Volume 18 Issue 4
Latest articles
- Researchpp 7923-7942Keskiväli, L., Seppänen, T., Porri, P., Pääkkönen, E., and Ketoja, J. A. (2023). “Atomic layer deposited TiO2 on a foam-formed cellulose fibre network – Effect on hydrophobicity and physical properties,” BioResources 18(4), 7923-7942.AbstractArticlePDF
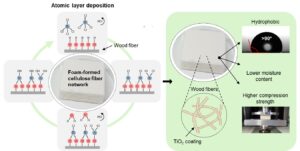
Climate change and plastic pollution challenge us to develop alternatives for fossil-based plastics, and cellulose-based materials are excellent candidates for this. Foam forming technology for cellulose fibre products increases process efficiency, widens the raw materials base, and enables low-density structures from fibres. Low-density cellulose-based materials can be used, for example, for packaging, insulation, and construction materials. However, to achieve optimal performance, the resistance against moisture and mechanical compression ought to be enhanced. In this research, the effect of atomic layer deposited (ALD) titanium dioxide on four foam-formed cellulose-based structures was studied. The hydrophobicity of these materials was analyzed with water contact angle measurements. Moisture content and mechanical properties were tested at high humidity (50% RH and 90% RH) by analyzing moisture uptake and compression strength. Furthermore, the morphology and microstructures were evaluated with scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM and TEM). ALD treatment changed the hydrophilic materials to hydrophobic with 5 cycles of TiO2 for all four substrates. The effect on moisture content was milder but was observed strongest with unrefined and partly refined samples at 50% RH. A clear trend between moisture content and mechanical strength was detected since the compression strength increased with decreasing moisture content.
- Researchpp 7943-7962Pei, P., Guo, L., Zou, R., Liu, C., Deng, X., Liu, L., Wang, X., Liu, J., Yu, M., and Li, S. (2023). “Preparation and optimization of chemically modified corn straw/chitosan/PLA composite using RSM,” BioResources 18(4), 7943-7962.AbstractArticlePDF
In this study, an optimized composite was prepared based on chemically modified corn straw, chitosan, and poly(lactic acid) using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). The composite was produced by screw extruding and hot pressing. The Box Behnken Design (BBD) software was used to design the test to optimize the composite composition. The optimum ratio of 3 factors, e.g. chemically modified corn straw (0.10 to 0.40 g), chitosan (0.25 to 0.75 g), and poly(lactic acid) (2.00 to 3.00 g) on the response value (bending strength) of the composite was investigated. RSM-BBD provided the optimum combination of composites. The novel composite prepared under the optimized factors was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, mechanical testing, water absorption tests, contact angle tests, and scanning electron microscopy. The results showed that the mechanical strength, e.g., bending strength, impact strength, and tensile strength of chemically modified corn straw based composite were 21.6 MPa, 4.43 kJ/m2, and 20.0 MPa, respectively, which increased by 23.5%, 13.9%, and 18.7% compared to native corn straw based composite. Improved mechanical strength and hydrophobicity for chemically modified corn straw/chitosan/poly(lactic acid) demonstrated that chemically modified biomass fibers and bio-based degradable polymers have the potential to produce environmentally friendly composites.
- Researchpp 7963-7980Ji, L., Lei, Y., Han, W., Fu, W., Feng, H., Wang, F., Xiong, C., and Wang. T. (2023). “Cold pressing and hot curing process for assembly of hexagonal pre-shaped bamboo culm sections,” BioResources 18(4), 7963-7980.AbstractArticlePDF
Bamboo is widely used in the construction industry due to its excellent mechanical properties, short production cycle, and environmental concerns. Reconstructing and processing bamboo into biomass-based composite materials that can replace wood alleviates the imbalance between wood supply and demand. This article uses cold press setting and hot press curing molding processes to prepare small samples of Hexagonal Recombinant Bamboo Material (glued HexBam). Through orthogonal analysis, the preparation process parameters, adhesive types, adhesive application amounts, and the relationship between the temperature and time of hot pressing solidification molding and the mechanical properties of glued HexBam were determined. A phenolic adhesive (PF) was used with a dosage of 200 g/m2, a heat setting and molding temperature of 130 °C, and a heat setting molding time of 10 minutes. Under these process conditions, the prepared glued HexBam had a longitudinal compressive strength of 73.8 MPa and a specific strength of 0.0535 N•m/kg, which is superior to ordinary steel.
- Researchpp 7981-7994Dönmez, S., and Önal, F. (2023). “Seed germination ability and biochemical features of two Teucrium taxa (germander) of Lamiaceae,” BioResources 18(4), 7981-7994.AbstractArticlePDF
Teucrium chamaedrys subsp. chamaedrys and Teucrium polium, from the Lamiaceae family, have ornamental, medicinal, and aromatic usage potentials. In this study, seed germination and biochemical features of samples of two taxa grown in natural habitat and cultivated were determined. Seed germination tests were carried out in petri dishes. Phenological and biochemical characteristics were performed on the seedlings and grown in viols obtained from two different origins. While germination rate was between 41% and 46% in T. chamaedrys, it was 33% in T. polium. In T. chamaedrys the seedling raising rate was between 16% and 26%, however, it was determined as 33.3% and 26.7% in T. polium, natural and cultivated plants, respectively. In terms of macro and micro elements, no statistical difference was observed in seedlings of both origins. Germacrene-D was determined with the highest amount in T. chamaedrys as 41.1% in natural plants seedlings and 40.46% in the cultivated ones. Moreover, β-myrcene in T. polium was found to be the major component in both seedlings as 20.2% and 23.4%, respectively.
- Researchpp 7995-8006Wang, C., Zhang, C-y., Ding, K.-q., and Jiang, M.-h. (2023). “Immersion polishing post-treatment of PLA 3D printed formed parts on its surface and mechanical performance,” BioResources 18(4), 7995-8006.AbstractArticlePDF
Steps were taken to improve the surface and mechanical performance of PLA 3D printed formed parts, reduce the “step texture” produced by the fused deposition process, and improve the quality of 3D printing by means of post-treatment. The PLA 3D formed parts were immersion polished with chloroform solution to investigate the effects of immersion polishing on the surface roughness, surface gloss, mechanical properties, and other factors of PLA formed parts. The results of the pre-experiment showed that 90% of the effect was due to the optimal concentration value of chloroform solution and 10% was the optimization of time for immersion polishing. Under the pre-experimental conditions, the surface roughness of the formed parts was reduced by 87%, and the surface gloss was increased by 510%, the surface quality and gloss were significantly improved, and the “step texture” was significantly reduced; meanwhile, the tensile and compressive ultimate strength of the formed parts were increased by 9.41% and 13.09%, respectively, and the mechanical performance were improved, and the quality of 3D printing post-treatment was significantly improved.
- Researchpp 8007-8019Uyup, M. K. A., Zhang, J., Feng, X., Chen, Z., Li, Z., and Siam, N. A. (2023). “Effect of tree age on the properties of Himalayan birch (Betula alnoides Buch.-H.ex D.Don) wood,” BioResources 18(4), 8007-8019.AbstractArticlePDF
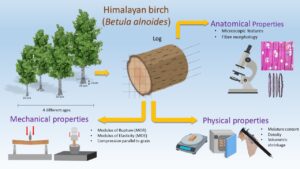
The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of four different age groups on wood properties, i.e., anatomical, physical, and mechanical, of Himalayan birch (Betula alnoides Buch.-H.ex D.Don). The correlation between the properties was also discussed. The results indicated age influences the anatomical, physical, and mechanical properties of Himalayan birch. Results were comparable with other plantation species. Moreover, mechanical properties were highly correlated with the fibre morphology in Himalayan birch. Results from this present study indicate that the 15-, 20-, and 25-year-old Himalayan birch are suitable to be used for parquet, furniture, and other products. Generally, plantation-grown Himalayan birch has the potential to be a raw material to fulfill the demand for the timber industry.
- Researchpp 8020-8036Erdem, R. (2023). “Changes in strontium levels in bark and over the past 40 years in the wood of trees exposed to high levels of air pollution,” BioResources 18(4), 8020-8036.AbstractArticlePDF
The present study aims to identify the most suitable tree species for monitoring and reducing strontium (Sr) pollution. Strontium is a heavy metal that is extremely harmful to human and environmental health even at low concentrations and is listed as a priority pollutant by the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry due to its potential harm. Samples were taken from Pinus pinaster, Cupressus arizonica, Picea orientalis, Cedrus atlantica, and Pseudotsuga menziesii species grown in Düzce, a location reported as one of the top 5 cities having the most polluted air in Europe by the World Air Pollution Report. The changes in Sr concentration over the last 40 years were evaluated by species, organ, direction, and age range. The results indicate that Sr pollution significantly increased due to traffic sources. This study also showed that the transfer of Sr within the wood is limited in all the species under consideration; hence, all these species can be used in monitoring the changes in Sr pollution. The most suitable species for reducing Sr pollution were Cupressus arizonica and Picea orientalis, which have the highest capacity to accumulate the most Sr in their wood.
- Researchpp 8037-8061Alghonaim, M. I., Alsalamah, S. A., Alsolami, A., and Abdel Ghany, T. M. (2023). “Characterization and efficiency of Ganoderma lucidum biomass as an antimicrobial and anticancer agent,” BioResources 18(4), 8037-8061.AbstractArticlePDF
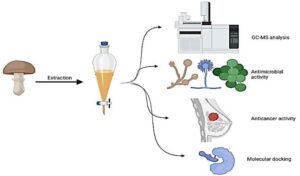
The microconstituents of Ganoderma lucidum biomass (GLB) were evaluated, along with its antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis, 12-octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z)- and n-hexadecanoic acid with area% values of 21.0% and 11.0% were recognized in GLB. Uncooked biomass (UCB) and microwave-cooked (CE) biomass of G. lucidum caused a significant inhibition of human breast cancer (MCF-7) cell line proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. The inhibition of MCF-7 cell proliferation was 27.22 ± 1.64% using 16 µg/mL of CB while it was 52.29 ± 1.09% using 16 µg/mL of UCB. The cytotoxicity test recorded low IC50 (25.63 ± 0.52 µg/mL) of UCE compared to the IC50 value (49.99 ± 0.94 µg/mL) of CB. Highest antimicrobial activities were recorded via using UCE, compared to CE against Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Candida albicans, and Aspergillus niger. The 9,12-octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z)- and n-hexadecanoic acid were able to induce both anticancer and antibiotic-resistant properties. A key therapeutic target enzyme for evolving this resistant pathogenic activity on MCF-7 and K. pneumonia, was accessed thoroughly in silico study. The compounds described, therefore, might provide a great potential for the development of new therapeutics such as anticancer and antimicrobial agents.
- Researchpp 8062-8075Daeepour, Z., Lashgari, A., Roohnia, M., Jahan-Latibari, A., and Safdari, V. (2023). “Pine wood extraction by fermentation to improve its acoustical efficiency,” BioResources 18(4), 8062-8075.AbstractArticlePDF
Wood is a main material in the construction of musical instruments and speaker boxes, especially in developed countries. This study investigated the changes in acoustic properties of pine wood during the processes of fermentation, water washing, and organic washing solvent. The results indicated that both methods of water washing and ethanol-acetone mixture washing of the samples improved the values of density, modulus of elasticity, elastic stiffness, acoustic coefficient, vibration damping, and acoustic conversion efficiency. The effect of ethanol-acetone mixture washing was greater than water washing the samples. Additionally, results revealed that pretreatment before ethanol-acetone mixture washing had the most effect on vibration damping and acoustic conversion efficiency values. In general, the values obtained from ethanol-acetone mixture washing resulted in more improvement in acoustic properties compared to water washing, but the results showed that the pretreatment before water washing had a greater effect on the values of density, modulus of elasticity, elastic stiffness, and acoustic coefficient.
- Researchpp 8076-8089Beram, A. (2023). “Improved performance of Brutian pine wood via impregnation with nanoclay,” BioResources 18(4), 8076-8089.AbstractArticlePDF
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of Brutian pine (Pinus brutia Ten.) wood impregnation with nanoclay in different concentrations on the chemical and thermal changes, and their impact on the physical and mechanical properties. The samples were impregnated with nanoclay in concentrations of 1%, 3%, and 5%, for 2, 24, and 48 h. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis revealed a shift in the typical peaks of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin depending on the impregnation time and nanoclay ratio. Thermogravimetric analysis and the limiting oxygen index indicated that the samples impregnated with clay solutions exhibited higher thermal stability than the unimpregnated wood. Impregnation with nanoclay caused a decrease water absorption and thickness swelling of the sample groups. The modulus of elasticity, modulus of rupture, and compression strength strength values of samples were improved via impregnation. In conclusion, the applied nanoclay are suitable substances to increase the durability and thermal stability of Brutian pine wood.
