Volume 17 Issue 3
Latest articles
- Researchpp 4432-4443Zainal Abidin, N. A., Mahmud, J., Manssor, N. A. S., and Che Abd Rahim, N. N. (2022). "Physical and mechanical properties of bamboo-silicone biocomposites (BaSiCs)," BioResources 17(3), 4432-4443.AbstractArticlePDF
Silicone rubber biocomposites were prepared with 0%, 4%, 8%, 12%, and 16% bamboo fiber as reinforcement. The compressive set behavior of the samples was compared between the samples that were tested before and after immersion in water. The compression set values for the samples that were immersed in the water were lower than the samples that were not immersed in the water. The moisture absorption rate of the bamboo-silicone biocomposites (BaSiCs) increased as the bamboo fiber content increased. As the bamboo fiber content in the BaSiCs increased, the impact energy and the deflection at peak load values decreased and increased, respectively. The results from this study showed that the addition of bamboo fiber into silicone rubber composites can substantially affect its compressive strength, moisture absorption, and impact strength. This study provided essential knowledge to the development of BaSiCs for cushioning applications, such as shoe insoles.
- Researchpp 4444-4451Nemati, M., and Samariha, A. (2022). "Evaluation of the effects of transition metal ions on the optical aging and whiteness of chemimechanical pulp," BioResources 17(3), 4444-4451.AbstractArticlePDF
The negative effects of metal ions were addressed relative to the whiteness characteristic of chemomechanical pulp samples prepared. Proper solutions were considered to mitigate this adverse effect. The chemomechanical pulp samples were supplied in an unbleached form. The samples were wetted using ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) chelating agent, and then each of the samples was wetted with EDTA after drying with solutions containing the transitional metal ions. The results showed that the greatest whiteness reduction resulted from Fe2+ ions, whereas the smallest effect resulted from Al3+ ions. Wetting of the samples in various concentrations of the chelating agent (EDTA) had an optimum value in improving the whiteness characteristic of the paper. Thereafter, no change was created in whiteness improvement and brightness stability by increasing the concentration of EDTA. Increasing the aging time reduced the whiteness characteristic of the chemomechanical pulp.
- Researchpp 4452-4469Anak James, A., Rahman, M. R., Huda, D., M. Aqlan, F. M., Matin, M. M., Bin Bakri, M. K., King Kuok, K., and Rahman, M. M. (2022). "Synthesis and characterization of novel nano-carbon mixture from Dabai (Canarium odontophyllum) nutshell," BioResources 17(3), 4452-4469.AbstractArticlePDF
The nanocarbon-based mixture was shown to be an effective adsorbent for removing dyes and heavy metals from wastewater via adsorption. The goal of this research was to prepare and investigate the properties of a bio-carbon mixture made from Dabai (Canarium odontophyllum) nutshell with the addition of titanium dioxide (TiO2) and montmorillonite (MMT) clay. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was used to determine the functional groups of raw carbon and potassium hydroxide (KOH)-activated carbon (AC). The FTIR analysis of the active carbon revealed that the active carbon had more surface chemistry than the non-AC. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis was used to compare the raw and AC morphologies and the developed nanocarbon. The results were confirmed using energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis to verify the elements in the studied sample. The SEM analysis revealed that the structure of both the carbon samples was irregular, granular, and porous. BET analysis showed that nano-activated carbon had higher surface area compared to activated carbon itself. Response surface methodology (RSM) was used in Design-Expert 13.0 software for the sample composition development to achieve the best performance of the developed nanocarbon as an adsorbent.
- Researchpp 4470-4479Erkan, N. (2022). "Lake Avlan drainage effects on radial tree growth at microecological level," BioResources 17(3), 4470-4479.AbstractArticlePDF
Lake Avlan is a natural lake located in the mountainous areas in southwestern Turkey. The lake was drained towards the end of the 1970s. However, some serious socioeconomic impacts were felt in the region surrounding the lake basin. Because the increasing ecological problems were realized within 20 years, the lake was restored towards the end of the 1990s. The present study considers the effects of lake drying on the radial growth rate of cedar and juniper forests on the slopes adjacent to the lake basin, during the drained period. Dendrochronological methods were used in two stands, one from cedar and the other from juniper forests. Results showed that mean index values derived from annual growth rate for the drained period were 15% and 14% less than that of the average of pre- and post-drying periods of the lake for cedar and juniper sites, respectively. Microecological change, namely decreasing air humidity, due to drying the lake may be the main reason of differentiation in the index values. Natural lakes, like Avlan, on mountainous areas are an important component of forest ecosystems and should not be overlooked by natural resource planners in such regions.
- Researchpp 4480-4498Dinh Giap, V., Huu Nghi, D., Huu Cuong, L., and Thu Quynh, D. (2022). "Lignin peroxidase from the white-rot fungus Lentinus squarrosulus MPN12 and its application in the biodegradation of synthetic dyes and lignin," BioResources 17(3), 4480-4498.AbstractArticlePDF
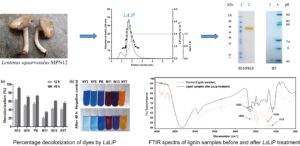
Lignin peroxidase (LiP), which has been studied extensively in white-rot basidiomycetes and their potential to degrade dyes from textile wastewater, plays a role in the biodegradation of lignin from pulp and paper industry wastewater, as well as agricultural waste. Lignin peroxidase (LsLiP) was successfully purified from the newly isolated Lentinus squarrosulus MPN12 with a 47.1-fold purification and a 15.7% yield. After 48 h-incubation, LsLiP was able to decolorize all tested dyes up to 92% for Acid Blue 62 (NY3), followed by Porocion Brilliant blue HGR (PB, 73.5%), Acid Blue 281 (NY5, 70.5%), Acid Blue 113 (IN13, 61%), Acid red 266 (NY7, 56%), and 34.5% for Acid red 299 (NY1), compared to the negative control with the heat-denatured enzyme. The biodegradation potential of LsLiP was further suggested by the change of lignin structure based on Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) analyses. Lignin structure was noticeably changed before and after LsLiP treatment, especially in the fingerprint regions (1600 to 1000 cm-1) and 2930 cm-1 corresponding to the stretching vibrations of various groups in lignin. Thus, LsLiP has potential application in both enzyme-based decolorization of synthetic dyes and lignin biodegradation.
- Researchpp 4499-4516Niu, Y., and Xiong, X. (2022). "Investigation on panel material picking technology for furniture in automated raw material warehouses," BioResources 17(3), 4499-4516.AbstractArticlePDF
The integrated development of the global economy has prompted the manufacturing industry of China to enter the era of intelligence, and manufacturing in the furniture manufacturing industry has gradually realized the transformation and upgrading from manual or semi-automation to automation and informatization. The traditional storage mode of receiving materials has been unable to coordinate and match the efficiency of its upstream supply and downstream processing. In order to coordinate production, reduce management costs, and achieve zero inventory, this paper integrates the common needs of the market, enterprises, actual production, and storage conditions. In addition, it designs a technical solution for the collection of sheet materials in furniture enterprises based on the environment foundation of automated three-dimensional warehouses. The research results show that the collation algorithm proposed in this study can reduce the amount of sheet material collated by 152 sheets, improve the pallet utilization rate by up to 21.6%, and increase the storage space utilization rate by up to 22.7%.
- Researchpp 4517-4531Gao, F., Wang, H., Li, F., De, Y., Ma, Y., Jiang, H., Jing, Y., Qu, H., and Li, P. (2022). "Evaluation of lignocellulose degradation and ethanol production via dilute acid and alkali pretreatment of hybrid Pennisetum," BioResources 17(3), 4517-4531.AbstractArticlePDF
Chemically pretreating lignocellulose has been widely used in the production of clean energy. An energy grass called hybrid Pennisetum was pretreated with different H2SO4 and NaOH concentrations to analyse the effects of an acid and alkali pretreatment on the degradation of hybrid Pennisetum lignocellulose. The chemical composition, hydrolyzed sugar yield, and microstructure were determined. The results showed that a NaOH pretreatment retained more cellulose and removed more lignins, while a H2SO4 pretreatment significantly inhibited the removal of lignins and increased hemicellulose degradation. X-ray diffraction analysis indicated that increasing the concentration of NaOH or H2SO4 could intensify the cellulose polymerization; this effect was stronger with NaOH compared to H2SO4. Scanning electron microscopy images showed that the cellulose bundles pretreated with H2SO4 were arranged tightly, while the cellulose bundles pretreated with NaOH were loose. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy exhibited that the ether/ester bond between lignins and carbohydrates was broken by the H2SO4 pretreatment. The NaOH pretreatment increased the number of carbonyl and hydroxyl groups, resulting in more hydrophilic lignins, enabling greater facile degradation. Although the two methods are different in terms of destroying the structure of lignocellulose, the NaOH pretreatment can retain more cellulose, which is beneficial to subsequent ethanol production.
- Researchpp 4532-4558Li, Y., Yao, L., Song, Y., Liu, R., Wu, Y., Chang, S., Yu, X., Zhang, Z., and Chen, C. (2022). "Uplift capacity evaluation of light-framed wood structure’s roof-to-wall connections," BioResources 17(3), 4532-4558.AbstractArticlePDF
The load-displacement curves of six types of roof-to-wall connection joints were obtained through uplift experiments, while the mechanical properties of each type of joint were compared and analyzed, and the applicability of each joint was verified by the Foschi load-displacement curve model simulation. The specimens were made of three kinds of wood (Pinus sylvestris (PS), Spruce-Pine-Fir (SPF), and Douglas fir (DF)) and two different metal connectors (A-type and B-type), and then the monotonic pullout tests were conducted on each specimen. The failure modes of each group of specimens were analyzed, and the characteristic values analysis method was used to analyze and compare the characteristic values of the load-displacement curves of each specimen, including six characteristic values: maximum load, yield load, deformation capacity, energy dissipation capacity, ductility ratio, and initial stiffness. The results showed that the load capacity of TA group (specimens with A-type metal connectors) was much greater than that of TB group (specimens with B-type metal connectors). The specimens made of DF had the best mechanical performance, but the specimens of DF group were prone to brittle failure. Finally, the fitting parameters of the Foschi model applicable to such joints were obtained.
- Researchpp 4559-4567Sefat, K. M., Kurose, T., Yamada, M., Ito, H., and Shibata, S. (2022). "Investigating the characteristics of a natural fiber composite fabricated from 9,9'-bis(aryl)fluorene-modified nanocellulose and bamboo fiber," BioResources 17(3), 4559-4567.AbstractArticlePDF
A composite fabricated from 9,9′-bis(aryl)fluorene-modified nanocellulose (FCF) and bamboo fiber was studied to explore its processing conditions and limitations. The FCF acted as a binding agent, and bamboo fibers were used as structural reinforcement. Two types of FCF were fabricated and studied: hydroxy and epoxy functional groups with FCF. The FCF solution was homogenized and coated on bamboo fiber sheets. These sheets were laminated with FCF by hot-pressing at various temperatures, pressures, and weight fractions. Flexural modulus and strength were determined at each processing condition. Epoxy type FCF composites exhibited superior flexural performance compared to the hydroxy type. The epoxy type showed better homogeneous dispersion, which increased interfacial area between fibers. The optimal processing temperature was 230 °C. It was considered that thermal degradation occurred above 250 °C and chemical reaction between binder and bamboo was not enough below 210 °C. Flexural performance in the composites showed that approximately 10 MPa was structurally better due to increase of contact area among fibers, which was crushed flat by pressure.
- Researchpp 4568-4579Wu, L., Wu, J., Fang, Y., and Liu, X. (2022). "Eco-friendly flame-retardant Xuan paper via layer-by-layer assembly organic/inorganic composite coating on pulp fiber," BioResources 17(3), 4568-4579.AbstractArticlePDF
Positively charged chitosan (CS) and negatively charged montmorillonite (MMT) were layer-by-layer (LBL) assembled on Xuan paper pulp fiber to fabricate an organic/inorganic flame-retardant coating. The Xuan paper achieved a limiting oxygen index (LOI) value of 24.6% when the pulp fiber was treated by 20 bilayers (BLs) of CS/MMT coating, and its vertical flame properties also improved with less after-flame and after-glow times compared to the untreated one. These results demonstrated that the flame retardancy of Xuan paper could be enhanced by this organic/inorganic composite coating. Thermogravimetric (TG) analysis results revealed that LBL assembly of CS/MMT coating on pulp fiber improved the thermal stability at higher temperature and promoted char formation, showing the obvious condensed phase flame retardant action. Scanning electron microscopy results further confirmed that the treated Xuan paper by CS/MMT coating on pulp fiber promoted the char formation and formed the stable covering layer. The ink wetting property of Xuan paper was not influenced through the LBL assembly flame-retardant treatment of the pulp fibers by CS and MMT. This research provides a new approach for flame-retardant Xuan paper without influencing its ink wetting property using the eco-friendly organic/inorganic composite flame-retardant system.
