Volume 18 Issue 4
Latest articles
- Researchpp 8432-8443Jia, X., Tang, G., Gao, J., Liao, Y., Zhang, Y., Jiang, X., Yang, H., Wu, D., You, F., Yu, P., and Yao, C. (2023). “Hydrophobic microcrystalline cellulose/polyethyleneimine composite aerogel for effective sound absorption,” BioResources 18(4), 8432-8443.AbstractArticlePDF
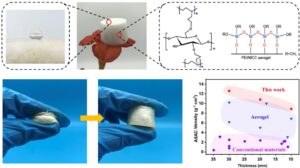
A hydrophobic and ultralight cellulose aerogel (CA) was reinforced by polyethyleneimine (PEI) and functionalized by methyltrimethoxysilane (MTMS). Adding PEI improved the mechanical strength and the elastic resilience of the resulting material due to the flexibility enhancement of the cellulose chains, which prevented the collapse of the pore structure and contributed to the uniform pore size distribution. The hydrophobic property of the aerogels with the functionalization of MTMS was improved, which can prevent the pore structure from collapsing due to the absorption of water. The maximum compression modulus of aerogel reached 1.1 MPa at the strain of 80%, and its hydrophobic water contact angle was up to 112°. The hydrophobic composite aerogels exhibited ultrahigh efficiency in sound absorption across a wide frequency range from 500 to 6300 Hz, and their average absorption coefficient was greater than 0.74. The light weight, high porosity, and environmentally friendly aerogels presented in this work are promising for efficient sound absorption. They have potential applications in noise pollution treatment.
- Researchpp 8444-8457Wang, M., Li, M., Cui, W., Xiang, X., and Duo, H. (2023). “TSW-YOLO-v8n: Optimization of detection algorithms for surface defects on sawn timber,” BioResources 18(4), 8444-8457.AbstractArticlePDF
The goal of this work was to better meet the demand for rapid detection of surface defects in sawn timber in forestry production. This paper introduces a two-way feature fusion network based on the YOLO-v8 algorithm and proposes a feature fusion network model that combines the attention mechanism and loss function optimization. In this way it increases the tiny target detection head in order to more effectively detect small defective targets in the wood, thus realizing the model’s high-efficiency and low-consumption functional design. The results show that the improved TSW-YOLO-v8n model realized the identification of eight kinds of defects in sawn timber with a high efficiency of 91.10% mAP50 and an average detection 6 ms, which is 5.1% higher than the original model’s mAP50 and 1 ms shorter than the original model’s average detection time. The comparison of the original model and its mainstream algorithms shows that the model of this paper had better performance and better detection capability. Thus, the improved model achieved better overall performance and stronger detection ability, which provides a new idea for the development of detection technology in the forestry industry.
- Researchpp 8458-8472Lee, S.-R., Kang, S. B., and Han, G.-S. (2023). “Reducing particulates and gaseous emissions through fuel switching from coal to wood pellets at power plants in South Korea during 2005 to 2022,” BioResources 18(4), 8458-8472.AbstractArticlePDF
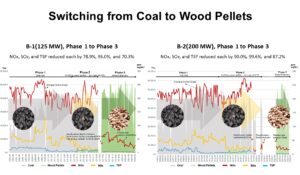
This study analyzed the particulates and gaseous emissions from 2005 to 2022 for power plants in South Korea (Utility scale: 125 MW (B-1) and 200 MW (B-2), respectively), which recently successfully converted from coal to wood pellets. The analysis showed that (1) NOx reduction was 78.9 to 90.0% (with outlet denitrification facility), (2) SOx reduction was 95.0 to 99.6% (without desulfurization facility condition), and (3) total suspended particles (TSP) reduction was 70.3 to 87.2% (with improved filtration and dust collection facility). This research confirmed the capabilities of wood pellets as a baseload power source and demonstrated their superior NOx reduction compared to coal. In the case of SOx, the desulfurization facility was discontinued at the stage of the fuel switch, so the value was affected by exogenous variable factors other than fuel. The TSP appears to be a combination of the ‘fine dust’ contained in the wood pellets and the performance of the filtration dust collector. The results suggest that fuel switching to wood pellets is a viable alternative to fossil fuels as an appropriate climate technology.
- Researchpp 8473-8483Takeyama, K., Yokochi, H., Nishio, S., and Tsuchikawa, S. (2023). “Characteristics of resonance sound in a circular saw enclosure,” BioResources 18(4), 8473-8483.AbstractArticlePDF
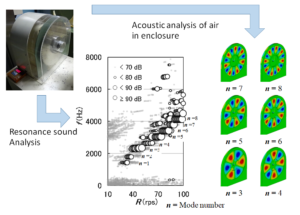
Several studies have been conducted to reduce the idling noise of circular saws because the sound level is extremely high and harms the environment. However, conventional noise suppression technology only controls the vibrations of the circular saw itself, whereas idling noise can be generated when the air inside the enclosure is resonant. In this study, the relationship between the rotational speeds of the circular saw blade and the frequencies of the resonance sound when the circular saw blade is running idle in an enclosure was examined. Additionally, the sound pressure modes and frequencies of the air in the enclosure were analyzed using the finite element method of acoustic analysis. The results showed that resonance sound was generated only when the circular saw blade was enclosed. The frequencies of the resonance sound generated by a circular saw blade made of acrylic plastic were the same as those generated by a steel saw blade. The resonance sound was generated regardless of the outer diameter of the circular saw blade. The peak resonant frequencies formed a step-like line during the analysis in which the rotational speed of the saw blade was steadily increased.
- Researchpp 8484-8502Aydın, M., and Aydın, T. Y. (2023). “Influence of growth ring number and width on elastic constants of poplar,” BioResources 18(4), 8484-8502.AbstractArticlePDF
The objective of this work was to evaluate the effect of growth ring number (specimens including 2, 4, and 6 rings from the bark) and growth ring width on elastic constants in the radial direction of Populus x canadensis, which has not been revealed before. The longitudinal (2.25 MHz) and transverse (1 MHz) ultrasonic waves were propagated to calculate the longitudinal (VRR) and shear (VRL, VLR, VTR, and VRT) wave velocities and used to determine the elasticity modulus (ER), and shear moduli (GRL and GRT). The average growth ring widths of specimens including 2, 4, and 6 rings were 17.0 mm, 17.8 mm, and 18.2 mm, respectively. According to the results, only VRL steadily increased with increased ring number, while other velocities fluctuated. The same fluctuations were observed for moduli except for GLR, which constantly increased with ring number. The influence of ring number on velocity was statistically significant only for VRL and VRT. However, all moduli were significantly affected by ring number. Linear regression statistics revealed that there were significant relations between the ring width and density, VRL, VLR, VRT, GRL, and GRT.
- Researchpp 8503-8514Kasdi, S. A., Lee, S. H., Tahir, P. M., S. S. O., al-Edrus, Salim, S., Ghani, M. A. A., Bakar, B. F. A., Lum, W. C., and Zhang, J. (2023). “Characterization of the properties of Buluh Madu (Gigantochloa albociliata),” BioResources 18(4), 8503-8514.AbstractArticlePDF
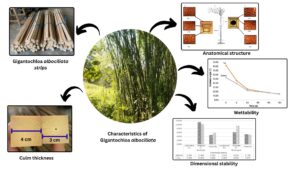
Thirteen bamboo species are reported to be in commercial use in Malaysia. However, Buluh madu (Gigantochloa albociliata) did not make to the list. As a species, G. albociliata is cultivated for its delicious bamboo shoot and is demonstrated to possess great potential to produce commercialised products such as laminated bamboo panel. Unlike common bamboo, which has hollow cylindrical culms, G. albociliata has thick culms at the base, with smaller hollow cavities at the top portion. Therefore, it can be easily converted into high-thickness strips, thus improving the processing efficiency of laminated bamboo. To validate this theory, the anatomical, chemical, physical, and mechanical properties of G. albociliata were evaluated. The round bamboo and strips from the top and bottom sections of the bamboo stem were tested. It was found that G. albociliata has a vascular bundle type similar to that of the Gigantochloa genus bamboo. The fibre in G. albociliata is long and strong. The top section of bamboo has longer fibres, a higher density, and a higher specific gravity than the bottom section. As a result, bamboo from the top section has greater bending strength than bamboo from the bottom section. The G. albociliata species was discovered to have high mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and good wettability, making it an ideal material for laminated products.
- Researchpp 8515-8527Conde-Ávila, V., Loera-Corral, O., Díaz, R., and Sánchez, C. (2023). “Cutinolytic esterases are induced by growth of the fungus Trichoderma harzianum on glyceryl monostearate in solid-state fermentation,” BioResources 18(4), 8515-8527.AbstractArticlePDF
Cutinolytic esterase are enzymes utilized in a wide variety of industrial applications, and they are capable of degrading emerging environmental pollutants. Due to the application and importance of these enzymes, it is crucial to develop an efficient method for cutinase production using a cost-effective inductor and an efficient microbial production system. In this work, the growth and cutinolytic esterase production of Trichoderma harzianum were evaluated in glucose-yeast extract media containing different glyceryl monostearate (GMS) concentrations (1, 3, and 5 g/L). It was used as inducer in solid-state fermentation. A medium lacking GMS was used as control. Biomass production and enzyme productivity were higher in inducer-added (1 g/L) medium than in the control medium. T. harzianum produced constitutive and inducible cutinolytic esterase, in which production was enhanced by GMS. In GMS-added cultures, two bands with cutinolytic esterase activity (60 and 150 kDa approximately) were observed by zymography, which were not observed in control culture. GMS represents a promising inducer for cutinolytic esterase production by fungi. This research represents the first approach for the study of cutinolytic esterase production using a synthetic molecule as an inducer.
- Researchpp 8528-8535Campos, P. H. S., Santos Junior, A., de Souza, M. V., Herradon, M. P., Libera, V. B. L., Dezen, L. E., da Silva, E. V., Silva, A. G. B. P., Rodrigues, F. R., Bispo, R. A., Cazella, P. H. S., da Silva, S. A. M., and Christoforo, A. L. (2023). “Evaluation and production of high-strength wood composite panels with polyethylene terephthalate (PET),” BioResources 18(4), 8528-8535.AbstractArticlePDF

To reduce dependence on wood and deforestation, alternative materials have been considered. This research evaluated particleboards panels of Pinus elliotti mixed with residues of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) in flakes with 50% of each material, glued with 10% of castor oil-based polyurethane resin (PUR). The temperature during board production was varied to evaluate its influence on the physical and mechanical properties of the boards. The study concludes that the increase in temperature did not result in a significant improvement in the particleboard properties, but their results showed application potential according to the normative standards.
- Researchpp 8536-8556Liu, X., Ren, X., Dong, J., Wang, B., Gao, J., Wang, R., Yao, J., and Cao, W. (2023). “Preparation and physicochemical properties of biochar from the pyrolysis of pruning waste of typical fruit tree in north China,” BioResources 18(4), 8536-8556.AbstractArticlePDF
Routine maintenance of fruit trees generates a substantial quantity of pruning waste each year. This waste is potential feedstock for producing energy, materials, and other products. The feasibility of making biochar from the waste via pyrolysis was evaluated. The effects of seven tree species, different pruning sites, and temperature on the pyrolysis process, and the physicochemical properties of the biochar were studied. Pyrolysis of different tree species at 500 °C yielded 27.5 to 33.3% biochar, with a high calorific value (approximately 30 MJ/kg), low ash content (approximately 4%), and capturing up to 60% of the carbon element present. Simultaneously, when the temperature was increased from 400 to 700 °C, the yield of biochar decreased from 35.8% to 24.3%, but the properties improved with the higher heating value rising from 29.2 to 31.3 MJ/kg and the iodine value from 234 to 252 mg/g. The biochar has a good pore structure with a specific surface area of 237 m2/g, total pore volume of 0.175 cm3/g, and average pore size of 2.96 nm. In general, biochar from the pyrolysis of fruitwood pruning waste generated here could be an ideal feedstock to produce high-value-added products, such as solid fuels, activated carbon, and electrode materials.
- Researchpp 8557-8572Ayan, S., Yer Çelik, E. N., Gülseven, O., Yer, B. M., and Eskiömer, M. (2023). “Effects of nanoparticle applications on seedling survival and morphological characteristics in Scots pine afforestation,” BioResources 18(4), 8557-8572.AbstractArticlePDF
This study was conducted in the afforestation area, using bare-root 2+0-year-old Scots pine seedlings from Kastamonu. The study aimed to determine the impact of nanoparticle (NP) applications on seedling morphological characteristics and seedling survival success. Three different concentrations (low, medium, high) and four different nanoparticle types [Fe₃O₄, CuO, ZnO, TiO2] were applied to the plant root-dipping method in the study. The effects of NP treatments on seedling height (SH), root collar diameter (RCD), stem fresh weight (SFW), root new weight (RFW), seedling fresh weight (SEFW), root dry weight (RDW), stem dry weight (SDW), seedling dry weight (SEDW), sturdiness quotient (SI), root: shoot ratio (R/S), and seedling survival in the field were evaluated. The study results revealed that NP types significantly affected all seedling variables except RFW, SDW, RDW, and SEDW, and NP doses significantly affected all seedling variables except RFW. The binary interaction effects of NP types and doses had a significant effect on all seedling variables, and higher values were obtained compared to the control treatment. Medium and high NP doses were more effective in seedling growth than low doses; the percentage of seedling survival was 61.4% in the control treatment and 95% in the TiO2-Medium NP treatment combination.
