Volume 16 Issue 4
Latest articles
- Researchpp 7578-7591Wang, X., Liu, S., Zhang, D., Bi, D., Wang, L., Zhang, J., and Yi, W. (2021). "Selective preparation of furfural via the pyrolysis of cellulose catalyzed with nitrided HZSM-5," BioResources 16(4), 7578-7591.AbstractArticlePDF
Furfural is a high-value compound that can be prepared by catalytic pyrolysis of biomass. In order to improve the selectivity of furfural in the process of cellulose catalytic pyrolysis, the ammonia-modified HZSM-5 (N-HZSM-5) was used as the catalyst for experimental research on a horizontal fixed bed. The effects of different nitriding temperatures and times on N-HZSM-5, and the effects of different catalyst to cellulose (CA to CL) ratios on furfural selectivity were evaluated. The results showed that N-HZSM-5 can effectively improve the selectivity for furfural. At the optimal conditions (nitriding temperature: 800 °C, nitriding time: 6 h, CA to CL ratio: 4), the selectivity of furfural was up to 24%, which was much higher than those of noncatalytic pyrolysis (1.2%) and HZSM-5 catalytic pyrolysis (3.6%). In order to better evaluate the performance of the catalyst, a series of characterizations were carried out on the N-HZSM-5. The results showed that compared with HZSM-5, N-HZSM-5 had an increased pore size, it was less acidic, and it had more uniform surface acidity. It was conducive to the selective formation of furfural. Therefore, the ammonia-modification can effectively control the structure and acidity of HZSM-5, and N-HZSM-5 exhibits a non-negligible potential in catalyzing the pyrolysis of cellulose for furfural.
- Researchpp 7592-7607Liu, Y., Wang, F., and Sun, Y. (2021). "Esterification of cellulose with betaine using p-toluenesulfonyl chloride for the in-situ activation of betaine," BioResources 16(4), 7592-7607.AbstractArticlePDF
A novel synthesis method was developed for betaine-modified cellulose ester using a mixed N,N-dimethylacetamide/lithium chloride solvent system; p-toluenesulfonyl chloride was used for the in-situ activation of the betaine. The influence of the reaction temperature and time, as well as the anhydroglucose unit to p-toluenesulfonyl chloride to betaine mass ratio on the degree of substitution of the product was evaluated. Increasing the proportion of betaine and p-toluenesulfonyl chloride was beneficial to the esterification reaction. The degree of substitution was 1.68 at 90 °C for 32 h with an anhydroglucose unit to p-toluenesulfonyl chloride to betaine molar ratio of 1 to 2 to 3. The physicochemical properties of the betaine-modified cellulose were closely related to the degree of substitution. Major changes in the morphologies, crystallinity, thermal properties, porosity, and the average degree of polymerization resulted from the modification. The introduction of betaine made cellulose esters thermally less stable than neat cellulose but more difficult to completely degrade. The crystalline structure of the cellulose esters was destroyed, and the products exhibited a porous nature. Dye sorption studies demonstrated that the betaine-modified cellulose holds the potential of adsorbing anionic substances, which is the premise of its application.
- Researchpp 7608-7622Hu, G., Hu, J., Chen, H., Song, S., and Chu, F. (2021). "Influence of pH and ionic strength on the aggregation behaviors of xylan rich hemicelluloses with alkaline lignins," BioResources 16(4), 7608-7622.AbstractArticlePDF
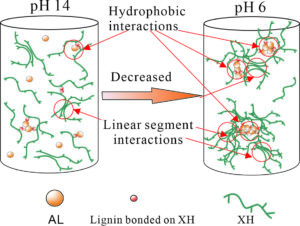
The evolution of xylan-rich hemicelluloses (XH) aggregation behaviors in the presence of alkaline lignins (AL) under a wide range of pH values and NaCl concentration were investigated via dynamic light scattering and turbidity measurements. XH isolated from wheat straw contain a xylose backbone with arabinose side chains and a small amount of phenol groups. XH tend to aggregate in solution due to their low ratio of arabinose to xylose and hydrophobic phenol groups. AL interact with XH through the phenol groups bonded to the hemicellulose main chain to form an AL-XH complex. As the pH value decreases, the particle size and turbidity of AL, XH and their bonded complex all increase. The size of the AL-XH complex agglomerate is greater than the size of a XH at the same pH value, which indicates that the self-assembly of lignin molecules initiate the aggregation of XH. The particle size and turbidity of XH and AL-XH complexes increase as the XH concentration increase. At low pH values, e.g., 6.0, the particle size of the AL-XH complex more obviously increases compared to the XH particles. The size and turbidity of the AL, XH, and AL-XH complex agglomerates increased as the NaCl concentration increased.
- Researchpp 7623-763Marques, J. P. R., Aferri, G., Montanha, G. S., Guedes, F. T. P., Soares, M. M., Muniz, L. F., Tomazello-Filho, M., Xavier, M. A., and de Carvalho, H. W. P. (2021). "Sugarcane as a forage plant: Structural and chemical traits that affect fiber quality," BioResources 16(4), 7623-7634.AbstractArticlePDF
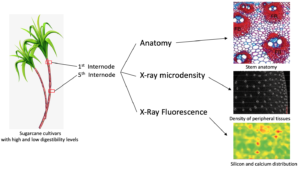
Sugarcane is widely used as feed for cattle, buffalo, goats, and sheep, primarily during drought periods. Some sugarcane cultivars contain low digestibility fibers, which compromises animal performance. Thus, the present study reports on anatomical, chemical, and elemental analysis along stem internodes of two sugarcane cultivars to better understand the structure-digestibility relationship of industrial cultivar cv. IACSP95-5000 compared to a forage cultivar (cv. IAC86-2480). X-ray microdensitometry assays revealed that the peripheral tissues of IACSP95-5000 were denser than IAC86-2480. In the first internode, cv. IACSP95-5000 has more vascular bundles and occupy a larger area. In addition, it had more fibers surrounding the vascular bundles compared to cv. IAC86-2480. However, fibers are prominent at the fifth internode in both cultivars but are more evident in cv. IACSP95-5000. The microprobe X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy analysis showed that silicon and calcium elemental distribution were similar for both cultivars. The structural features of the forage sugarcane presented herein are able to explain the digestibility differences between cultivars.
- Researchpp 7635-7647Vaysi, R., and Ebadi, S. E. (2021). "Thermal yellowing of hornbeam chemi-mechanical pulps bleached with hydrogen peroxide and sodium dithionite," BioResources 16(4), 7635-7647.AbstractArticlePDF
The thermal yellowing of hornbeam chemi-mechanical pulps (CMP) after bleaching with hydrogen peroxide and sodium dithionite was investigated. The hornbeam chips were randomly chosen from Mazandaran wood and paper industries. The CMP pulps prepared with 85% yield were separately bleached with diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA), without DTPA, and hydrogen peroxide. Some pulps were bleached with sodium dithionite. The optical properties of prepared hand-sheets of 60 g/m2 after spraying with 0.5% DTPA were measured using TAPPI standard methods. All prepared papers were thermally aged separately in an oven at 105 °C for 0, 10, 20, 30, and 40 h. The optical properties, such as brightness, yellowness, coefficient of absorption, k/s ratio, post color (PC) number, and a* factor, before and after thermal aging were measured. The results showed that from 0 to 40 h, the optical properties of paper increased except brightness and greenness. This increase was more extensive up to 15 h. Additionally, among the various treatments, DTPA treatment in long-term thermal aging and the use of sodium dithionite and hydrogen peroxide in the short-term aging had noticeable effects on brightness durability and decrease in the color reversion. Thus, there was an increase in the durability of the paper against thermal deterioration.
- Researchpp 7648-7670He, Z., Lu, W., Hua, G., and Wang, J. (2021). "Factors affecting enterprise level green innovation efficiency in the digital economy era – Evidence from listed paper enterprises in China," BioResources 16(4), 7648-7670.AbstractArticlePDF
The Guidelines on Building a Market-Oriented Green Technology Innovation System, which was released by China in 2019, has become a powerful signal to guide the development of green technology innovation (GTI). In the current digital strategy of China, the public media has become a key factor for promoting the transparency of enterprise environmental information. This paper measures the GTI efficiency of the listed paper enterprises in China as well as incorporating media attention into the research framework to explore the influencing factors of GTI of the listed paper enterprises in China during the digital economy era. The results showed that a positive media report had a positive impact on GTI and has become a new driving factor in promoting sustainable production in the digital era. Government support and openness also have a positive impact on GTI. However, negative media reports, environmental regulations, and technological innovation abilities have an inhibitory effect on the GTI efficiency of paper making enterprises.
- Researchpp 7671-7683Nlandu, H. M., Chorfa, N., Bekacemi, K., and Hamoudi, S. (2021). "Potato starch nanocrystal preparation via supercritical carbon dioxide pretreatment combined with enzymatic hydrolysis," BioResources 16(4), 7671-7683.AbstractArticlePDF

In this work, starch nanocrystals were successfully produced from downgraded potatoes using enzymatic hydrolysis combined with a supercritical carbon dioxide pretreatment to improve the accessibility of the enzyme to the starches. Enzymatic hydrolysis was carried out using the pullulanase enzyme at a temperature of 60 °C and a pH of 4. Following hydrolysis, the starch nanoparticles were recovered via precipitation and recrystallization. Comparative characterization of the native, supercritical carbon dioxide-pretreated, and hydrolyzed-recrystallized starch materials was conducted via transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction. The scanning electron microscopy images revealed alterations, e.g., layered strips, on the surface of the potato starch granules after the supercritical carbon dioxide pretreatment. The transmission electron microscopy images revealed that spherical nanostructures from 80 nm to 150 nm were successfully produced. The Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy spectra displayed several absorption bands corresponding to the molecular structure of starches. The X-ray diffractograms exhibited a typical B-type scattering pattern for all the samples. In addition, it was found that the crystallinity of the potato starch nanoparticles was considerably increased compared with native starch.
- Researchpp 7684-7701Panchan, N., Wattanapan, P., Sungsinchai, S., Roddecha, S., Dittanet, P., Seubsai, A., Niamnuy, C., and Devahastin, S. (2021). "Optimization of synthesis conditions for carboxymethyl cellulose from pineapple leaf waste using microwave-assisted heating and its application as a food thickener," BioResources 16(4), 7684-7701.AbstractArticlePDF

Pineapple leaf waste, with its high cellulose content, can serve as alternative starting material for the production of carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC). In this study, synthesis conditions of CMC from pineapple leaves via the use of microwave heating were optimized. Box-Behnken design and response surface methodology were applied to schedule the experiments and to optimize the synthesis condition, respectively. Preparation of CMC was investigated by varying three factors, namely, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) concentration, monochloroacetic acid (MCA) dose, and etherification time. The process of carboxymethylation was optimized to produce CMC with high degree of substitution (DS). Optimal condition for CMC synthesis was noted to be 50% (w/v) NaOH solution, 8 g of MCA/g cellulose, and etherification time of 16 min; such optimal condition resulted in the maximum DS of 0.78. Synthesized CMC was utilized as a thickener for liquid foods (water, orange juice, milk, and mushroom cream soup) where 2% (w/v) as-synthesized CMC increased the viscosity of the foods and changed their characteristics from thin to nectar-like liquids.
- Researchpp 7702-7715Alishiri, M., Hemmasi, A. H., Khademi Eslam, H. K., Basirjafari, S., and Talaeiypour, M. (2021). "Evaluation and comparison the properties of acoustic boards made of date palm fiber," BioResources 16(4) 7702-7715.AbstractArticlePDF
Applying acoustic panels made of natural fibers, due to their high biodegradable characteristics, light weight, low density, cheap price and non-toxicity, are proper alternatives to acoustic absorbers made of synthetic fibers. Considering their stance and vast applicability in industry, the possibility of producing them of natural palm fibers with sodium silicate adhesive of 10 and 20% in two 16 and 32 mm thicknesses, 350 and 450 kg/m3 densities, 50 and 100 mm particles length (strands), as variable factors in 16 types of matched panels with 3 repetitions is proposed in this article. The palm-trunk discs constituted the control sample. The effect of variables on sound absorption coefficient was assessed. The effect of variable thickness and adhesive percentage on all frequencies was significant and the effect of density variable on all frequencies except 250 and 2000 Hz was also significant. The effect of particle length was significant except at the 500 Hz frequency. The effects of all variables on porosity were significant. The results of this study suggest that by applying date palm-trunk (an agricultural waste) combined with sodium silicate adhesive, industrial environment-friendly panels can be produced with proper sound absorption coefficient in the field of acoustics. This 32-mm-thick panel was composed of 80% date palm-trunk particles of 50 mm length, 450 kg/m3 density, and 20% sodium silicate adhesive.
- Researchpp 7716-7728Lee, M., Kang, D., and Seo, Y. (2021). "Development of post hybrid calcium carbonate for high loaded paper," BioResources 16(4), 7716-7728.AbstractArticlePDF
In papermaking, pre-flocculation of fillers such as ground calcium carbonate (GCC) improves the tensile strength of paper sheets. However, the pre-flocculated fillers mostly suffer from the instability of the floc shape such as the decrease in floc diameter with time elapse after preparation and no improvement of bulk and stiffness. The addition of calcium compounds such as calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide to the pre-flocculated GCC, and injection with carbon dioxide caused pre-flocculated GCC flocs to be covered with newly formed calcium carbonate. This product, called post hybrid calcium carbonate (pHCC), was found to be more stable in size and gave better sheet strength than the pre-flocculated ones. Furthermore, pHCC gave remarkably higher bulk and stiffness than the pre-flocculated flocs did without impairing smoothness that was essential in printing paper. The proper use of pHCC in papermaking could allow the production of high loaded paper with more than 10% higher filler contents, which could reduce paper production cost and save drying energy. The proportion of the newly formed calcium carbonate in pHCC, turbulence intensity at preparation stage, and the effect of storage time were investigated.
