Review Articles
Latest articles
- Reviewpp ###-###Alba Fierro, C. A., Escobedo Bretado, M. A., Núñez Ramírez, D. M., Martell Nevárez, M. A., and Ríos Fránquez, F. J. (2024). “Are biological pretreatments of lignocellulosic residues a real option for biofuels production?” BioResources 19(2), Page numbers to be added.AbstractArticlePDF
The use of lignocellulosic residues as feedstocks for biofuels production represents an economic and ecofriendly option, since they are generated as byproducts or wastes from different industrial areas. Nevertheless, a pretreatment method aimed at eliminating the lignin content of these residues must be performed. This is required in order to increase cellulose bioavailability, which favors the production of reducing sugars through microbial or enzymatic attack. Some performed pretreatments can be classified as physical, chemical, and physicochemical methods. Although such methods are the most used pretreatments, they are expensive and generate or make use of harmful compounds. Biological methods, by the action of microorganisms or their enzymes for lignin content reduction, may be regarded as an alternative, being cheaper and more friendly to the environment than the aforementioned methods. However, until now, biological pretreatments have not shown the same yield as the previously mentioned methods in both sugar recovery and biofuel production. In that sense, the aim of this work is to review the efficiency of these methods, with the goal of clarifying their advantages and disadvantages for improvement of biofuel production.
- Reviewpp ###-###Ntifafa, Y., Ji, Y., and Hart, P. W. (2024). “Polyamidoamine epichlorohydrin (PAAE) wet-strength agent: Generations, application, performance, and recyclability in paperboard and linerboard,” BioResources 19(2), Page numbers to be added.AbstractArticlePDF
Polyamidoamine epichlorohydrin (PAAE) is the preeminent permanent wet strength additive used in papermaking. Wet strength additives are used to improve paper resistance to a rupture force in wet environments. The invention of PAAE in 1957 was an innovation, as it improved paper properties by giving superior wet strength in humid or wet conditions. It was rapidly adopted by the industry. Despite PAAE’s long history, the mechanism of PAAE interaction with fiber has not been fully understood. Therefore, fundamental understanding of PAAE mechanism needs to be investigated to improve its utilization in making sustainable paper products. These areas include an understanding of repulping methods and optimal PAAE dosages for better cost and performance. This paper investigates different generations of PAAE, the application method, and its impact on paper recyclability. Three generations of PAAE are currently on the market with at least two newer iterations under development. Critical application parameters that need to be understood include determination of the bonding mechanism, optimal dosage, and retention parameters. The main drawback of PAAE application is it makes paper recycling difficult. Several repulping methods are proposed for better recyclability and sustainability in the papermaking process.
- Reviewpp ###-###Kuok, K. K., Bin Bakri, M. K., Chan, C. P., Rahman, M. R., Namakka, M., Said, K. A. M., Yun, C. M., and Rahman, M. M. (2024). “Merits of bamboo utilization in earth preservation, water, and wastewater treatment: A mini review,” BioResources 19(2), Page numbers to be added.AbstractArticlePDF
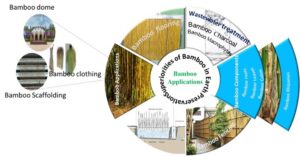
This paper reviews the positive attributes and challenges of bamboo usage in carbon absorption, water, and wastewater purification. Bamboo can serve as a habitat for a variety of creatures and supports a diversified ecology. Bamboo roots can cast a fibrous net into the ground to prevent soil erosion and degradation. As the water passes through this woven mesh, the bamboo roots act as a filter, drawing toxins and other contaminants out of the water. Bamboo can treat wastewater effectively in free-water surface, horizontal flow, and vertical flow constructed wetlands. Bamboo charcoal has exceptional filtering properties for cleaner drinking water and better air quality. Additionally, bamboo can be used to form cellulose-based membranes. Bamboo is a renewable resource for creating paper, furniture, and building materials. Bamboo has various benefits. Thus, bamboo forests offer opportunities for rural communities to thrive economically.
- Reviewpp ###-###Téllez-Téllez, M. (2024). “Wild edible mushrooms as an alternative for the consumption of antioxidants and phenolic compounds: An overview,” BioResources 19(2), Page numbers to be added.AbstractArticlePDF
Fungi are a diverse group, and they are essential for health, the economy, and food. Interest in these organisms has increased because of the importance and effect of their chemical components viz., phenolic compounds, which are considered an alternative source of antioxidants. Antioxidants are compounds that prevent cell damage and can help prevent or counteract certain diseases (cardiovascular, neurodegen-erative, cancer, etc.) because they can improve cell function (changes in enzyme activity, enzyme patterns, membrane fluidity, and responses to stimuli), among others. To date, no adverse side effects have been reported. The difference in production is due to several factors, such as the growth environment, nutrition, cell age, the part from where the phenolic compounds are obtained (pileus, stipe, or mycelium), the extraction method, etc. This article aims to provide an overview of wild edible mushrooms, to promote the study of their antioxidant capacity, and to better understand the nutraceutical potential of edible mushrooms consumed in different parts of the world.
- Reviewpp ###-###Li, P., Wu, S., and Ding, Y. (2024). “Research progress on lignin-based carbon electrode materials in rechargeable batteries,” BioResources 19(2), Page numbers to be added.AbstractArticlePDF
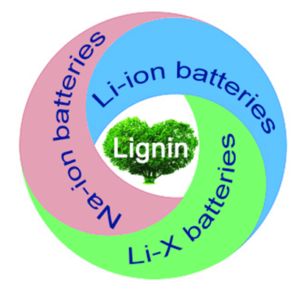
Lignin, with its carbon content of up to 60%, can be an ideal precursor for the preparation of carbon materials. Carbonaceous materials obtained from lignin can be transformed into porous and structural morphologies at different scales, providing a biomass approach to energy conversion and storage in batteries. Focusing on lignin-derived carbon materials, this paper summarizes the different morphologies and structures of lignin-based carbon obtained through different preparation methods, and the different electrochemical properties exhibited by these materials as electrode materials for rechargeable batteries (lithium-ion batteries, sodium-ion batteries, lithium-sulphur batteries, etc.). In addition, the development prospects and challenges of lignin-based carbon materials in the field of rechargeable batteries are summarized, providing ideas for the next step in the design and development of high-performance lignin-based carbon-based electrode materials.
