Volume 19 Issue 4
Latest articles
- Researchpp 8844–8859Sagaste, C. A., Coronado, M. A., Ayala, J. R., Rojano, B. A., Montes, D. G., García, C., and Valenzuela, E. (2024). "Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of essential oils from orange peels and eucalyptus leaves wastes," BioResources 19(4), 8844–8859.AbstractArticlePDF
Oranges and eucalyptus trees are abundant sources of waste and pruning, generating secondary streams that can be converted into valuable products. Both species are broadly cultivated in Mexico. Essential oils from orange peels and eucalyptus leaves possess antimicrobial and antioxidant properties, making them useful in various applications. In this study, the essential oils antioxidant potential was determined through radical scavenging activity and ferric reducing capacity, and the total phenolic content was measured. These essential oils also demonstrated inhibition capacity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. GC-MS analysis of the oils revealed the composition of representative compounds, with D-limonene constituting almost 75% of the orange essential oil and 1,8-cineol comprising 15.2% of the eucalyptus oil. The antioxidant test results between essential oils showed that they are similar, except for the FRAP test, where eucalyptus essential oil obtained a value three times higher than orange essential oil. The findings suggest that these essential oils can serve as natural and sustainable alternatives to synthetic antimicrobial and antioxidant agents.
- Researchpp 8860–8881Muthuramamoorthy, M., Aldalbahi, A., Radi Alanzi, K. M., Pandiaraj, S., and Karuppiah, P. (2024). "Rubber seed shell as low-cost medium to produce lactic acid using Lactobacillus plantarum LB2 and fabrication of a polylactic acid-chitosan composite for fish fillet packing," BioResources 19(4), 8860–8881.AbstractArticlePDF
Rubber seed shell (Hevea brasiliensis) was used as a low-cost substrate to produce lactic acid via Lactobacillus plantarum LB2. The medium components were initially screened by two-level full factorial design. Three variables (pH, moisture, and polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate (PSM)) were used in the central composite design and response surface methodology. The amount of PSM was found to be a significant variable in lactic acid production. Lactic acid was purified and used for the chemical fabrication of a polylactic acid-chitosan composite film. Compared with the polylactic acid, the composite film improved the tensile strength, elongation strength, and tearing strength. The film prepared with 1% chitosan-polylactic acid exhibited the maximum antibacterial activity against Bacillus cereus (21 ± 1 mm) and the lowest activity against Escherichia coli (10 ± 1 mm). The polylactic acid-chitosan film prepared with 1% chitosan was used as a packing material to store the fish fillets and presented reduced mesophilic (4.3 ± 0.1 Log CFU/g) and psychrotropic (3.2 ± 0.2 Log CFU/g) bacterial populations compared with those of the control (4.9 ± 0.2 Log CFU/g and 3.7 Log CFU/g). Rubber seed shells can be used as an alternative culture medium for lactic acid production, to reduce the production cost of polylactic acid.
- Researchpp 8882–8893Al-Rajhi, A. M. H., Bazaid, A. S., Abdulfattah, A. M., Abdelghany, T. M., Shater, A.-R. M., and Selim, S. (2024). "Evaluation of lignocellulatic activity of enzymes from microwave-irradiated Pleurotus sajor-caju cultivated with wheat straw," BioResources 19(4), 8882–8893.AbstractArticlePDF
The production of lignocellulytic enzymes by microwave-radiated Pleurotus sajor-caju was assayed. Wheat straw was employed as substrate to P. sajor-caju for production of laccase, manganese peroxidase (MnPase), filter-paperase (FPase), carboxmethyl cellulase (CMCase), and cellulase (as evaluated using microcrystalline cellulose). P. sajor-caju exposed to 10 s of microwave radiation (MR) showed maximum growth with colony radius of 7.17 ± 0.45 cm, while with increasing the exposure time up to 50 s the growth decreased up to 2.67 ± 0.22 cm. Moreover, it failed to grow at 80 s of exposure time. Cellulase, MnPase, FPase, CMCase, and laccase activities were induced to 37 ± .0.54, 49 ± 2.36, 189 ± 2.12, 0.37 ± 0.06, and 1.58 ± 0.03 U/mL compared to that at control 31 ± 0.25, 46 ± 1.25, 177 ± 1.65, 0.28 ± 0.03, and 1.37 ± 0.12 U/mL, respectively as a result of P. sajor-caju exposure to 10 s of MR. As the exposure time increased, these enzymes activity decreased. Different levels of moisture with surfactant (polysorbate 80) were applied to optimize the enzymes activities at 10 s of exposure time. The optimum activities 3.15 ± 0.23, 0.62 ± 0.06, 269 ± 5.36, 65 ± 1.63, and 48 ± 0.98 U/mL were recorded for cellulase, MnPase, FPase, CMCase, and laccase, respectively at 70% of moisture and 0.15 mL/L of polysorbate 80.
- Researchpp 8894–8911Jiang, Q., Gao, W., Ding, Z., Lu, C., Yan, Y., Yu, M., Gao, J., Zhou, L., and Liu, S. (2024). "Interactions between geometrical forms and microstructural features in culm of square bamboo," BioResources 19(4), 8894–8911.AbstractArticlePDF
Bamboo culms can alter the bamboo’s geometric shape by adjusting the hierarchical organization of anatomical components as a means of adapting to different living conditions. Therefore, a square-like culm has been found commonly in the Chimonobambusa bamboo species. However, the underling mechanism for how these anatomical components assemble into a square culm in the species remains to be considered. Furthermore, the relationship between the geometrical construction of culm and its corresponding organization of anatomical components within also needs clarification. Therefore, the geometrical construction of cross-sections was examined in this work. A super-ellipse based on the Lamé curve was confirmed. Additionally, the transitional zone, at 3/4 in the radial direction, was detected as an inflection point where the geometric parameters clearly changed. Meanwhile, anatomical observation also suggested that the transitional zone can be identified as an inflection point because the fibre morphology difference in circumferential regions becomes more apparent in this area. It is worth mentioning that there is a coherence between the geometrical and microstructural features in circumferential and radial variation. These findings are meaningful to manifest the controlling mechanism of hierarchical structures on the geometrical shape of bamboo culm.
- Researchpp 8912–8919Zemskova, O., Erofeev, V., Samchenko, S., Kozlova, I., Dudareva, M., and Korshunov, A. (2024). "Biocidal properties of gypsum stone modified with Reynoutria sachalinensis raw materials," BioResources 19(4), 8912–8919.AbstractArticlePDF
The current stage of the construction industry development implies increased requirements for building materials to maintain and improve global environmental processes. The understanding by ecologists globally of the danger of anthropogenic impact on the global environment has been reflected in the formulation of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Thus, scientists and engineers are turning to safe plant-based raw materials as innovative building materials. Of particular interest for practice is the use of Reynoutria sachalinensis, which may exhibit biocidal properties. The purpose of this study was to obtain a gypsum stone modified with an extract from the green mass of R. sachalinensis, as resistant coating to fouling by microscopic fungi. The results indicated 10% decrease in the required water addition to gypsum paste when using plant extract, a slowdown of the initial and final setting time of the modified gypsum paste samples compared to the control samples by 6 and 7 min, respectively, and a slight decrease in bending and compressive strengths of the samples of 12.5% and 6%. The 100% resistance of the modified samples to fouling by microscopic mould fungi was also revealed.
- Researchpp 8920–8934Zuber, S. H. binti, Abdul Hadi, M. F. R., Hashikin, N. A. A., Mohd Yusof, M. F., and Aziz, M. Z. A. (2024). "Attenuation coefficients of soy-lignin bonded Rhizophora spp. particleboard as a potential phantom material using Monte Carlo GATE," BioResources 19(4), 8920–8934.AbstractArticlePDF
This work aimed to determine the linear and mass attenuation coefficients of soy-lignin bonded Rhizophora spp. particleboard intended for use as a phantom material using Monte Carlo GATE simulation. At a desired density of 1.0 g cm-3, particleboard constructed of Rhizophora spp. wood trunk bonded with soy flour and lignin was created. The sample’s elemental composition was identified using energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The GATE software was used to simulate the setup with the histories of 1 × 107, and comparison was made between the experimental and simulation data. The disparities between the linear and mass attenuation coefficients of the samples experimentally measured and calculated using GATE at low energy photons were quite small. The result revealed a good agreement between the experimental and simulation data, and the attenuation coefficients were in close proximity with XCOM of water. The outcome revealed GATE adequacy for validation of attenuation coefficient measurement in bioresources phantom material for medical physics application.
- Researchpp 8935–8946Özder, C., Atar, M., and Atılgan, A. (2024). "Determination of the antimicrobial effect of varnishes modified with nano particles on the surface of wood materials," BioResources 19(4), 8935–8946.AbstractArticlePDF
This study was conducted to determine the effect of modifying some varnishes used in wood materials with different nanomaterials on the antimicrobial properties of wood surfaces. For this purpose, samples prepared from Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) Oriental beech (Fagus orientalis Lipsky), and sessile oak (Quercus petraea Liebl.) were varnished with water-based and synthetic varnish with 0.1% and 0.3% nano boron and nano silver added according to ASTM D3023 (2017). Four different microorganisms (Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcus epidermidis) were used to determine the antimicrobial effect on wood surfaces. Among the microorganisms, the highest growth was found in S. aureus and the lowest growth was found in S. epidermidis. In terms of antimicrobial activity, the lowest growth was found in samples with 0.1% nano boron synthetic varnish and highest growth was found in 0.1% water-based varnish. As a result, it is thought that the use of nano materials together with varnishes applied to the surface of wood materials in areas where antimicrobial properties are desired will be beneficial for human and environmental health.
- Researchpp 8947–8958Sun, Y., Sun, R., Jia, X., An, P., Liu, Y., Wu, J., Song, X., and Xu, G. (2024). "Effect of furfural residue ash (FRA) as additive on Portland cement and magnesium oxysulfate cement," BioResources 19(4), 8947–8958.AbstractArticlePDF
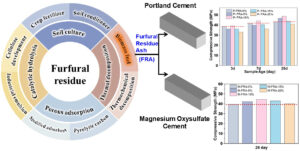
The global production of furfural generates substantial amounts of furfural residue waste annually, which, if not properly managed, can lead to significant environmental pollution. However, the ash produced from the combustion of this biomass waste shows promise as a cement additive, offering an innovative solution for furfural residue management. In this study, ash obtained from the combustion of furfural residue in industrial boilers was used as an additive in both Portland cement and magnesium oxysulfate cement, with concentrations ranging from 5% to 20%. Mortar specimens were then prepared and tested for compressive and flexural strength at 3, 7, and 28 days. The results indicated that at a 10 wt% addition, the formation of cotton-like structures and ettringite needles was most pronounced, resulting in the highest compressive and flexural strengths in the Portland cement specimens. Similarly, in magnesium oxysulfate cement, a 10 wt% ash addition significantly promoted the formation of the 5·1·7 phase, leading to the highest compressive strength. In summary, under appropriate conditions, furfural residue ash can be effectively utilized as a cement additive, contributing to resource recovery and sustainable waste management.
- Researchpp 8959–8975Xu, J., Wei, D., Zhang, X., Li, X., and Chen, Y. (2024). "Dining table design research based on user needs hierarchy and DEMATEL-ISM," BioResources 19(4), 8959–8975.AbstractArticlePDF
This study aimed to address the demand for furniture by developing a user-oriented design pathway for intelligent furniture products, using dining tables as a case study. According to Maslow’s hierarchy, the user needs are classified, and then the Decision-Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (DEMATEL) method was used to calculate the causal relationship, as well as the centrality and weight of each demand. The logical relationship between these factors was analyzed with Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) to create a hierarchical logic diagram. To ensure the feasibility of the theoretical framework, the System Usability Scale (SUS) was used for evaluation. This study systematically sorted out the logical relationship and hierarchical structure in the table demand system and identified the core elements and factor categories in the table design. The results confirmed that this design pathway effectively met user needs for dining furniture and provided practical guidance for developing the same type of furniture products, offering valuable reference for similar design endeavors.
- Researchpp 8976–8987Zhang, K., Guo, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, M., and Zhang, W. (2024). "Preparation and slow-release properties of nanocellulose composite hydrogels," BioResources 19(4), 8976–8987.AbstractArticlePDF
Nanocellulose (CNF) was obtained from carrots using a combination of chemical treatment, mechanical milling, and ultrasonic treatment. Ultrafast preparation of maleic anhydride esterified nanocellulose was achieved by a hydrated hydrogen ion-driven dissociation, chemical cross-linking strategy based on a “one-pot” reaction method. Esterification modification with maleic anhydride reduced the crystallinity of nanocellulose and enhanced its thermal stability. High-strength drug-carrying hydrogels (MACNF/SA) with different drug loading capacities were prepared using cefixime (CFX) as a drug model and maleic anhydride esterified nanocellulose (MACNF) and sodium alginate (SA) as the main raw materials. The compressive strength of MACNF/SA hydrogels made from MACNF reached a maximum of 80.3 kPa when the mass ratio of CNF to MA was 2.5:12. Rheological property tests showed that the MACNF/SA hydrogels were pseudoplastic fluids with shear thinning. The drug release from the drug-carrying hydrogels followed non-Fickian diffusion.
