Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 1643-1658Ambrose, E., Jusoh, I., Duju, A., and Welman, N. (2022). "Effects of incision, forced-air drying, and pressure pretreatments on wet pockets, drying rate, and drying defects of Acacia mangium wood," BioResources 17(1), 1643-1658.AbstractArticlePDF
The pretreatment of 7- and 10-year-old Acacia mangium wood using incision, forced-air dying, and pressure were conducted to evaluate the effects on wet pockets, the drying rate, and drying defects. Quarter and rift sawn boards were used in this study. Results showed that the incidence of wet pockets in the incised, forced-air drying, and pressure-treated quarter and rift sawn boards of 7-year-old A. mangium alleviated up to 35% and 79%, 60% and 54%, and 54% and 82%, respectively. In 10-year-old A. mangium, the occurrence of wet pockets was reduced by 68% and 60%, 31% and 73% and 82% and 73% in quarter and rift sawn boards, respectively. Drying rates of 7-year-old A. mangium pressure-treated boards increased by 5% and 40% in quarter and rift sawn boards, respectively. The drying rate was 10% faster for 10-year-old A. mangium pressure-treated boards. The application of the pressure pretreatment yielded no severe drying defects at the end of the drying period, except for a mild collapse in one of the 10-years old A. mangium sample boards. Incision and forced-air drying pretreatments improved the drying rate; however, pressure treatment was found to be superior in reducing wet pockets and drying defects.
- Researchpp 1659-1669Özderin, S. (2022). "Determination of some chemical properties of wild pear (Pyrus spinosa Forsk.)," BioResources 17(1), 1659-1669.AbstractArticlePDF

Wild pear plant species Pyrus spinosa Forsk., naturally grown in woodlands in Turkey, are one of the most important wild fruits consumed by local people as food, as well as used for medical purposes. In this study, some chemical properties were determined such as fruit seed and fruit pulp antioxidant and antimicrobial activities, fruit seed fatty acid components of Pyrus spinosa determined, which grow naturally in Ödemiş, İzmir, in the south of Turkey. The qualitative and quantitative analyses of fatty acid components of fruit seed of P. spinosa were determined by GC/MS analysis. A total of 16 fatty acids in the fruit seed were found in the analysis results and 44.8% linoleic acid (C18:2n6c), 40.5% oleic acid (C18:1n9c), and 7.6% palmitic acid (C16:0) components were found in higher proportions. Free radical removal effects of fruit seed and fruit pulp extracts were determined using the DPPH method. The antimicrobial activity of fruit pulp extract of P. spinosa was determined by the disk diffusion method against E. coli, S. aureus, and C. albicans. This study revealed that the fruit pulp and fruit seed of P. spinosa, which had a significant level of antioxidant activity, antimicrobial activity, and fruit seed had high levels fatty acids components.
- Researchpp 1670-1679Hamdan, S., Rahman, M. R., Zainal Abidin, A. S., and Musib, A. F. (2022). "Study on vibro-acoustic characteristics of bamboo-based angklung instrument," BioResources 17(1), 1670-1679.AbstractArticlePDF
The frequency (or pitch) content of bamboo angklung musical instruments was analyzed. The pitch of the rattle tubes was determined via a Pico oscilloscope recording both the time and frequency spectrum. Fast Fourier transform analysis identified the fundamentals and overtones of the individual tubes, which were compared with the calculated theoretical resonance frequency. The pitch, due to the coupling effects of two rattle tubes, slightly varied from the pitch of the individual rattle tubes. Although both rattle tubes (played simultaneously) displayed the fundamental frequencies in both tubes, the individual tubes played separately did not produce the exact frequency obtained from both tubes played simultaneously. The spectrum of both tubes produced sound output from the individual tube, which is shown by two prominent peaks, corresponding to the pitch of the individual tube. Although the long and short tube show an individual fundamental frequency of 528 Hz and 1095 Hz, respectively, for C5 tube (when played separately), the coupling of both tubes produced the first and second peaks (when played simultaneously) at 546 Hz and 1093 Hz. Due to the disparity of the fundamental frequency, the inner diameter and length of the tube was utilized for the theoretical resonance frequency calculation.
- Researchpp 1680-1689Zhao, C., Quan, W., and Ding, G. (2022). "SPME-GCMS combined AMDIS and KOVÁTS retention index to analyze the volatile organic compounds in Russula rubra (Krombh.) Bres. essential oil," BioResources 17(1), 1680-1689.AbstractArticlePDF
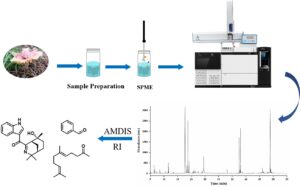
Volatile components in Russula rubra (Krombh.) Bres. were determined with the use of a solid-phase microextraction (SPME)/gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) method. The compounds were identified by the automatic mass spectral deconvolution and identification system (AMDIS) and Kováts retention index (RI). Under the optimized conditions of GC-MS, 52 volatile components were identified in Russula rubra, with the relative percentage accounting for 80.2% of the total ion peak. Notably, aristolone (20.4%), benzaldehyde (20.2%), geranyl acetone (11.0%), and 3-octanone (10.7%) were all at higher levels in samples. The main identified compounds were aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, ethers, and alkanes.
- Researchpp 1690-1702Dzurenda, L. (2022). "Range of color changes of beech wood in the steaming process," BioResources 17(1), 1690-1702.AbstractArticlePDF
Changes in color were evaluated for beech wood Fagus sylvatica L., caused by a steaming process using either a mixture of saturated steam and air or saturated water steam in the temperature range: t = 95 °C to 125 °C for a duration of T = 3 h to 12 h. The initially light white-gray color of beech wood with a yellow tint darkened during the thermal treatment process. It changed to a pale pink-brown and then to dark brown color. According to the visible changes in the color of beech wood obtained by the thermal treatment process with the human eye, , a color scale was proposed as a means to categorize the severity of treatment. The color ranged from a pale pink-brown color to a dark brown-red color depending on the value of the total color difference ∆E*.
- Researchpp 1703-1716Sözen, E. (2022). "Determination of changes in the mechanical and color properties of some wood species treated with shellac," BioResources 17(1), 1703-1716.AbstractArticlePDF
The properties of wood, which is a natural and sustainable substance, change under biotic and abiotic factors. Different methods along with chemical/natural substances are used to extend the service life of wood and increase its performance under different conditions. Shellac is a natural product secreted by insects onto host trees. It is used extensively as a coating, especially in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Its natural properties and biocompatibility increase the areas where it is used. This study investigated the effects on the physical and mechanical properties of pine, beech, and fir species impregnated with shellac solutions at different concentrations (1%, 3%, and 5%) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH). The study found that 10% NaOH solution caused significant decreases in the bending strength values. The highest bending strength values were obtained for the Scots pine and fir woods at 5% shellac concentration and for the beech wood at 1% concentration. The highest modulus of elasticity (MOE) values were reached at 1% shellac concentration in all three tree species. Although the lightness (L*) of the wood samples decreased with shellac impregnation, the chromatic coordinate (a* and b*) values increased. According to the Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy results, changes were determined in the chemical structures of the wood samples impregnated with NaOH, whereas the shellac did not cause a change in the chemical structure of the wood samples.
- Researchpp 1717-1728Li, H., Dai, Y., Qiu, H., and He, X. (2022). "Application of multi-camera digital image correlation in the stability study of the long timber column with the circular cross-section under axial compression," BioResources 17(1), 1717-1728.AbstractArticlePDF
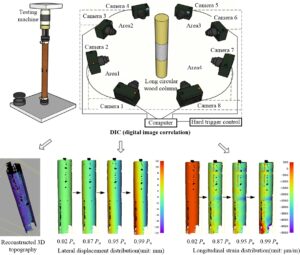
Displacement meter synthesis (DMS), as a traditional method, is widely used to capture the local deformation of a specimen. However, for axis-symmetrical circular columns, the axial compression instability cannot be accurately evaluated using the DMS method due to the uncertain bending direction. To address this problem, a 360° full-surface digital image correlation (DIC) system composed of eight cameras is proposed to capture the full-field deformation information of the column surfaces under axial compression. The objective of this study was to experimentally validate the efficiency of the proposed novel measurement in tracking the full-filled compressive deformation of a long wooden column with the circular cross-section. The test results showed that the columns experience instable failure. The multi-camera DIC system can completely reconstruct the three-dimensional shape of the circular column and obtain the whole process deformation state at any position on the surface of the timber column. The DIC method also can capture the uncertain lateral deformation direction and obtain the data of lateral deflection at the mid-span of timber columns. The multi-camera DIC provides an intuitive and comprehensive new test method for the test and analysis of the stability of axisymmetric long timber columns.
- Researchpp 1729-1744Ren, R., Zhong, Y., and Fan, Y. (2022). "A high-performance electrode based on reduced graphene oxide/lignosulfonate/carbon microspheres film for flexible supercapacitors," BioResources 17(1), 1729-1744.AbstractArticlePDF
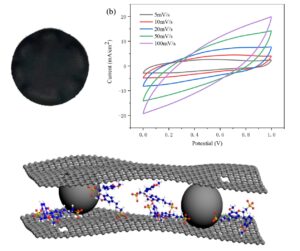
Reduced graphene oxide (RGO) flexible film pillared with lignosulfonate (LS) and carbon microspheres (CM) was fabricated via a facile vacuum-filtration process to serve as a high-performance electrode material for supercapacitors. Composite electrodes comprising graphene and biomass materials have the advantages of being flexible, lightweight, cheap, and environmentally friendly. The addition of LS and CM between the RGO layers mitigated the self-restacking of reduced graphene oxide flakes. Composite film electrode displayed a high specific capacitance of 641 mF cm-2 at 0.2 mA cm-2, which was much higher than that of the RGO film (117.9 mF cm-2). The present findings indicate a great potential of the graphene films composited with biomass materials in fabricating flexible supercapacitor electrodes.
- Researchpp 1745-1763Aydın, M. (2022). "Effects of annual ring number and width on ultrasonic waves in some softwood species," BioResources 17(1), 1745-1763.AbstractArticlePDF
The effect of annual ring number and width on the longitudinal (P) and transverse (S) ultrasonic wave velocities in the radial direction of black pine, Scots pine, Turkish red pine, and cedar softwoods was evaluated in this study. Annual rings were evaluated using high-resolution images captured with a Lumix camera. The 2.25 MHz P and 1 MHz S wave frequencies were propagated through the radial direction of small clear samples. An increase in ring number caused different changes in the P and S wave velocities. Only Scots pine and cedar presented continuous decreases in P and S wave velocities with the increase in annual rings. On the contrary, VR of Red pine slightly decreased and surpassed the initial value when the ring numbers increased from 5 to 10 and 15, respectively. Furthermore, the greatest decrease (4%) in the velocities was observed for VRL of Red pine. According to one-way ANOVA results, significant relations were only observed for VR vs. ring number of Black pine and cedar. R2 values ranged from 0.0001 (Red pine VR) to 0.18 (Cedar VR) for ring number and 0.0002 (Cedar VR) to 0.44 (Scots pine VR) for ring width. Furthermore, ANOVA results for linear regression analysis showed that VR of Scots pine and VR, VRL, VRT of Red pine can be statistically significantly predicted by the ring widths.
- Researchpp 1764-1780Wang, W., Yao, J., and Cao, X. (2022). "Alkaloids from tobacco leaves: Isolation, alkaloid contents, and potential application as a natural pesticide against Bactrocera dorsalis," BioResources 17(1), 1764-1780.AbstractArticlePDF
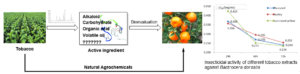
The essential oils from three different kinds of discarded tobacco leaves (flue-cured tobacco, burley tobacco, and sun-cured yellow tobacco) were extracted and isolated, and their isolation method, alkaloid contents, and potential application as a natural pesticide against Bactrocera dorsalis were investigated. The yields of the crude extracts were ranked as follows: sun-cured yellow tobacco was greater than flue-cured tobacco, which was greater than burley tobacco; all their alkaloid contents were analyzed via high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. The total contents of the 4 primary alkaloids (nicotine, anatabine, nornicotine, and anabasine) in the extracts were as follows: flue-cured tobacco (62.1%) was greater than sun-cured yellow tobacco (58.2%), which was greater than burley tobacco (50.7%). The insecticidal activities of the extracts against Bactrocera dorsalis were evaluated via the stomach poisoning method, and the results indicated that sex had no considerable effect on the activity. Surprisingly, the activity of burley tobacco, which contained the lowest nicotine content, showed the best toxicity against Bactrocera dorsalis.
