Volume 19 Issue 1
Latest articles
- Researchpp 405-415Suhaya, Y., Sumardi, I., Alamsyah, E. M., Sutrisno, and Hidayat, Y. (2024). “Environment’s effect on wood characteristics of white jabon grown in West Java and Banten area, Indonesia,” BioResources 19(1), 405-415.AbstractArticlePDF
This study analyzed the diversity of physical properties and mechanical properties of white jabon (Neolamarckia cadamba (Roxb.) Bosser) from various locations and ecological conditions in West Java and Banten Indonesia. White jabon wood samples were taken from 8 locations in West Java and the Banten region. Tree ages ranged from 5 to 6 years. This wood was then tested to compare physical characteristics (density or specific gravity) and mechanical characteristics (modulus of rupture (MOR) and modulus of elasticity (MOE)). The results showed that wood density ranged from 0.29 to 0.43 g.cm-3, MOR ranged from 361 to 641 kg.cm-2, and MOE ranged from 31,117 to 58,910 kg.cm-2. The highest density average (0.43 ± 0.004 g.cm-3) was produced from Cianjur, and the lowest density average (0.29 ± 0.010 g.cm-3) was from Tanjungsari Sumedang. Environmental factors (precipitation and altitude) affect the density of wood. Separately, rainfall has a low effect and a negative relationship to jabon wood density, while altitude has a high influence and a negative relationship to jabon wood density. Andosol soil types tend to produce low density wood.
- Researchpp 416-433Li, H., Zhang, W., Zhang, Y., Zhai, F., and Chen, F. (2024). “Thermal bridging and its mitigation in bamboo panel construction with steel frameworks and mineral wool insulation,” BioResources 19(1), 416-433.AbstractArticlePDF
An energy-efficient and environmentally conscious bamboo-constructed residential structure was created, comprising bamboo composite panels, steel framework, and mineral wool insulation. To ascertain the efficacy of this particular type of wall in enhancing thermal capabilities, the finite element method was employed to analyze the factors influencing the thermal performance of the exterior wall panels, insulation layer, framework, and interior wall panels. A more judicious design and implementation strategy, known as the 3# and 8# combination scheme, was evaluated in practical applications to assess the thermal efficiency of the wall system. The findings indicated that augmenting the thickness of the inner and outer wall panels and insulation layer, reducing the framework thickness, and incorporating wooden framework as a substitute for steel framework within a certain range enhanced the thermal capabilities of bamboo-constructed walls and mitigated the adverse effects of thermal bridges. The thermal performance of the residences employing the newly developed bamboo-constructed walls surpassed that of conventional iron container houses, thereby warranting broader adoption and application in practical projects. These outcomes offer valuable insights for the optimized design of thermal performance in bamboo-constructed walls.
- Researchpp 434-455Miao, Y., Xie, X., Qi, W., and Xu, W. (2024). “Design of kindergarten toy lockers,” BioResources 19(1), 434-455.AbstractArticlePDF
In this work, kindergarten toy storage, defined as the construction area, puzzle area, scientific observation area, and role-playing area, and the toy characteristics of the four areas, was studied. Interviews and grounded theory were used to observe and summarize the behavioral needs of 3- to 6-year-old children and preschool teachers. Analytical hierarchy process (AHP) was used to analyze behavioral needs. It was concluded that the kindergarten toy locker optimization was designed to improve storage efficiency. However, the current layout of kindergarten toy lockers is chaotic, and children cannot efficiently and autonomously take toys from toy lockers. The best toy locker layout scheme was selected through an eye tracking experiment. The subjects were all 3- to 6-year-old children, a total of 30 people. By comparing the data such as hot spot map, trajectory map, area of the first viewpoint, and gaze time when children observed different lockers layout during the experiment, the optimal layout scheme of kindergarten toy lockers was comprehensively analyzed. Optimizing the zoning, classification, and storage of kindergarten toys is conducive to improving the efficiency of children’s independent storage, creating a kindergarten game and teaching environment conducive to children’s development.
- Researchpp 456-477Elan Solan, T. D., Mahmad Rozi, S. K., Md Saleh, N., Mohamad, S., Ishak, A. R., Rahim, N. Y., and Elan Solan, M. D. (2024). “Surface functionalization of magnetite nanoparticles for remediation enhancement of phenol from aqueous solutions,” BioResources 19(1), 456-477.AbstractArticlePDF
Phenol is a toxic pollutant generated by industries. It can diminish the supply of clean water and is hazardous to human health. Hence, an effective abatement method is important to remove phenol from water sources. The following amine-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles, ethylenediamine (EDA), diethylenetriamine (DETA), triethylenetetramine (TETA), tetraethylenepentamine (TEPA), and polyethylenehexamine (PEHA), were used to study the adsorption performances of phenol from the prepared samples. The morphological study revealed long rod shapes with rough and sharp edges, while the elemental analysis presented the addition of two elements, C and N atoms. In addition, the TETA@MNP possessed weaker magnetism compared to MNPs, showing that the surface functionalization of MNPs was successful. TETA@MNP showed the highest percentage for phenol removal compared to others. The TETA@MNP achieved a removal efficiency of 99.2% at optimum conditions of 60 mg dosage, contact time of 25 min, and pH of 7. TETA@MNP obeyed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and the Freundlich isotherm model, with coefficients of determination (R2) of 0.9765 and 0.9682, respectively. The reusability study has demonstrated that TETA@MNP can be reused approximately 6 times with extremely minor loss. Therefore, TETA@MNP is a good adsorbent for the adsorption of phenol from prepared sample solutions.
- Researchpp 478-499Huan, J., Chu, T., Guo, X., Sun, Z., Zhou, X., Wang, W., and Yang, Y. (2024). “Experimental study on seismic performance of Chinese traditional mortise and tenon joints with different lengths that tenons pull out of mortise,” BioResources 19(1), 478-499.AbstractArticlePDF
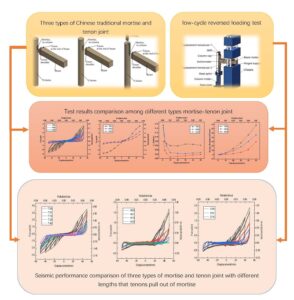
This paper presents the results of a study on seismic performance of mortise-tenon joints with different lengths that tenons pull out of joints. Three 1:3.52 scaled mortise-tenon joint specimens were fabricated: one with through-tenon joints, one with half-tenon joints, and one with dovetail joints. Seismic data of the joints, such as hysteretic curves, skeleton curves, stiffness degradation rules, and energy dissipation capacity curves, were obtained by low-cycle reversed loading test. The influence of lengths that tenons pull out of joints on the mortise-tenon joints was analyzed. The seismic performance of three types of mortise-tenon joints was compared. The results showed that all hysteretic loops are z shaped. The seismic performance of the through joint was the best among three types of mortise tenon joint. The length that the tenon pulls out of the joint significantly affected the performance of the mortise and tenon joints.
- Researchpp 500-509Wang, C., Yu, J., Jiang, M., and Li, J. (2024). “Effect of slicing parameters on the light transmittance of 3D-printed polyethylene terephthalate glycol products,” BioResources 19(1), 500-509.AbstractArticlePDF
To manufacture 3D-printed polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) products with excellent light transmittance performance, this study evaluated the principle of light transmission and the influencing factors of fused deposition methods (FDM) 3D-printed PETG products. This study explored the influence of different slicing parameters (layer height, extrusion rate, and printing speed) on the light transmittance of PETG products via a UV-visible spectrophotometer. The results showed that, in the range of 0.1 to 0.3 mm, the PETG specimens with 0.2 mm layer height had the best light transmittance performance; in the range of 100% to 120%; the PETG specimens with 110% extrusion rate had the best light transmittance performance; in the range of 20 to 40 mm/s printing speed, the PETG specimens with 40 mm/s printing speed had the best light transmittance performance. Comparison of image visibility showed that PETG products with layer height of 0.2 mm, extrusion rate of 110%, and printing speed of 40 mm/s had the best image visibility.
- Researchpp 510-524Kim, J. H., Purusatama, B. D., Savero, A. M., Prasetia, D., Jang, J. H., Park, S. Y., Lee, S. H., and Kim, N. H. (2024). “Convolutional neural network performance and the factors affecting performance for classification of seven Quercus species using sclereid characteristics in the bark,” BioResources 19(1), 510-524.AbstractArticlePDF
Based on the sclereids in the bark of oak species, a convolutional neural network (CNN) was employed to validate species classification performance and its influencing factors. Three optimizers including stochastic gradient descent (SGD), adaptive moment estimation (Adam), root mean square propagation (RMSProp), and dataset augmentation were adopted. The accuracy and loss stabilized at approximately 15 to 20 and 70 to 80 epochs for the augmented and non-augmented condition, respectively. In the last five epochs, the RMSProp-augmented condition achieved the highest accuracy of 89.8%, whereas the Adam-augmented condition achieved the lowest accuracy of 73.8%. Regarding the loss, SGD-non-augmented condition was the lowest at 0.498, whereas Adam-augmented condition was the highest at 2.740. The highest accuracy was influenced by RMSProp at 0.194. Dataset augmentation had a significant influence on accuracy at 0.456. Homogeneous subsets among the validation conditions indicated that the accuracy and loss were classified into the same subset using an augmented dataset during the training, regardless of the optimizer. Only Adam and RMSProp with non-augmented datasets were categorized into the same subset during the test. Hence, species classification using CNN and sclereid characteristics in the bark was feasible, and RMSProp with augmented datasets showed optimal performance for species classification.
- Researchpp 525-538Zheng, G., Wang, S., and Bohoussou, N. Y. (2024). “The impact of Fe2+ and Na+ concentrations on hydrogen production with three different fermenter bacteria,” BioResources 19(1), 525-538.AbstractArticlePDF
Batch experiments were conducted to investigate the effects of Fe2+ and Na+ on the hydrogen (H2) production performance from three different metabolic type hydrogen-producing bacterial strains. The appropriate amount of Fe2+ significantly promoted the H2 production of all three hydrogen-producing bacteria. The combination of H2 production and liquid products showed that Fe2+ was more suitable for the H2 production and metabolism of E. harbinense ZGX4. When the Fe2+ concentration was 0.05 g/L, the H2 production and liquid products concentrations were 2170 mL/L-medium and 6530 mg/L, respectively. Na+ enhanced the H2 production of E. harbinense ZGX4 and C. butyricum 1.209 but inhibited the H2 production of E. cloacae 1.2022. Na+ made C. butyricum 1.209 exhibit the best H2 production and metabolic performance when the Na+ concentration was 2 g/L, while the H2 production, and liquid products concentration were 2460 mL/L-medium and 5350 mg/L, respectively. At the end of the experiment, it was found that the addition of Fe2+ could change the type of fermentation in C. butyricum 1.209. Therefore, further exploration of the effects of other metal ions on model hydrogen-producing strains has great potential for achieving high hydrogen production rates, among other things.
- Researchpp 539-551Tu, W.-L., Hsiung, Y.-C., Liang, C-H., Huang, J.-M., Ou, C.-M., and Guo, G.-L. (2024). “Polyhydroxyalkanoate production from food packaging waste paper,” BioResources 19(1), 539-551.AbstractArticlePDF
This study evaluated the production of marine biodegradable plastics, specifically polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), using waste paper from food containers as a novel material source. The results showed that adding dilute sulfuric acid as a pretreatment may have a negative impact on enzyme hydrolysis efficiency. Without pretreatment, the highest glucose concentration was observed in the 50-min heating group. In the experimental group with 1% dilute sulfuric acid as a pretreatment, the highest average glucose concentration was observed in the 25-min treatment group. In flask scale experiments, the C/N ratio was controlled at 10, 20, and 30. The results showed that when the C/N ratio was 10, the PHA/CDM ratios were 16.3 and 23.6 at 48 and 72 h, respectively. After 96 h of cultivation using hydrolysis liquid from the waste paper container as the sole carbon source in a 5-L scale experiment, the PHA/CDM ratio was 28.7 and the PHA concentration was 0.95 g/L. The potential bacterial strain in this study was confirmed to be a Bacillus genus bacterium after strain identification. The signal peaks indicated that the PHA obtained from the Bacillus sp. production process was PHB.
- Researchpp 552-567Lu, Y. (2024). “Agricultural products supply chain risk assessment model construction and application in IOT environment,” BioResources 19(1), 552-567.AbstractArticlePDF
This paper constructs the operation model of agricultural products supply chain under an IoT (Internet of Things) environment, based on which the HHM (Hodrick-Prescott Filter) model is used to identify the risk. The ISM (Internal Supply Management) model was used to analyze risk factors. A risk index system was constructed, which was divided into three primary indexes and 18 secondary indexes. The backpropagation (BP) neural network approach was used to establish the risk assessment model. The sample data from 2017 to 2020 was employed as the test sample to test the network assessment model. There was a very small error in the risk level assessment and training results. The results showed that the risk level assessment model was highly operable and can have practical value for effective assessment of the risk level.
