Volume 19 Issue 2
Latest articles
- Researchpp 2286-2298Du, J., Su, H., Qian, S., and De, X. (2024). “Design optimization and performance evaluation of corn straw crushing and rubbing filament machine,” BioResources 19(2), 2286-2298.AbstractArticlePDF
China produces a large amount of corn straw after the harvest of staple grains every year. Fodder application of corn straw can reduce the waste of straw resources. Such usage also can guarantee the supply of high-quality coarse fodder for livestock and help the development of husbandry and the increase of production and income of farmers and herdsmen in China. Based on the requirements of livestock for straw feed consumption, the corn straw treatment process engineering was studied, and the overall structure, transmission scheme, and main working components of the corn straw crushing and rubbing filament machine were designed. The equipment was developed with three-dimensional modeling and solid design. Key components were verified through finite element analysis. Finally, a prototype was produced for testing. The experimental results showed that when the moisture content of corn straw was tested to be 20%, the percentage of filamentous straw of the equipment was 97.2%, and the calibrated unit power productivity could reach 82.8 kg/(kW · h). Through experiments, all indicators of the equipment met the relevant technical standards of the straw crushing and rubbing filament machine, providing theoretical basis and technical support for the design of the straw crushing and rubbing filament machine.
- Researchpp 2299-2313Yuan, Y., Wei, L., Sun, X., Sun, G., Ma, Y., Xu, S., He, J., and Li, S. (2024). “Optimization of deep eutectic-like solvent-based ultrasound-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Leonurus residues,” BioResources 19(2), 2299-2313.AbstractArticlePDF
Effects of the different types of deep eutectic-like solvents (DESs), molar ratio, water content, extraction temperature, extraction time, and ratio of liquid to solid were studied relative to the yield of Leonurus residue crude polysaccharide (LRCP). Extraction amounts of LRCP were determined. The extraction process parameters were optimized by response surface methodology, and an optimal extraction process was achieved. The results showed that DESs comprising choline chloride and ethylene glycol (CCEG) were suitable for the extraction. The optimum extraction process was as follows: water content, 27%; extraction temperature, 62 °C; and extraction time, 48 min. With the abovementioned parameters, the predicted extraction yield of LRCP was 14.1%. It was found that with these optimal extraction conditions, a 52.9% higher extraction yield could be achieved compared with hot water extraction. Therefore, a type of DES was found to be an excellent extraction solvent alternative for the extraction of polysaccharides and has a practical value.
- Researchpp 2314-2326Kim, C.-K., Lee, H. W., Lee, M., and Lee, S.-J. (2024). “Shear resistance for lateral force of light-frame wall sheathed with structural particleboard (PB),” BioResources 19(2), 2314-2326.AbstractArticlePDF
The shear resistance of a structural particleboard (PB) wall was evaluated as a means to utilize recycled wood and low-grade logs for long periods. The wall was composed of spruce-pine-fir (SPF) lumber, nails, and structural PB, which was developed by improving the water resistance of default PB. Structural PB has a higher density than OSB, which is a commonly used covering material for light wooden structural walls, so a longer end distance for nailing at edge of sheathing is needed for structural PB. In this study, it was confirmed that structural PB walls sufficiently resisted lateral load when the end distance was 15 mm. In this case, the shear strength, shear modulus, and ductility of the structural PB wall for lateral cyclic load were confirmed as 9.2 kN/m, 2.0 kN/mm, and 6.2, respectively. When compared to the design value, the shear strength value was higher than that of the OSB wall and the plywood wall. The shear modulus was lower than that of OSB walls, but higher than plywood walls. Based on the above results, it was considered that structural PB light-frame wall could be used in residential load-bearing applications.
- Researchpp 2327-2341Qiu, Y., Liu, Y., Fang, C., Ju, M., Xia, R., and Wang, Y. (2024). “Supercritical water gasification of oily sludge and its life cycle assessment,” BioResources 19(2), 2327-2341.AbstractArticlePDF

A supercritical water gasification strategy was employed to investigate the effects of different conditions on hydrogen-rich gas production from oily sludge, based on the Aspen Plus platform. Meanwhile, the entire process was assessed with a life cycle assessment (LCA) method. The results indicated that the gas yield was decreased by increasing the sludge concentration. The yield of hydrogen-rich gas (H2 and CH4) was improved with increasing temperature. Higher temperatures were more favorable to gas production. Excessive addition of oxidants could reduce the CH4 yield, thereby lowering the energy efficiency of the process. The LCA analysis found that, in comparison to the stages of raw material transportation, heat recovery, and wastewater treatment, the effect of more CO2 produced in cooling and separation stage on global warming potential (GWP) was more obvious. The corresponding process can be improved to mitigate the environmental effect of the whole gasification.
- Researchpp 2342-2352Pradhan, S., Mohammadabadi, M., Entsminger, E. D., and Ragon, K. (2024). “Influence of densification on structural performance and failure mode of cross-laminated timber under bending load,” BioResources 19(2), 2342-2352.AbstractArticlePDF
The effect of densification of the laminas was studied relative to the shear performance of cross-laminated timber (CLT) specimens submitted to the bending test. The three-layered CLT panels were fabricated using loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.). A compression ratio (CR) of 50% was used to densify the lumber using the thermomechanical densification technique. The process included plasticizing the lumbers by soaking them in boiling water for 10 minutes and then hot-pressing to the target thickness at 140 °C. Four groups were made, i.e., a control sample with all three layers non-densified, only mid-layer densified, all layers densified, and all layers planed to the same thickness of densified layers. Specimens were tested in short-span bending with a span-to-depth ratio of eight. For specimens having densified mid-layer, the failure mode changed from rolling shear to tensile failure of the outer layer, and the maximum shear stress was increased by 34%. Densification of the mid-layer at CR of 16% was sufficient to change the failure mode from rolling shear in mid-layer to tensile in outer layer. In the case of all-layer-densified specimens, the maximum rolling shear strength was increased by 129% compared to the control.
- Researchpp 2353-2370Ramasubbu, R., Kayambu, A., Palanisamy, S., and Ayrilmis, N. (2024). “Mechanical properties of epoxy composites reinforced with Areca catechu fibers containing silicon carbide,” BioResources 19(2), 2353-2370.AbstractArticlePDF
The physical and chemical attributes of Areca catechu fiber (ACF) were explored. ACF is attractive because of its high cellulose content at 63.2 wt%. The mechanical properties were evaluated for Areca catechu fiber-reinforced epoxy composites, in which silicon carbide (SiC) was used as filler. The studied properties included water absorption, flexural strength, impact strength, tensile strength, and hardness properties. The tensile and flexural properties improved when the filler content increased from 40 to 50 wt%, but further increment in the filler content reduced the strength values. The addition of SiC adversely affected the bending and flexural properties of the composites at 40 and 50 wt% filler content, but it positively affected the properties at 60 wt% filler content. The hardness of the composites increased with the addition of 10% silicon carbide. From the results of this study, it is recommended that the ratio of silicon carbide in the composite should not exceed 10 wt% due to agglomeration. The composites containing 10 wt% SiC can be used for outdoor applications such as decking, railing, garden fencing, cladding, and siding applications.
- Researchpp 2371-2382Al-Rajhi, A. M. H., Alharbi, A. A., Alsalamah, S. A. and Abdelghany, T. M. (2024). “Nanoparticles enhanced ligninolytic enzymes activity of rotten wood fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium,” BioResources 19(2), 2371-2382. AbstractArticlePDF
White-rot fungi are vital microorganisms that can decay lignocellulosic biomass. This study investigated the ability of white-rot fungus found on rotten wood to produce ligninolytic enzymes and their enhancement using nanoparticles (NPs). Phanerochaete chrysosporium was isolated from decayed wood. Its ability to produce ligninolytic enzymes, namely CMCase, FPase, Laccase, and MnPase, was recorded. The enzymes’ productivity was enhanced via utilization of the surfactant polysorbate 80 with optimum concentration 0.20 mL/L for maximum CMCase (201.33 ± 2.31 U/mL) and FPase (66.33 ± 0.58 U/mL), whereas the corresponding value was 0.15 mL/L for laccase and MnPase production. Mn2O3NPs and CuONPs enhanced the enzymes’ productivity but with different levels according to their concentrations, where the maximum productivity of CMCase (220.67 ± 2.31 U/mL) and (FPase 74.63 ± 3.51 U/mL) were at 50 ppm, but MnPase (0.52 ± 0.01 U/mL) and laccase (2.88 ± 0.01U/mL) were at 25 ppm and 75 ppm of CuONPs, respectively. Mn2O3NPs at 75 ppm enhanced the productivity of CMCase (219.33 ± 1.15 U/mL) and FPase (74.63 ± 3.51U/mL); but at 25 ppm and 75 ppm enhanced the productivity of laccase (2.40 ± 0.04U/mL) and MnPase (0.73 ± 0.03 U/mL), respectively. Thus, NPs were found to play a vital role in improving the productivity of ligninolytic enzymes.
- Researchpp 2383-2403Chen, Y., and Bian, J. (2024). “Research on color matching model for wood panel furniture based on a back propagation neural network,” BioResources 19(2), 2383-2403.AbstractArticlePDF
The wood furniture manufacturing industry continues in the direction of customized furniture. The analysis of color collocation is important for developing customized furniture. This study summarizes the common color collocation application area for porch cabinets. After selecting the appropriate color model, C # language was used to simulate a real scene setting experimental system in the Unity graphics engine. Colors were generated randomly in the corresponding area, and subjects evaluated the harmony. Then, the Python language was used to build the BP neural network model. The BP neural network models were trained using the Hue, Saturation, value (HSV) of the depicted colors and their corresponding scores. Finally, the evaluation model of color collocation and harmony was obtained. The model can be used to improve the prediction of color matching in customized furniture, which will promote enterprise productivity and industry development.
- Researchpp 2404-2416Villalba, M. E., Olson, J. A., and Martinez, D. M. (2024). “Understanding the limits of a screening operation. Part 1: Characterization of screen plugging,” BioResources 19(2), 2404-2416.AbstractArticlePDF
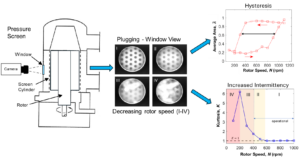
Pressure screening is a critical step in the production of high-quality paper. In efforts to meet sustainable market demands, mill operators are forced to push the limits of screening operation to the point where plugging becomes a recurrent issue. This two-part study provides insights into the limits of screening operations. In the first part, some published imaging data was analyzed to delve into the plugging mechanisms. The observed hysteresis and intermittency were measured by image processing techniques, which revealed that an intermittent behavior of plug-and-release events is intensified as permanent, stable plugs start to form. The intermittency was characterized as changes in the distribution of open area fluctuation peaks. Thus, the kurtosis of the fluctuation peak distribution is proposed as a metric for a plugging soft-sensor. In part 2 of this investigation, the limits of screening operation were characterized by performing a series of screening trials. The utility of the soft-sensor metric for plugging was assessed with the pressure fluctuation data.
- Researchpp 2417-2435Wu, J., Zhao, L., and Song, G. (2024). “Carbon dots prepared from waste wood and residual adhesive and their use as catalysts for hydrogen production,” BioResources 19(2), 2417-2435.AbstractArticlePDF
Large quantities of waste wood with residual resin adhesives are not recycled efficiently. To address this issue, waste wood with residual resin adhesives was synthesized into carbon dots (CDs) via a facile hydrothermal self-assembly method to enhance the H2 evolution performance of graphite C3N4 (g-C3N4), a metal-free photocatalyst. Among all samples, the most significant enhanced sample was MCN-UF-3.5, which has an H2 evolution of 22.1 mmol·g-1·h-1, which is 3.91 times that of unmodified g-C3N4. The band gap and recombination of photogenerated charges were both improved by the doping of CDs. Meanwhile, the DFT calculation showed that adding CDs, especially with the -NH2 group, can significantly deform the structure and destroy the symmetry. This consequence implies an enhancement in the activity of the hydrogen evolution reaction, confirming the feasibility of the modification.
