Volume 19 Issue 1
Latest articles
- Researchpp 568-581López-Salazar, H., Camacho-Díaz, B. H., Arenas Ocampo, M. L., Campos-Mendiola, R., Martínez-Velarde, R., López-Bonilla, A., and Jiménez-Aparicio, A. R. (2024). “Microwave-assisted extraction of β-Sitosterol: A by-product from Agave angustifolia Haw bagasse,” BioResources 19(1), 568-581.AbstractArticlePDF
β-sitosterol (BSS) and β-sitosterol glucoside (BSSG) were extracted from Agave angustifolia Haw bagasse using microwave-assisted extraction (MAE). The quantification and characterization of BSS and BSSG were performed through high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS), and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). With an extraction time of 9 seconds using MAE, a higher amount of BSS (103.6 mg of β-sitosterol per gram of dry weight of extract) was obtained compared to BSSG (61.6 mg of β-sitosterol glucoside per gram of dry weight of extract). MAE emerges as a promising method for the efficient recovery of β-sitosterol (BSS) and β-sitosterol glucoside (BSSG) from A. angustifolia bagasse. This enriches scientific knowledge regarding phytochemical extraction and holds great potential for various industries, such as pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals. Additionally, by valorizing the by-products of the agave industry, this research contributes to the sustainable utilization of resources, aligning with the principles of green and circular economy practices.
- Researchpp 582-594Altun, B. (2024). “Possibilities of using organic wastes as a growing medium in soilless culture for cut flower rose,” BioResources 19(1), 582-594.AbstractArticlePDF
The possibilities of using organic wastes, such as hazelnut shells (HS), walnut shells (WS), hazelnut skins (HzS), and spent mushroom compost (SMC), as growth medium in cut flower rose cultivation in soilless substrate culture were investigated. The parameters, such as the date of cutting the flower (day), flower stem length (cm), flower stem diameter (mm), flower length (cm), flower diameter (cm), flower color, color of the top and bottom of the leaf, and yield (piece), were examined. In addition, samples taken from the growth medium at the beginning and ending stages of the experiment were analyzed. The first flowers were cut from the HzS +P medium 38 days after planting. The highest yield value (20.6 flower/plant) was obtained from SMC medium. The longest flowers (63.89 ± 0.947 cm) and the thickest stem flowers (5.86 ± 0.136 mm) were cut from the control medium. It was determined that the media also affected the flower and leaf colors. According to the results obtained, SMC and HzS+perlite mediums can be recommended as an alternative to cocopeat in the production of cut roses in soilless substrate culture.
- Researchpp 595-604Pradhan, S., Entsminger, E., Mohammadabadi, M., Seale, D., and Ragon, K. (2024). “Evaluation of rice husk composite boards prepared using different adhesives and processing methods,” BioResources 19(1), 595-604.AbstractArticlePDF
Rice husks, a byproduct of rice milling, were used to develop composite boards. Different processing methods, grinding, and treating with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), were adopted to improve the bonding and mechanical performance. NaOH solution was prepared at 5% (wt/v) concentration. The effect of different adhesives, phenol formaldehyde (PF), and polymeric diphenylmethane diisocyanate (pMDI), was evaluated. Rice husks mixed with resin were hot pressed to the target density of 768 kg/m3 and thickness of 12.7 mm. Specimens cut from these flat panels were submitted to bending, internal bond, water absorption, and thickness swelling tests. Results revealed that chemical treatment with NaOH significantly improved fiber-to-fiber bonding of rice husks. Internal bond strength of specimens made from chemically treated rice husks increased at least 1000% compared to others. Considering the mechanical properties and water uptake, rice husk boards fabricated with unprocessed rice husks and pMDI showed a better performance.
- Researchpp 605-619Ibrahim, M. I., Bakhori, N. M., Mohd Nor, A. F., Mohammad, R., Aziz, S. A., Md Daud, M. Y., Kuan, H. T. N., Mahardika, M., and Hassan, M. Z. (2024). “Central composite design for optimization of kenaf-reinforced epoxy composite bonding performance,” BioResources 19(1), 605-619.AbstractArticlePDF
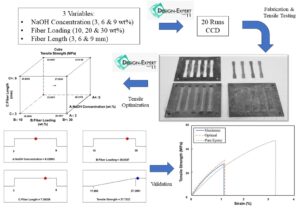
Kenaf fiber is gaining prominence because of its ability as a natural-based reinforced material in advanced composites. However, kenaf contains a hygroscopic natural waxy substance that covers the fiber layer, providing a low surface tension and preventing strong bonding with the polymer matrix. The goal of this study is to optimize the blending parameters of kenaf fiber-reinforced epoxy composites by alkali treatment concentration, length, and fiber-matrix loading using central composite design. The maximum tensile strength was obtained at 6.03 wt% of NaOH concentration, fiber loading of 26.02 wt%, and fiber length at 7.39 mm, which showed a strong correlation between experimental and predicted values. The analysis of variance function model indicated that fiber length, sodium hydroxide concentration, and fiber loading all play important roles in mechanical properties of composites. Based on the fracture surface observations, kenaf fiber composite strength was closely related to bonding at fiber-matrix interfaces. The most common failure modes in the samples were voids, matrix fracture, fiber breakage, weak bonding, and fiber pull-out.
- Researchpp 620-634Teangtam, S., Yingprasert, W., and Somboon, P. (2024). “Production of micro-lignocellulosic fibril rubber composites and their application in coated layers of building materials,” BioResources 19(1), 620-634.AbstractArticlePDF

Novel composite materials were made by combining micro-lignocellulosic fibrils and natural rubber applied as spray coated layers for building materials. The micro-lignocellulosic fibrils were produced based on the mechanical pulping process with jute bast as the raw material. The obtained micro-lignocellulosic fibrils had a good content of water-suspended materials with fibril widths of about 0.1 to 1.0 µm and fibril length of about 100 to 150 µm. The composites were produced using natural rubber mixed with the micro-lignocellulosic fibrils at 0, 5, and 10 parts per hundred of rubber, vulcanizing sulfur, and activated zinc oxide. The fibril-rubber suspension was formed in the composite sheets with a thickness of 0.5 to 1.5 mm using a spray coating technique and was oven-dried at 100 °C. The rubber composite had a homogenous fibril distribution in the rubber composite matrix, with good bonding between the fibrils and the rubber polymers. The fibrils contributed to the strength reinforcement of the rubber composite layers. The application of the micro-lignocellulosic fibril rubber composites coated onto industrial fiber cement boards enhanced the thermal insulation properties, which had a lower degree of thermal conductivity and heat diffusivity and enhanced the toughness and waterproofing of the fiber cement boards.
- Researchpp 635-655Jevtović, D., Zivković, P., Milivojević, A., Bezbradica, D., and Van Der Auwera, L. (2024), “Reduction of fines in recycled paper white water via cellulase enzymes,” BioResources 19(1), 635-655.AbstractArticlePDF
Due to the high wastepaper recyclability and water-loop system closure, packaging paper mills struggle with increased fines, causing runnability issues. Cellulase enzymes are a preferred treatment choice for the improvement of the pulp refining in stock preparation area but are not widely used or easy to introduce in the production process. Different cellulase enzymes were tested, and those with the highest activity were introduced to the white-water (WW) samples with the aim to reduce fines content as potentially new enzyme applications on the paper machine. The first portion of the study involved the development of an experiment model to find and confirm the optimal enzyme process parameters (40 °C, pH 5.7, reaction time 3 h, and 0.18% v/v enzyme addition) for laboratory made white-water. The second portion of the study included turbidity, colloidal charge, flow cytometry (FCM), and chemical oxygen demand (COD) analysis on industrial and laboratory made white-water samples at optimized process parameters. Obtained results corresponded to reduced fines content in white-water samples, which justified commercial usage of cellulase enzymes on recycled paper machine short loop and potentially increased machine runnability without negative influence on wastewater treatment plant.
- Researchpp 656-669Suchta, A., Barański, J., Vilkovská, T., Klement, I., and Vilkovský, P. (2024). “The impact of drying conditions on the surface color changes of pine wood,” BioResources 19(1), 656-669.AbstractArticlePDF
The article presents the impact of drying process and selected parameters on the color changes on the surface of pine wood (Pinus sylvestris L.). Three predetermined process conditions (modes), mild, normal, and intensive, were investigated. The experiments were conducted using a semi-industrial scale dryer designed at the Gdańsk University of Technology with a loading capacity of 0.55 m3. The drying process was applied to pine wood grown in the northern part of Pomeranian region in Poland. The specimens were selected taking into consideration the radial angle of the growth rings. During each drying mode, 25 pieces of wood with dimensions (thickness, width, length) of 0.03 m, 0.2 m, and 1.5 m, respectively, were dried. The total color change (ΔE) after drying process and color saturation (h*) before and after drying processes of the wood surface was determined using the normalized CIELAB methods. The obtained results indicated that the color change of the pine wood surface increased simultaneously with the intensification of the drying process. However, the normalized wood quality after drying under intensive drying process conditions remained within the standard limits. The application of intensive drying process conditions remarkably changes the surface color of the obtained material, while remarkably reducing the drying process duration.
- Researchpp 670-682Li, D., Yu, L., Li, L., Liang, J., Wu, Z., Yang, G., Yin, S., and Gong, F. (2024). “Comparison of nail-holding performance of Pinus massoniana and Cunninghamia lanceolata dimension lumber based on round steel nails,” BioResources 19(1), 670-682.AbstractArticlePDF
In this study, the influence of the diameter of round steel nails, the guiding bores, and the wood sections on the nail holding performance of Pinus massoniana and Cunninghamia lanceolata dimension lumber was explored. The results showed that the nail-holding power of round steel nails mainly came from their friction with wood fibers, while the radial and tangential sections were also affected by the shearing action of wood fibers. The tangential section reached the largest nail-holding power, followed by the radial section and cross section. Greater wood density was associated with higher nail holding power. Under a large nail diameter, however, high-density wood was prone to plastic cracking, which influenced the nail holding power greatly. Prefabricated guiding bores could prevent plastic cracking in wood to some extent and improve the nail holding power of Pinus massoniana and Cunninghamia lanceolata dimension lumber when diameter of round steel nails was more than 3.0 mm. For Cunninghamia lanceolata characterized by low density and rigidity, the wood fiber was in close contact with the round steel nail and internal cracking could not be easily generated under a large diameter of round steel nails.
- Researchpp 670-682Ghorbani, M., Khalilian, A. M., Dastoorian, F., and Shahmirzadi, A. N. (2024). “Potential of walnut shell flour as a binder in briquette production from industrial and garden wastes,” BioResources 19(1), 670-682.AbstractArticlePDF
Briquettes as a product of biomass compaction is considered a renewable product for replacing fossil fuels. Briquettes can be produced from several sources using the development of technology. In this study, the effect of walnut shells as an organic binder on the properties of biofuel briquettes made of industrial and garden wastes was investigated. Cylindrical briquettes from walnut shell flour with weight ratios of 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, and 25% were prepared from industrial sawdust and ground garden residue with a weight ratio of 50/50. Briquettes were compacted under a temperature of 170 °C and pressure of 150 kg/cm2 for 30 s. Results indicated that the chemical analyses of compounds, compaction ratio, and density of the briquettes containing different proportions of walnut shells were not significantly different. The lowest fixed carbon was measured for briquettes containing 5% of walnut shell, and increasing the ratio of walnut shell significantly increased the compressive strength of the resulting briquette.
- Researchpp 695-715Tenorio, C., Moya, R., Murillo, O., and Loría, J. (2024). “Energy production and its characteristics from four tropical trees species planted in short rotation woody systems in Costa Rica,” BioResources 19(1), 695-715.AbstractArticlePDF

Short-rotation crop (SRC) systems with woody species have been planted in Costa Rica. However, information about different tree species and spacing is limited. The objective of the present study was to examine biomass production and the physical, energy, and chemical properties of feedstock of four tropical tree species (Cordia alliodora, Dipteryx panamensis, Gmelina arborea, and Tectona grandis) in 34-month-old plants planted at four spacings (0.5×1.0 m, 1.0×1.0 m, 1.0×2.0 m, and 2.0×2.0 m). The highest mortality rate (50%) was found in G. arborea; however, diameter, height, basal area, and biomass production in G. arborea plantations were higher than T. grandis, C. alliodora, and D. panamensis. Spacing effects on diameter, height, basal area, and biomass production were observed in 10-month-olds. Wide spacing presented the highest values in diameter and height, but the highest biomass production was found in the narrow spacing. Also, biomass distribution was different in D. panamensis in relation to other species. Specify gravity, density, and moisture content of biomass showed high variation between species and spacing, but the energy and chemical properties of biomass showed few differences. These results suggest that these four species were uniform in terms of their energy and chemical properties, regardless of the spacing used. Finally, three species (G. arborea, C. alliodora, and T. grandis) presented important potential for use in SRC systems. G. arborea was the species with the highest production but a high mortality rate.
