Research Articles
Latest articles
- Researchpp 2693-2706Atılgan, A. (2023). “Effects of plant extract and wood on anatomical structure in ecological environment interaction,” BioResources 18(2), 2693-2706.AbstractArticlePDF
In this study, the impregnation of a 3% solution of a mixture of medicinal aromatic plant extract, borax, and ferula plant extract on wood of eastern spruce (Picea orientalis L. (Link)) and mahogany were carried out and the changes in the anatomical structure of the impregnated wood were determined. Through obtaining extracts of various medicinal aromatic plants (ferula) and dual treatment with borax, the anatomical properties of wood material were examined and the related adhesion scale was determined. The highest retention (retention) was in mahogany wood borax (1.86%), and the lowest retention was again in mahogany wood ferula extract (0.31%). Both wood types demonstrated improved outcomes in comparison to the control sample when the air-dry and fully-dry specific gravity changes were investigated. The maximum air-dried specific gravity value was found in mahogany at 3% borax and ferula + borax (0.56 g/cm3), and the lowest at 3% ferula and borax (0.37 g/cm3). Mahogany wood with 3% borax had the greatest full dry specific gravity value (0.54 g/cm3), and spruce wood with 3% ferula and ferula + borax had the lowest (0.35 g/cm3). There was no retention in the tracheid and trachea cells that perform the transmission function. Because the sapphire cells are the cells that act as storage, adhesion has occurred in these cells.
- Researchpp 2707-2725Chen, Y., Liang, X., Aliya, K., Zheng, Z., He, C., Jiao, Y., Tao, H., Chang, C., and Xu, G. (2023). “Ethanolysis of glucose into biofuel 5-ethoxymethyl-furfural catalyzed by NH4H2PO4 modified USY zeolite,” BioResources 18(2), 2707-2725.AbstractArticlePDF
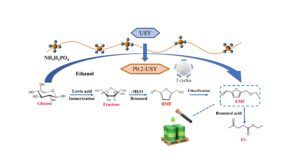
5-Ethoxymethylfurfural (EMF) can be considered as a potential biofuel because of its excellent combustion properties, such as high energy density and low carbon smoke emissions. In this study, Ultra-stable Y (USY) zeolite was modified with NH4H2PO4 and then used as an efficient solid catalyst for the catalytic synthesis of EMF via ethanolysis of glucose First, the NH4H2PO4-modified USY was characterized by FT-IR, XRD, BET, and NH3-TPD. The effect of reaction temperature, reaction time, substrate concentration, and catalyst loading on the yield of EMF was investigated. The P0.2-USY optimal EMF yield was 39.6 mol%, which increased by 20.7% compared to USY, and still had better activity after being reused for 5 cycles. Moreover, the pseudo-homogeneous first-order kinetics model was developed to elucidate the kinetics of EMF formation from glucose, and the kinetics results showed that the activation energy of EMF formation (64.2 kJ⋅mol-1) was lower than that of humins formation (73.2 kJ⋅mol-1). Finally, the ethanolysis pathway was proposed based on the product distribution.
- Researchpp 2726-2745Scholz, P., Vrabcová, P., Linderová, I., and Kotoučková, H. (2023). “Integrated application of selected elements of sustainability, circular economy, bioeconomy, and environmental management system in guesthouses,” BioResources 18(2), 2726-2745.AbstractArticlePDF
Efforts to minimize negative effects on the environment are manifested in the hospitality sector in the form of integrated application of elements of sustainable business, circular economy, bioeconomy, and environmental management. Those who run accommodation facilities are becoming environmentally aware and feel that they should be more involved in sustainable practices and thus contribute to improving the environment both locally and nationally. The main goal of this study is to identify and evaluate the application of selected elements and measures of sustainable business, circular economy, bioeconomy, and environmental management in guesthouses of the Czech Republic. A questionnaire survey (n1 = 343) was carried out together with a qualitative focus group method (n2 = 5); the data evaluation was carried out using advanced statistical methods (Tukey HSD test, Kruskal-Wallis test, correspondence analysis). The results showed that a higher classification in the guesthouse is associated with an increasing trend in the number of environmentally friendly operating methods used. Measures related to waste sorting containers (74%) and energy-saving and LED light bulbs (68%) showed the highest values. The results are useful for the practice of national professional associations that support the careful handling of resources and thereby influence the entire hospitality sector.
- Researchpp 2746-2755Danielewicz, D. (2023). “The effect of treating pine regular kraft pulp with peracetic acid before O2-delignification on the consumption of ClO2 in D0ED1 bleaching,” BioResources 18(2), 2746-2755.AbstractArticlePDF
Effects of pre-treating pine kraft pulp kappa number 31.5 with peracetic acid (Paa) (0.33% and 0.66% as active oxygen based on oven-dried pulp) before O2-delignification were studied relative to the consumption of chlorine dioxide in a subsequent Elemental Chlorine Free (ECF) bleaching process. The study showed that such pre-treatment is an effective way to extend the delignification of the pine pulp and to reduce the consumption of chlorine dioxide required to bleach the pulp to a brightness of 87%. The reduction in chlorine dioxide required to bleach the pine pulp depended on the amount of Paa used for pre-treatment. Furthermore, the research showed that decreasing the kappa number of the pine pulp to approximately 7.5 units (with Paa pre-treatment and lengthening of O2-delignification process) caused an over-proportional reduction (by approximately 62.5%) in chlorine dioxide consumption to bleach the pulp to 87% brightness.
- Researchpp 2756-2772Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Ma, Y., Wang, J., and Su, L. (2023). “Effect of roller layout on biomass bales quality and baling energy consumption during rotary compression,” BioResources 18(2), 2756-2772.AbstractArticlePDF
Baling cellulosic biomass into round bales is an effective way to reduce the cost of storage and transportation. To improve the quality of bales and reduce the baling energy consumption, this paper introduces the steel roller layout parameters of the round baler into the biomass baling process. Alfalfa was used as an experimental material for five levels pitch value of roller circumferential layout baling experiments. The results showed that the introduction of chamber non-roundness (pitch value of roller circumferential layout) destroyed the formation of the entanglement high density ring cylindrical shell lamination of the outer layer of bales, which was beneficial to the compression of bales core material. When the pitch value was 30 mm, the maximum baling pressure, radial pressure transfer loss, and the baling energy consumption of baler were reduced by 30.4%, 33.4%, and 13.7%, respectively. When the pitch value was 60 mm, the relaxation ratio and radial density difference were reduced by 6.3% and 35.8%, respectively, and the radial density uniformity of alfalfa bale was increased by 32.0%. The experimental results provide a theoretical basis and technical support for the chamber structural optimization design of the round baler.
- Researchpp 2773-2788Chang, Y., and Dai, J. (2023). “Parameter analysis on longitudinal lateral force resistance of Song dynasty timber frame with Panjian,” BioResources 18(2), 2773-2788.AbstractArticlePDF
The Panjian structure is an important longitudinal connecting member of Song Dynasty hall-type buildings in China. To study the lateral force resistance of such structures, a refined finite element model of Song-style hall-type single-room four-column space timber frame containing Panjian structure was established based on the official building code Yingzao Fashi of Song Dynasty. The Panjian and inner E’fang in the lower-ping part, the Panjian in the upper-ping part, and Guazi-gong Panjian and Man-gong Panjian in the roof ridge part were investigated. The model hysteresis curves of all three parts of the longitudinal timber frame were found to be S-shaped, with obvious pinching effect, fuller at both ends and centrosymmetric shape. The Panjian structures in the lower-ping and upper-ping parts, and the Guazi-gong Panjian in the roof ridge part increased the energy dissipation and lateral stiffness of the timber frame. The Man-gong Panjian in the roof ridge part, however, was detrimental to the lateral resistance of the structure. Throughout the test, the Panjian structures were relatively intact, with large plastic damage occurring at both ends of the E’fang. For the repair and testing of similar ancient buildings, some reference suggestions are provided.
- Researchpp 2789-2799Orlowski, K. A., Chuchala, D., Stenka, D., and Przybylinski, T. (2023). “Capacity of surface production of band sawing in manufacture of oak floor upper layers,” BioResources 18(2), 2789-2799.AbstractArticlePDF
Thin lamellae, corresponding to the layer components of structural glued members, i.e., 2-ply or 3-ply glued flooring, can be manufactured in re-sawing operations of kiln-dried wood blocks or in wet technologies, which currently seem to be more common because of the shorter drying time. The re-sawing process in wet technology is conducted on dedicated thin-cutting band sawing machines with stellite-tipped band saws. The goal of this research was to demonstrate the capacity of surface production (m2/ tool life) of visible layers of oak engineered flooring composites in a function of both a new band saw and a re-sharpened band saw blade. Additionally, the state of teeth of each band saw blade was examined at the end of the tool life. A series of cutting tests were performed in sawmill production conditions. The conducted tests revealed that a three times higher capacity of surface production was obtained for the new tool compared to re-sharpened tool. Additional microscopic observations of some re-sharpened teeth showed deformed plastic characteristics.
- Researchpp 2800-2814Arabi, M., Haftkhani, A. R., and Pourbaba, R. (2023).“Investigating the effect of particle slenderness ratio on optimizing the mechanical properties of particleboard using the response surface method,” BioResources 18(2), 2800-2814.AbstractArticlePDF
Restricted formaldehyde gas emissions and a scarcity of lignocellulosic raw materials have particleboard companies in Iran concerned about raw materials and adhesive use. The particle slenderness ratio is one of the main parameters that leads to the required mechanical characteristics of particleboard, together with the simultaneous decrease of density (raw materials) and the quantity of adhesive. The objective of this study was to evaluate the mechanical properties of particleboard composed of poplar particles with variables of density, adhesive quantity, and slenderness ratio using response surface technique. The variables were then optimized for the examined responses according to the EN 312-3 (1993) standard for the manufacturing of particleboard for domestic use as well as home and office furniture. Particleboard with minimum allowable properties according to EN 312-3 (MOR = 11 MPa, MOE = 1.6 GPa, and IB = 0.35 MPa) with a density of 0.65 g/cm3, adhesive percentage of 10.54, and a slenderness ratio of 37.5 can be produced, according to optimization findings. Through raising the density to 0.69 g/cm3 and the slenderness ratio to 46.99, the quantity of adhesive utilized in particleboard manufacturing could be decreased from 10.54 to 8.9% while keeping the minimum allowable resistances of EN 312-3 (1993) standard.
- Researchpp 2815-2825Kuzmin, A. M., Ayrilmis, N., Özdemir, F., and Kanat, G. (2023). “Effect of content and particle size of used beverage carton pieces on the properties of HDPE composites,” BioResources 18(2), 2815-2825.AbstractArticlePDF
This study investigated the tensile properties and thermal behavior of virgin and hot press molded HDPE composites filled with different particle size and content of used beverage cartons which were the Tetra Pak® cartons. The mechanical properties of the composites were positively influenced by particle size of the used beverage carton, such that the smallest particle size gave the highest tensile strength and tensile modulus. The tensile strength of the specimens decreased with increasing filler content (40 to 70 wt%), while the tensile modulus rose. Furthermore, the filler size and its content affected the thermal behavior of the specimens. Calorimetry analysis of composite specimens showed that melting temperature and enthalpy values of virgin HDPE and recycled-HDPE decreased with increasing Tetra Pak® content. In all composite groups produced by adding Tetra Pak®, the degree of crystallinity decreased as a function of Tetra Pak® addition compared to the pure HDPE. Increasing particle size adversely affected the crystallization degree, which decreased with increasing particle size while the HDPE maintained its crystalline form. As for the recycled-HDPE composites, the degree of crystallization was reduced by increasing the Tetra Pak® content, but this was still noticeably higher than that of the HDPE.
- Researchpp 2826-2841Yi, K., Fu, S., Yi, Z., Yang, X., and Lan, X. (2023). “Nanocellulose and polysiloxane coatings for strength enhancement and oil-proof and hydrophobicity improvement of recycled pulp sheets,” BioResources 18(2), 2826-2841.AbstractArticlePDF
Recycled fibers are essential raw materials used by the paper industry. However, the strength of the formed paper may fall off excessively after several cycles of reuse of the fibers. Herein, the authors measured the changes in physical properties and fiber size after multiple recycling of fibers and prepared a handsheet from fiber recycled different times. Then the handsheets made with fibers that had been recycled 5 times were double-coated with nanocellulose derivatives to obtain oleophobic and hydrophobic paper. The first layer applied to the paper was cellulose nanofibril (CNF), and the second coating contained polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and CNF (CNFmp). The physical properties and barrier performance of coated paper were greatly improved compared to recycling paper. The water contact angle of the coated paper was as high as 139.8° and the Cobb60 value was 35.18±2.15 g/m2. The oil contact angle was 97.1°, and the oil kit number was 12/12.
