Volume 17 Issue 3
Latest articles
- Researchpp 4280-4296Gao, Z., and Huang, R. (2022). "Mechanical properties of surface-compressed wood resulting from the compression ratio and density distribution," BioResources 17(3), 4280-4296.AbstractArticlePDF
Surface-compressed wood, with controllable mechanical properties according to the production process, could be utilized in timber products as a substitute for energy-intensive adhesives, concrete, and metals. The surface compression of wood was carried out in an open hot-pressing system at 180 °C with a compressed thickness of 2 to 18 mm. The surface-compressed wood was treated by atmospheric heat treatment or 0.30 MPa pressurized superheated-steam heat treatment at 180 °C for 2 h. This study investigated the mechanical properties of surface-compressed wood, namely, its bending, compression, and hardness properties. The results showed that the maximum density and average density of the compressed layer surpassed 1.10 g/cm3 and 0.80 g/cm3 when the compression ratio was 33%. Moreover, the surface-compressed wood with a sandwich density structure had properties that were comparable to, or even surpassed, raw wood, traditional compressed wood, and some engineered timber products. The specific strength (179 to 203 × 103 m2/s2) of surface-compressed wood was slightly higher than other wood-based materials (65 to 197 × 103 m2/s2). And the contribution of sandwich structure to MOR and MOE increase was positively correlated with wood surface density. The results obtained from this study could help engineers utilize more fast-growing wood and develop new products and wood connectors. This work may contribute toward the substantial use of surface-compressed wood in the building and construction industries with great benefits to the environment.
- Researchpp 4297-4305Bui, V. T., Nguyen, V. A. T., Chu, T. H. T., Dinh, T. T., Do, H. G., and Nguyen, T. D. (2022). "Anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic chemical constituents from the trunks of Berberis wallichiana," BioResources 17(3), 4297-4305.AbstractArticlePDF
 The chemical compositions and biological activities of the Berberis wallichiana trunk were evaluated for the first time. The alkaloid berberine was found as the main constituent of this plant. In the essential oil fraction, safrole was the most abundant component. The isolated 8-oxypalmatine compound exhibited cytotoxic effects on all three cancer cell lines A549 (human lung carcinoma), MDA-MB-231 (human breast carcinoma), and DU145 (human prostate carcinoma), while berberine was the most active to DU145 cells (IC50 of 4.99 μM). This alkaloid compound also potently inhibited the production of nitric oxide with IC50 at 0.017 μM. These findings suggested that the trunks of B. wallichiana might be a good source of bioactive compounds.
The chemical compositions and biological activities of the Berberis wallichiana trunk were evaluated for the first time. The alkaloid berberine was found as the main constituent of this plant. In the essential oil fraction, safrole was the most abundant component. The isolated 8-oxypalmatine compound exhibited cytotoxic effects on all three cancer cell lines A549 (human lung carcinoma), MDA-MB-231 (human breast carcinoma), and DU145 (human prostate carcinoma), while berberine was the most active to DU145 cells (IC50 of 4.99 μM). This alkaloid compound also potently inhibited the production of nitric oxide with IC50 at 0.017 μM. These findings suggested that the trunks of B. wallichiana might be a good source of bioactive compounds. - Researchpp 4306-4322Chen, Q., Wei, L., Lai, Y., and Liu, Y. (2022). "Preparation and characterization of tea polyphenols-chitosan-based nanoparticles and their application in starch films," BioResources 17(3), 4306-4322.AbstractArticlePDF
Green composite starch films were prepared using tea polyphenols-chitosan-based nanoparticles as active agent and nanocellulose as strength agent, which showed good mechanical and antioxidant activities and is a candidate for food packaging in this work. Here, chitosan-based nanoparticles containing tea polyphenols (CNTP) were prepared by the ionic gel method. The best utilization of tea polyphenols could be achieved when the mass ratio of tea polyphenols to sodium tripolyphosphate was 3:1, the concentration of tea polyphenols was 0.01 g/mL, and the pH of chitosan solution was 4. Uniform and stable CNTP with a particle size of approximately 200 nm was prepared. CNTP release rates were 45.9% after 6 h, showing the ability to release slowly. Using starch as the substrate, nanocellulose as the enhancer, and tea polyphenols as the antioxidant and antibacterial agent, an active film was prepared that demonstrated improved transparency, mechanical properties, and antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Its transmittance reached 83.9%, and the tensile strength was 33.4 MPa. The scavenging efficiency of 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) by the composite film was 42%, and the OD value of the composite film was 0.9348. The results showed that CNTP can prolong the release period and activity of tea polyphenols, and the composite film with CNTP had antibacterial and antioxidant activities to prolong the shelf life of food.
- Researchpp 4323-4330Majeed, Z., Ajab, Z., Mansoor, N., Alqahtani, Y., Mahnashi, M., Alyami, B., and Alqarni, A. (2022). "Anaerobic biodegradation of urea cross-linked starch: Effect of lignin on tensile properties," BioResources 17(3), 4323-4330.AbstractArticlePDF
Lignin was used as a natural filler to improve the recalcitrance of environmentally friendly biocomposites made from starch. The tensile properties of lignin-starch biocomposites prepared by lignin reinforcing of urea cross-linked starch (UcS) were investigated in this study. The amount of lignin loaded into UcS was from 5 to 20%. These various compositions were buried in a microcosm of anaerobic soil. After 7 days of burial, biodegraded biocomposites were tested for changes in tensile characteristics. Changes in biodegradation were measured by comparing them to pristine samples, which were utilised as a benchmark for estimating. Through reinforcing polymeric starch in UcS, lignin was discovered to slow down the rate of loss in tensile characteristics of composites. With increasing lignin loadings from 5 to 20%, biodegraded biocomposites showed a constant reduction in elongation at break, Young’s modulus, and tensile strength. As a result, the biodegraded biocomposites’ metrics exhibited a substantially slower decrease than the control biodegraded film. The reduction in tensile properties of biodegraded biocomposites was explained by a significant difference (p < 0.05) using a paired t-test. This study found that lignin increased the strength of UcS and reduced the loss of tensile characteristics, probably as a result of soil microorganisms’ biodegradation activity being inhibited.
- Researchpp 4331-4346Huang, X., Ding, Z., Cai, Z., Wang, T., Yang, X., and Shang, S. (2022). "Preparation and characterization of hydrogels based on dehydroabietyl polyoxyethylene glycidyl ether grafted hydroxyethyl chitosans and their capability for loading and controlled release of chloramphenicol," BioResources 17(3), 4331-4346.AbstractArticlePDF
Dehydroabietol polyoxyethylene(10) ether (DHA(EO)10H) was reacted with epichlorohydrin (ECH) using BF3 as catalyst and transformed into DHA(EO)10H-ECH, then dehydrochlorinated in the presence of sodium hydroxide and converted into dehydroabietyl polyoxyethylene(10) glycidyl ether (DHA(EO)10GE). Hydroxyethyl chitosan (HEC) was modified with DHA(EO)10GE, and a series of different DHA(EO)10GE-grafted HECs (DHA(EO)10GE-g-HECs) were prepared. Finally, the hydrogels based on DHA(EO)10GE-g-HECs were obtained through the reaction between genipin (GE) and DHA(EO)10GE-g-HECs. Effects of the grafting degree (DG) of DHA(EO)10GE and the dosage of GE on the gelation ability of mixed solution composed of DHA(EO)10GE-g-HECs and GE were investigated, and the behaviors of DHA(EO)10GE-g-HEC/GE hydrogels as carriers for loading chloramphenicol (CAP) were studied. It was found that the gelling time of the DHA(EO)10GE-g-HEC with high DG was longer than that with low DG, and a higher GE dosage could improve the capability of DHA(EO)10GE-g-HEC to form hydrogels. The relation between the cumulative release rate of CAP, which was loaded in DHA(EO)10GE-g-HEC/GE gel, and the release times in artificial intestinal fluid could be well described by Boltzmann function. Increasing the DG or decreasing the GE dosage could improve the final cumulative release.
- Researchpp 4347-4359Zhu, Y., Zhang, J., Zhao, P., Wang, D., Shi, Z., Yang, J., and Yang, H. (2022). "Fabrication of cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) in choline chloride-citric acid (ChCl-CA) solvent to lodge antimicrobial activity," BioResources 17(3), 4347-4359.AbstractArticlePDF
Surface-modified cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) have gained substantial interest in industry. The renewability and abundance of the raw material to prepare CNCs make them a promising green material. In this study, two types of CNCs were prepared by sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and stepwise H2SO4 and choline chloride-citric acid (ChCl-CA) deep eutectic solvent-like (DES) treatments. The DES treatment led to esterification and further degradation of the CNCs. The obtained nanoparticles were distributed in size range of 50 nm to 500 nm and 20 nm to 70 nm for the H2SO4 and stepwise treatments, respectively. The effects of the nanoparticles on the mechanical properties, thermal stability, and antibacterial activity of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVOH) were determined using a universal mechanical testing machine, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and the agar diffusion method. The results indicated that nanoparticles had good compatibility in PVOH at a concentration below 10%. The CNCs had greater effect on the mechanical properties and the thermal stability of films than the esterified CNCs. However, the CA modified CNCs showed more favorable antibacterial activity than the CNCs from H2SO4 treatment. Taking the mechanical properties, the thermal stability, and the antibacterial activity into consideration, 5% was selected as a suitable concentration for composite film preparation.
- Researchpp 4360-4377Alfaifi, T. (2022). "Evaluation and assessment of metal(loids) adsorptions by Cenchrus ciliaris L. in a cement contaminated area," BioResources 17(3), 4360-4377.AbstractArticlePDF
The adsorbed amounts of Ni, Cu, Zn, and As metal(loids) were evaluated on Cenchrus ciliaris L. Results showed that C. ciliaris grass was able to collect these elements from soils in an active way. Several factors, such as the concentrations of elements in soils, pH, sunlight intensity, and temperature, contributed to enhance the adsorption of these toxic elements. The analysis for arsenic and phosphorus was conducted by Flameless Atomic Absorption Spectrometry and ICP-AES. It was found that the C. ciliaris plant managed to absorb phosphorus and keep the arsenic out of the root; thus, a selective behavior of absorption of elements by plants in contaminated sites was observed.
- Researchpp 4378-4394Bakri, M. M., Al-Rajhi, A. M. H., Abada, E., Salem, O. M. A., Shater, A-R., Mahmoud, M. S., and Abdel Ghany, T. M. (2022). "Mycostimulator of chitinolytic activity: Thermodynamic studies and its activity against human and food-borne microbial pathogens," BioResources 17(3), 4378-4394.AbstractArticlePDF
Chitinolytic activity and antibiosis are gaining prominence in various biotechnological fields. Dead fungal biomass (DFB) was used as a mycostimulator of chitinase production and antibiosis by Aspergillus fumigatus. The presence of DFB stimulated the synthesis of various secondary metabolites by A. fumigatus that were detected by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis such as 6,8-Di-C-á-glucosylluteolin; bistrimethylsilyl N-acetyl eicosasphinga-4,11-dienine; curan-17-oic acid, 19,20-dihydroxy-, methyl ester, (19S)-; spiro[5à-androstane-3,2′-thiazolidine; retinal; Androsta-1,4-dien-3-one; Panaxydol; Costunolide; Cyclo-(glycyl-L-tyrosyl); and 2-amino ethane thiolsulfuric acid. Chitinase activity was 42.9 Units/mL with the presence DFB, where it was 10.3 Units/mL without DFB. The maximum activity of chitinase was observed at 1.5 g of dead fungal biomass, at 4 h, 50 °C and pH 6. Thermodynamic properties showed ∆H° and ∆S° values of 126 KJ mol-1 and 432 J mol-1 K-1, respectively, indicating an endothermic reaction up to 60 °C. Deviation in ∆G° values confirmed that the reaction at 10 to 20 °C is a nonspontaneous reaction, and at 30 to 60 °C the reaction has a spontaneous nature. DFB encouraged the antimicrobial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Aspergillus fumigatus, Mucor circinelloides, and Candida albicans with 2.3, 2.2, 2.8, 0.8, 0.7, and 2.2 mm inhibition zones, respectively.
- Researchpp 4395-4409Bin, Y., Li, S., Jiao, F., Zhong, S., and Yuan, Y. (2022). "Comparative effects of pretreatment on composition and structure of corn stalk for biocomposites," BioResources 17(3), 4395-4409.AbstractArticlePDF
The outer surface of corn stalk (CS) plays a key role in the interfacial compatibility of non-wood-based panel products. To improve the bonding performance of the stalk surface, changes to the outer surface before and after four pretreatments (oxalic acid, oxalic acid + ultrasound, NaOH, NaOH + ultrasound) were investigated. Changes in the chemical composition, surface elements, aggregation structure, and microstructure of CS before and after pretreatment were analyzed. The results revealed that the wax layer, benzene–alcohol extract, and ash content of the outer surface of CS were decreased under different pretreatment conditions. The degree of reduction decreased in the order of NaOH + ultrasound > oxalic acid + ultrasound > NaOH > oxalic acid. The crystallinity of CS was obvious after pretreatment, and it increased in the order of oxalic acid + ultrasound > oxalic acid > NaOH + ultrasound > NaOH. Considering the properties of CS after pretreatment and the lignin activation modification of the CS surface, the optimal pretreatment conditions of CS were determined as oxalic acid + ultrasound, i.e., 5% oxalic acid and ultrasonication at 50 °C for 1 h.
- Researchpp 4410-4431Wang, D., Wang, X., Wang, Y., and Wang, X. (2022). "Selective adsorption of metal ions on Salix psammophila fibre activated carbon," BioResources 17(3), 4410-4431.AbstractArticlePDF
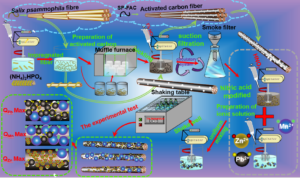
As an adsorbent of metal ions, activated carbon is often used to purify sewage. However, activated carbon fibres typically show similar adsorption capacity for different metal ions. Salix psammophila fibre (Spsf) was used as raw material to prepare activated carbon fibres (SP-FAC). This was modified with nitric acid (HNO3) to obtain HNO3-SP-FAC (FACHNO3). At 65 wt% concentration of HNO3, the impregnation ratio was 1:35 during 12 h, at 100 °C drying temperature, and the adsorption effect of FACHNO3 on Pb(II) was the best. At CHNO3 = 75 wt%, the impregnation ratio was 1:25. After an impregnation time of 36 h at the same drying temperature, the effect of FACHNO3 on Mn(II) was the best. At CHNO3 = 55 wt%, the impregnation ratio was 1:35, impregnation time was 36 h at 120 °C drying temperature, and the adsorption effect of FACHNO3 on Zn(II) was the best. These results indicate the existence of a close relationship between the pore structure of activated carbon fibres and the adsorption capacity of metal ions, and that the control variables changed the pore structure of activated carbon fibres so that it can achieve a competitive adsorption effect for different ions.
