Volume 19 Issue 1
Latest articles
- Researchpp 716-731Wan, Z., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Fang, X., and Gong, M. (2024). “Study on bearing capacity of LVL asymmetric truss of lightweight poplar wood,” BioResources 19(1), 716-731.AbstractArticlePDF
Compared with natural wood, laminated veneer lumber has the characteristics of high strength, flexible specifications, excellent stability, and good economy. In order to study the bearing capacity of LVL trusses, the mechanical properties of LVL materials were tested. The static load test was carried out by using 3 pieces of LVL truss, and the load-deflection relationship, load-strain relationship, bearing capacity and failure mode of LVL trusses were studied. Based on the simplified joint analysis method, the metal plate connection and bolted truss were analyzed, and the bearing capacity calculation formula was developed. The results show that the upper chord instability is the main failure mode for large-span light LVL truss. A simplified formula for bearing capacity of LVL truss was proposed, and the predicted results were in good agreement with the experimental results. Finally, an application example of LVL truss engineering design and construction is briefly introduced. The research can provide technical support for the promotion and application of LVL truss of lightweight poplar wood.
- Researchpp 732-750Sugahara, E. S., Dias, A. M. A., Botelho, E. C., Dias, A. M. P. G., and de Campos, C. I. (2024). “Environmental evaluation of experimental heat-treated oriented strand board,” BioResources 19(1), 732-750.AbstractArticlePDF
The use of wood-based panels such as Oriented Strand Board has grown in civil construction. This follows the contemporary trend towards low environmental impact materials. However, there is a lack of relevant information about their life cycle assessment, appearing as a current and relevant research topic. Experimental panels made with Eucalyptus wood and castor oil-based polyurethane adhesive already demonstrated great physical-mechanical performance. Therefore, this study aimed to continue the evaluation of this innovative product, estimating their potential environmental impacts using life cycle assessment from a cradle-to-gate perspective and comparing the results with traditional panels and literature data. System boundaries, environmental impacts and environmental hotspots were identified using the ReCiPe H method in terms of ten impact categories. Comparing experimental (heat-treated) and traditional panels, the experimental versions performed better in most categories and showed safer behavior in categories related to human health in addition to not using paraffin, termiticide, and other organic chemicals presented in the traditional panels. Though made of different types of adhesives, the adhesive was the main environmental hotspot for both types.
- Researchpp 751-765Hosseinihashemi, S. K., Hosseinashrafi, S. K., Kelkian, M., Shafighi, Z., and Barbosa, L. C. A. (2024). “Chemical composition and content of essential oil from cultivated bald cypress (Taxodium distichum L.),” BioResources 19(1), 751-765.AbstractArticlePDF
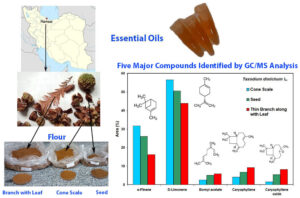
The essential oils extracted from the cone scale (CS), seed (SE), and thin branch with leaf (BL) of Taxodium distichum harvested during the winter season were analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Up to 37 components were identified, accounting for more than 96% of the total oil volume in all samples. Monoterpenes (CS 93.4%, SE 85.2%, and BL 72.8%) represented the major constituents of the essential oils, followed by smaller quantities of sesquiterpenoids. Monoterpene hydrocarbons (MH) dominated, with limonene (CS 56.5%, SE 50.5%, and BL 43.8%) and α-pinene (CS 31.7%, SE 26.1%, and BL 16.2%) being the main constituents. Representative minor constituents in the CS oil are camphene (1.3%) and bornyl acetate (2.6%); in the SE oil, β-myrcene (1.7%) and bornyl acetate (5.1%) were found; and in BL essential oil, β-myrcene (3.1%) and bornyl acetate (6%). Sesquiterpene hydrocarbons (CS 4.6%, SE 7.8%, and BL 12.9%) were the other major subclasses of components, with caryophyllene (CS 4.1%, SE 6.8%, and BL 9.3%) as the main constituent. The only oxygen-containing sesquiterpene found was caryophyllene oxide (CS 1.5%, SE 5.5%, and BL 8.3%). The compounds could be of great interest in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical applications.
- Researchpp 766-788Ren, Y., Teng, C., Gao, T., Zhang, Y., Liu, H., and Dong, X. (2024). “Frictional properties of red pine cones harvested under different conditions,” BioResources 19(1), 766-788.AbstractArticlePDF
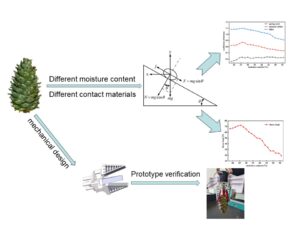
The climbing of trees to pick pinecones is a high-risk exercise. In this study, a mechanical gripper jaw was designed. Frictional characteristics between the pinecones and the mechanical gripper jaw during pinecone picking under different conditions were investigated using a workbench simulation, homemade inclined friction meter, and mass tester. Three-level orthogonal and one-factor tests were conducted. The relationship between the water content and friction properties and between the water content and hardness were investigated, and conclusions were drawn on how water content affected friction properties by influencing hardness. The results showed that the contact material greatly affected the friction properties. The pinecone water content was maintained between 24% and 28% to ensure that the coefficient of friction was maximized and that the pinecones were sufficiently hard to dislodge. Additionally, a prototype machine was used to perform pinecone-gripping experiments to validate the experimental and simulation results. Consequently, the results of this study provide a useful reference for the structural design of pinecone picking robots and the picking reason.
- Researchpp 789-804Ha, S. Y., Jung, J. Y., Lee, J. M., and Yang, J.-K. (2024). “Effect of hydrosol obtained from Camellia japonica branch on α-MSH-induced melanin and tyrosinase activity in B16F10 melanoma cells,” BioResources 19(1), 789-804.AbstractArticlePDF
Hydrosols that originate from various aromatic botanical sources in natural or organic settings contain a spectrum of fragrant compounds, which can be extracted from leaves, stems, peels, flowers, and roots. These compounds are known to exhibit diverse medicinal properties. However, there is limited research on hydrosols extracted from Camellia japonica branches, specifically in terms of their potential to inhibit tyrosinase. Hence, the aim of this study was to investigate the chemical composition of these hydrosols and their effects on inhibiting tyrosinase. Hexamethyl-cyclotrisiloxane (38.1%) and vanillin (25.3%) were identified as the primary constituents in the hydrosol through gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis. The inhibitory effects of the hydrosol, in comparison with the positive control arbutin, were evaluated against mushroom tyrosinase, revealing significant tyrosinase inhibitory properties for both the hydrosol and arbutin. Furthermore, in the presence of α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone, the hydrosol notably diminished melanogenesis, resulting in a substantial reduction in melanin production. Genetic and protein analyses were conducted to uncover the mechanisms behind the hydrosol’s inhibition of tyrosinase and reduction of melanin. The results suggest that the hydrosol may effectively shield melanocytes from detrimental factors associated with tyrosinase-related proteins. The anti-tyrosinase activity of the hydrosol indicates its potential for promoting skin lightening.
- Researchpp 805-822Lin, Q., Cai, J., and Xue, Y. (2024). “Affective response difference to the viewing of different styles of solid wood furniture based on Kansei engineering,” BioResources 19(1), 805-822.AbstractArticlePDF
Homogeneity of products is a serious problem in China’s solid wood furniture market, especially reflected in the fact that the furniture form cannot meet the individualized demand of consumers. To explore the differences of consumers’ affective response for different styles of solid wood furniture, this study used Kansei engineering to perform perceptual semantic experiments on Ming-style, Qing-style, and modern Chinese-style furniture. The perceptual images of three styles of solid wood chairs were compared by single factor variance. Additionally, it deconstructed the morphological elements of solid wood seats using morphological analysis and established a mapping model between morphological elements and affective response by quantification theory type-I and multivariable linear regression model. The results show that there are differences in affective response between Ming-style, Qing-style, and modern Chinese style solid wood furniture. Qing-style solid wood furniture tends to be “ornate” and “personalized”. Modern Chinese-style solid wood furniture tends to be “modern” and “streamlined”, Ming-style solid wood furniture is in between the two styles. This study can provide furniture designers with a way to compare the differences in affective responses of different products, and the resulting relationship between affective responses and morphological elements can assist in designing products.
- Researchpp 823-841Dhayalan, M., Parveen, S., Thirumalaisamy, S., Mohammad, F., Al-Lohedan, H. A., Riyaz, S. U. M., Dinesh, R. A., Giri, J., Stalin, A., Reddy, G. R., Anandakumar, N., and Mallik, S. (2024). “Evaluating the therapeutic importance of gold nanoparticles formed by the biogenic synthesis route of Madhuca longifolia reduction,” BioResources 19(1), 823-841.AbstractArticlePDF
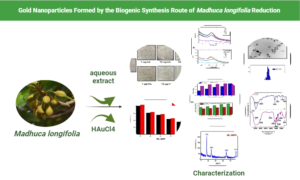
Herbal plants have been used, in light of their responsiveness and wide availability, for the construction of a pioneering nanomaterial. In this study, a colloidal suspension of gold nanoparticles (GNPs) was synthesized from an extract of Madhuca longifolia (ML) using chloroauric acid. For biomedical applications, Madhuca longifolia (ML) was used as a bioreductant as well as a capping agent The formed ML-GNPs were analyzed using different analytical techniques, antioxidant assays, and thiazolyl blue formazan assay against A549 cell lines to evaluate clinical relevance. They were further evaluated for their influence on antimicrobial activity using a disc diffusion test against two different microorganisms, Proteus vulgaris and Micrococcus luteus. The ML-GNPs produced had good antioxidant, antibacterial, and anticancer activities. The conformation of the XRD spectra with prominent characteristic planes was indexed to the face-centered cubic (fcc)-structured GNPs. Surface morphology analysis was used to determine the particle size of the GNPs. Fourier transform infrared spectra of the samples were used to determine the analogs for strong H bonding. The MIC values of biogenic GNPs against both strains of Proteus vulgaris and Micrococcus luteus was calculated as 0.29 and 0.96 g/mL, respectively, and triclosan was considered as 0.4 and 2 g/mL, respectively. The findings of this study will be beneficial for future studies of the therapeutic potential of ML-GNPs. Actively, ML-GNPs can be a capable material for formulating nanomedicines after subsequent clinical experiments.
- Researchpp 842-857Coman, N.-A., Babotă, M., Nădășan, I., Lucian, R., Ștefănescu, R., Frumuzachi, O., Mocan, A., Nicolescu, A., and Tanase, C. (2024). “Exploring polyphenols extraction from Thuja occidentalis L. bark: Optimization, phytochemical profiling, and biological evaluation,” BioResources 19(1), 842-857.AbstractArticlePDF
Polyphenols were extracted from Thuja occidentalis L. bark and characterized in terms of phytochemical composition and biological activity. The optimization process investigated the impacts of extraction duration, ultrasound amplitude, and ethanol concentration on the total phenolic content in the extract. The antioxidant capacity was examined using DPPH and ABTS assays, and anti-enzyme activity against alpha-glucosidase, alpha-amylase, lipase, acetylcholinesterase, and tyrosinase was determined. The experimental model revealed optimal extraction parameters: a hydroethanolic solvent with 44% v:v ethanol, a 15-minute extraction time, and a 40% ultrasound amplitude. These parameters were validated and confirmed by reaching the target Total Phenolic Content (TPC) predicted by MODDE software. The resulting lyophilized extract exhibited a high polyphenolic content (161.84 ± 23.48 mg GAE/g dry extract) and demonstrated strong antioxidant properties. Notably, it showed significant inhibition of alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase, suggesting potential antidiabetic effects, though its inhibition of tyrosinase activity was relatively weak. These findings provide a foundation for further investigations to confirm the qualitative and quantitative presence of specific polyphenolic metabolites in the extract and elucidate the mechanisms underlying its bioactive properties.
- Researchpp 858-871Widsten, P., West, M., Vaidya, A., and Murton, K. (2024). “Isolation of arabinose and galactose from industrial sidestreams in high yield and purity,” BioResources 19(1), 858-871.AbstractArticlePDF
Monosaccharides such as L-arabinose (Ara) and D-tagatose (derived from D-galactose, Gal) are low-calorie sweeteners associated with improved glycaemic and insulin control compared to disaccharides such as sucrose. However, alternative sources and better sugar-sugar separation methods are needed to improve the sustainability and economics of their production. Here, these sugars were obtained from purified and ultrafiltered compression screw pressate (CSP) of thermo-mechanical pulping of softwood (Pinus radiata) and orange peels (OPs). Ba-substituted zeolite X (BaX) molecular sieves showed superior separation performance of Ara from other sugars compared to conventional Ca-form ion exchange resin. To facilitate subsequent separation of sugars, OP hydrolysates were fermented to leave just Ara and Gal, while OP pectin was hydrolysed to generate a Gal-rich mixture. Overall, BaX has good potential for separating Ara from Ara-rich hydrolysates containing several different sugars. It is also suited for separating Ara and another monosaccharide such as Gal or Xyl in the absence of other sugars.
- Researchpp 872-885Hızal, K. T. (2024). “Species and deterioration of woods used in a traditional Turkish house,” BioResources 19(1), 872-885.AbstractArticlePDF
This study identified the wood species and evaluated the weathering and biological degradation of historical timber from a traditional Turkish house in Konuralp, Türkiye. The wood material was obtained from the floorboards, window frames, cabinets, cripple studs, ceiling boards, and joists. The species were identified as Pinus spp. for the cabinet, window frame, and cripple stud, Abies spp. for the floorboards, Populus spp. for the ceiling boards, and Quercus spp. for the joist. The macroscopic observation revealed multiple types of degradation caused by weathering, fungi, and insect attacks. The cripple studs made of pine and the floorboards made of fir had become completely unusable due to insect damage. Relatively less biological damage was observed on the cabinet made of pine wood and the ceiling boards made of poplar wood.
