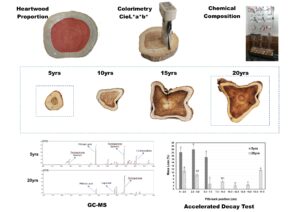
Teakwood from fast-growth plantations is commercialized at increasingly younger ages for economic reasons. However, wood features are influenced by the age of the tree. This study examined how age affects heartwood proportion, color parameters, chemical composition, and natural teakwood durability. Trees with 5, 10, 15, and 20 years of fast-growth at commercial plantations located in Mato Grosso, Brazil were evaluated. The base diameter of the trees ranged from 13.1 (5 years) to 28.3 cm (20 years), and the heartwood percentage increased from 16.3 to 60.0%, respectively. The color parameters in the CIELab system indicated that wood became darker and more saturated, and the predominance of yellow color decreased compared with red as age advanced. The total extractive content ranged between 7.4 (5 years) and 9.6% (15 years), without a clear trend of age affecting the extractive content. The extractives from five-year-old wood were mainly composed of tectoquinone (43.3%), phthalic acid (19.1%), and 1,3-indandione (9.2%), while those from 20-year-old wood were mainly composed of tectoquinone (60.7%), lapachol (13.8%), and phthalic acid (9.7%). Teakwood can be classified as resistant (5 years) to very resistant (20 years) after being submitted to an accelerated decay test.
- Researchpp 4132-4142Zuo, L., Qu, M., Song, Z., Zhang, Y., Su, X., Yue, X., Li, C., and Xu, B. (2023). “Decay resistance of Pterocarpus erinaceus Poir. and the antifungal properties of its extract,” BioResources 18(2), 4132-4142.AbstractArticlePDF
The processing residue of Pterocarpus erinaceus was used to obtain an ethanol-extract, whose anti-fungal properties and mode of action was investigated using multi-omics principles and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The results showed that the decay resistance of the heartwood of Pterocarpus erinaceus was in Grade I; it showed strong decay resistance. The effective concentration of 70% ethanol extract of the heartwood of Pterocarpus erinaceus was 13.8%. It showed high inhibition against Coriolus versicolor and Gloeophyllum trabeum, and the content of the extract was positively correlated with the diameter of the inhibition zone. Transcriptomics analysis showed there were 93 genes differentially expressed in Gloeophyllum trabeum. Among them, 42 genes were up-regulated and 51 genes were down-regulated. These genes were mainly related to oxidoreductase activity, integral components of the membrane, carbohydrate metabolism, lipid metabolism, and other related Gloeophyllum trabeum life activities. In total, 31 substances were separated and observed using GC-MS, and their peak areas accounted for 91.8% of the total peak area. Of these, 16 substances including ketones, esters, amines, alkanes, olefins and aromatic compounds showed a relatively high content. Ketones accounted for the most abundance at 29.1%. These compounds may represent the main active components of antifungal and decay resistance.
- Researchpp 4143-4152Chai, H., Cai, L., Xu, T., and Ma, Y. (2023). “Digital image correlation method for detecting strain in wood drying process,” BioResources 18(2), 4143-4152.AbstractArticlePDF
Stress and strain monitoring is of great significance for wood drying. Using digital image correlation (DIC), this study measured displacement and strain changes during wood drying in real time. The results showed that when wood is dried below the fiber saturation point, the difference of the radial and tangential shrinkage ratio gradually increased. An analysis of tangential and radial shrinkage ratio revealed that in the early stage of drying, the tangential and radial shrinkage ratio was relatively flat; in the middle stage of drying, the shrinkage ratio began to gradually increase; and in the later stage of drying, the tangential shrinkage ratio was approximately twice as large as that in the radial direction. Further, regarding the tangential and radial strain distribution, the radial strain distribution was more scattered than that in the tangential direction. The radial strain distribution exhibited compressive strain on both ends of the specimen, and the tensile strain was in the center. The tangential strain distribution was tensile strain on the left side of the specimen and compression strain on the right. Overall, DIC is stable and reliable, and it can be used to monitor well the stress and strain changes during wood drying.
- Researchpp 4153-4167Ghahrani, N., Nazarnezhad, N., Ramezani, O., and Asadpour, G. (2023). “The impact of an acidic post-treatment on surface-modified old corrugated cardboard (OCC) with NaOH-urea as a reinforcing agent,” BioResources 18(2), 4153-4167.AbstractArticlePDF
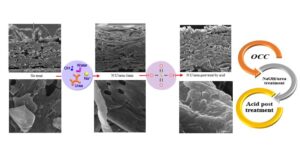
Chemical surface modification is one method for enhancing the mechanical and barrier properties of packaging paper. The NaOH/urea solvent system has been deemed an effective, inexpensive, and cost-effective solvent for paper modification and cellulose dissolution due to its unique self-reinforcing qualities and the fact that it can be utilized on an industrial scale, although it is ineffective for porous paper and requires pre- or post-treatment. This study examined the influence of acid as a post-treatment on the surface modification of paper with NaOH/urea to improve properties relative to packaging uses. The results indicated that NaOH/urea modification on OCC as a semi-crystalline material did not result in materials with superior resistance and barrier qualities. While acid treatment increased tensile and burst strength and air permeability, it was ineffective at increasing tear strength. Properties of control, NaOH/urea treatment, and acidic post treatment papers were respectively 33.31, 29.4, and 37.46 mn/g in the tensile index, 1.7, 1.58, and 1.74 Kpa.m2/g in burst index, 9.94, 9.07 and 8.87 mn.m2/g in tear index, 2.04, 1.34 and 1.32 s-1 in smoothness, 37.2, 38.2 and 45.4 s in air resistance, and 77.5, 90.8 and 80.5 water absorption. Therefore, with or without acidic post-treatment, the sheets became hydrophilic.
- Researchpp 4168-4181Sagdic-Oztan, C., Koschella, A., Heinze, T., Karaguler, N. G., and Tuter, M. (2023). “Preparation of bacterial cellulose using enzymatic hydrolysate of olive pomace as carbon source,” BioResources 18(2), 4168-4181.AbstractArticlePDF
Bacterial cellulose has superior physical and chemical properties, biocompatibility, and purity. However, the high production cost obstructs the common use of this polymer. This study investigated the efficiency of olive pomace, an important by-product of olive oil industry in Turkey, as a carbon source for Novacetimonas hansenii. Olive pomace pretreatment with 1% H3PO4 was followed by enzymatic hydrolysis. The maximal reducing sugar concentration upon enzymatic process was 9.3 g/L with 1 enzyme: 6 substrate (dry matter) ratio. After incubation in the growth media prepared with the obtained reducing sugar as carbon source, the highest bacterial cellulose production was 0.68 g/L. Structural analysis indicated that bacterial cellulose from the enzymatic media and the conventional Hestrin-Schramm medium possess similar characteristics. The present work provides a favourable method to reduce the cost of bacterial cellulose production.
- Researchpp 4182-4194Xie, L., He, X., Hu, Y., Wei, X., and Shen, L. (2023). “Wooden cantilever covered bridges in Anhua, China,” BioResources 18(2), 4182-4194.AbstractArticlePDF
Wooden cantilever covered bridges are known for their marvelous shapes and manufacturing technique. Many wooden cantilever covered bridges were constructed during Ming and Qing Dynasties in Anhua province, China, due to the “Tea-Horse Trade” policy. The excellent performance of wooden materials and exquisite building techniques have kept these wooden bridges well-preserved and worthy of investigation. This paper conducted a comprehensive review of wooden cantilever covered bridges in Anhua, especially for the eight bridges listed as historical and cultural heritage protected at the provincial or the national level. The discussions covered the historical background of the bridges, their locations and dimensions, and the details of their structures including the cantilever systems, corridors, and roofs. Moreover, the cultural background was introduced to better understand the meaning of the decorations carved on the bridges and the logic of location selections.
- Researchpp 4195-4211Liu, G., Shi, K., Sun, H., Yang, B., and Weng, Y. (2023). “Nano-SiO2-modified xylan-PVOH-based composite films: Mechanical and barrier properties investigation,” BioResources 18(2), 4195-4211.AbstractArticlePDF
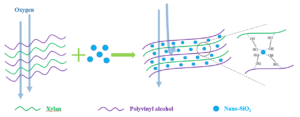
Hemicellulose from a wide range of sources and abundant reserves shows good biocompatibility, degradability, and renewability. Because of its low degree of polymerization and a large amount of hydroxyl groups, hemicellulose-based films exhibit low strength and tend to be hydrophilic, which hinders some potential applications. Therefore, hemicellulose-based films with improved strength and barrier properties are needed. In this study, nano-SiO2 was incorporated into polyvinyl alcohol/xylan matrix for the purpose of preparing an inorganic-organic hybrid composite film with elevated mechanical and barrier performance. The addition of nano-SiO2 can serve this purpose. A 1% nano-SiO2 loading resulted in an increase of contact angle of the composite film from 89.6° to 110.4°, an increase of the tensile strength from 11.2 to 14.8 MPa, and a decrease of oxygen permeability from 1.83 to 0.27 (cm3×µm)/(m2·d·kPa), which corresponds to a contact angle that was increased by 23%, tensile strength increased by 32%, and oxygen permeability decreased by 85%. These results indicated that the nano-SiO2 modified xylan film might have great application prospects as a barrier film in food packaging.
- Reviewpp 4212-4230Dong, Z., Liang, C., and Zhao, J. (2023). “Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D) as a way to study adsorption and adsorbed layer characteristics of hemicelluloses and other macromolecules on thin cellulose films: A Review,” BioResources 18(2), 4212-4230.AbstractArticlePDF
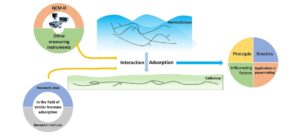
Cellulose and hemicellulose are abundant renewable resources. Thus, studying the adsorption mechanism of hemicellulose adsorption onto cellulose will contribute to further understanding of the fiber network, promote the development of new materials, and improve the utilization rate of resources. Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipative (QCM-D) is a research tool that can monitor quality changes at nanograms level; it is often used in the field of adsorption. Starting from the interaction between cellulose and hemicellulose, this paper outlines research on the principle, influencing factors, and kinetics of hemicellulose adsorption onto cellulose by QCM-D and expounds the research methods and means in the field of adsorption of similar biomass that can be used for reference. It provides a reference for further study of adsorption mechanism.
- Reviewpp 4231-4261Du, X., Wu, S., and Li, P. (2023). “Catalytic hydrogenolysis lignin to obtain phenols: A review of selective cleavage of ether bonds,” BioResources 18(2), 4231-4261.AbstractArticlePDF
Lignin depolymerized phenolic compounds and biofuel precursors are ideal value-added products for lignin residues generated in biorefineries and modern paper pulp facilities. Hydrogenolysis of lignin is an efficient depolymerization method for the production of carbon-neutral sustainable fuels and platform chemicals. Lignin is underutilized due to its complex structure, mainly because of its complex interunit linkage crosslinks such as α-O-4, β-O-4, 4-O-5, and β-5. This paper centers on the hydrolysis reaction of three major ether bonds (α-O-4, β-O-4, 4-O-5) in lignin and lignin model compounds based on different catalysts for hydrogenative degradation and catalytic systems. The methods and strategies to inhibit the condensation reactions are summarized. In particular, density functional theory calculation of the reaction pathways are combined with isotopically labeled reaction pathways to deeply analyze the hydrogenation degradation mechanism of biomass and further improve the yield of monophenols during the hydrogenation degradation of lignin. Finally, a brief summary of the challenges and prospects of lignin hydrogenation degradation is proposed.
- Reviewpp 4262-4331Hubbe, M. A., Trovagunta, R., Zambrano, F., Tiller, P., and Jardim, J. (2023). “Self-assembly fundamentals in the reconstruction of lignocellulosic materials: A review,” BioResources 18(2), 4262-4331.AbstractArticlePDF
This review article considers processes by which the main components of wood have been reported to arrange themselves into various kinds of organized structures, at least to a partial extent. The biosynthesis of wood provides the clearest examples of such self-organization. For example, even before a cellulose macromolecule has been completely synthesized in a plant organism, the leading parts of the polymer chains already will have assembled themselves into organized crystals, i.e., nano-fibrils. This review then considers a challenge that faces industrial engineers: how to emulate the great success of natural systems when attempting to achieve favorable materials properties, process efficiency, and environmental friendliness when developing new engineered wood structures, barrier films, and other desired products composed of lignocellulosic materials. Based on the reviewed literature, it appears that the main chemical components of wood, even after they have been isolated from each other, still have a remnant of their initial tendencies to come back together in a somewhat non-random fashion, following mechanisms that can be favorable for the production of engineered materials having potentially useful functions.
