Volume 18 Issue 1
Latest articles
- Researchpp 1545-1553Wang, C., and Zhou, Z. (2023). "Optical properties and lampshade design applications of PLA 3D printing materials," BioResources 18(1), 1545-1553.AbstractArticlePDF
The optical properties of PLA 3D printing materials and their influencing factors were considered relative to the manufacture of personalized 3D printing PLA lampshades. Rectangular PLA 3D printing specimens were designed, and their light transmittance and haze were analyzed in terms of color, layer height, and wall thickness using UV spectrophotometer. Using the preferred molding parameters for 3D printing of PLA lampshade, three lampshades were designed and completed via 3D printing model fabrication. The results revealed that the milky white specimen had stronger light scattering and better luminous uniformity than the colorless specimen, making it more suitable for the manufacturing of 3D printing lampshades. Among the 3D printing molding parameters, the effect of layer height on the light transmittance and haze of the specimen was not significant. Considering the factors such as time and cost, a 0.3 mm layer height was selected as the preferred molding parameter. The effect of wall thickness on the light transmittance and haze of the specimen was significant. As the wall thickness of the specimen increased, the light transmittance of the specimen decreased, and the haze increased. Considering the factors such as optical performance, time, and cost, a 0.8 mm wall thickness was selected as the preferred molding parameter.
- Researchpp 1554-1576Qanash, H., Alotaibi, K., Aldarhami, A., Bazaid, A. S., Ganash, M., Saeedi, N. H., and Abdel Ghany, T. M. (2023). "Effectiveness of oil-based nanoemulsions with molecular docking of its antimicrobial potential," BioResources 18(1), 1554-1576.AbstractArticlePDF
The biological properties of plant oils are improved by their conversion to nanoemulsions (NEs). This study evaluated the antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-hemolytic efficacy of coconut and salad rocket oils and their NEs. The result of the gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy analysis of the oils showed varied constituents such as palmitic acid, trimethylsilyl ester; 2,3-bis(acetyloxy)propyl laurate in salad rocket oil, 2-lauro-1,3-didecoin, n-butyl laurate; laurin, tri-; laurin in coconut oil. NEs diameter of salad rocket and coconut oils was 24.6 and 29.2 nm, respectively. More inhibitory activity of NEs compared with non-NEs form against Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhi, Candida albicans, and Aspergillus flavus was detected. Coconut oil and its NEs caused 14.3% (anti-hemolysis 85.7%) and 22% hemolysis (anti-hemolysis 78%), respectively. Salad rocket oil and its NEs caused hemolysis 3.4% and 20.9%, respectively at 1000 µg/mL. Antioxidant activity of salad rocket and coconut oil reflected more IC50 (39.3 and 109.4 µg/mL) than its NEs (35.8 and 80.5 µg/mL), respectively. Molecular docking of trimethylsilyl ester and 2-lauro-1,3-didecoin against S. aureus (PDB=7BGE) and C. albicans protein (PDB=3DRA) revealed optimal binding mode that had the most energy interaction with the binding sites.
- Researchpp 1577-1589Yang, G. U., Purusatama, B. D., Kim, J. H., Prasetia, D., Savero, A. M., and Kim, N. H. (2023). "Proximate analysis of bamboo culm and wood carbonized at low temperatures: A comparative study," BioResources 18(1), 1577-1589.AbstractArticlePDF
To obtain basic data for further use of bamboo culms and wood as eco-friendly bioenergy resources, the proximate analysis of Dendrocalamus giganteus, D. asper, Bambusa vulgaris, Gigantochloa apus, Phyllostachys pubescens, Pinus densiflora, and Quercus variabilis carbonized at 200 to 320 °C at 40 °C intervals was undertaken. Proximate analysis of moisture content, ash content, volatile matter, and fixed carbon content was performed according to JIS M 8812 (2004) with 60-mesh carbonized powder. Carbonized bamboo showed higher ash and volatile content than carbonized wood, whereas carbonized wood had a higher fixed carbon content than carbonized bamboo. At all temperatures, giant bamboo had the highest ash content. In bamboo and wood, the ash and fixed carbon contents increased with increasing carbonization temperature, whereas the volatile substances decreased.
- Researchpp 1590-1601Yang, L., Peng, H., He, H., Liu, L., Fu, G., Liu, Y., and Wan, Y. (2023). "Interaction mechanism between cellobiose and imidazolium halide-based ionic liquids," BioResources 18(1), 1590-1601.AbstractArticlePDF
Ionic liquids (ILs) are excellent solvents for cellulose, but the dissolution mechanism is not deeply understood. In the present study, cellobiose was used as a model of cellulose, and the imidazolium halide-based ILs with the same cation of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium (Bmim+) including BmimCl, BmimBr, and BmimI were used as solvents. The interaction mechanism between the ILs and cellobiose was analyzed by carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance (13C NMR). The results showed that the strength of hydrogen bonds formed between the hydroxyl groups of cellobiose and the ILs was greatly affected by the position of hydroxyl groups and the electro-negativity and size of the anions. Compared with the secondary alcoholic hydroxyl groups, the primary alcoholic hydroxyl groups (C6–OH and C12–OH) on the glucopyranose rings of cellobiose more easily formed hydrogen bonds with the ILs. The strength of hydrogen bonds formed between the protons on the imidazolium cation and cellobiose varied with the positions of the protons. The formation of hydrogen bonds between the halogen anions and cellobiose was the main reason for the dissolution of cellobiose in the ILs. The ability of the three ILs to form hydrogen bonds with cellobiose followed the order: BmimCl > BmimBr > BmimI.
- Researchpp 1602-1615Wen, R., Fu, S., and Zhang, H. (2023). "Synergy of modified lignin and p-coumaric acid for improving the function of sun-protection in sunscreen," BioResources 18(1), 1602-1615.AbstractArticlePDF
Lignin is a potential natural sunlight protector because its benzene derivative structure can absorb UV rays. Pure lignin is not good enough for sunblock because lignin is not fully dispersed in cream, and the range of absorbed UV rays is not broad. In this work, lignin was modified with polybutyl acrylate (PBA) and self-assembled into microspheres (L-PBA-NPs) to enhance its compatibility in cream, and it was blended with p-coumaric acid (CA) to extend its light absorbance. The hydrophobicity of grafted PBA on lignin and the microsphere of the modified lignin provided an ability to disperse in oily pure cream. To improve the sun protection factor (SPF) of the blended lignin-based sunscreen, CA with different UV absorbing ability was mixed inside the modified lignin to form CA@L-PBA-NPs. When CA and L-PBA-NPs (1:1) were added in cream with 5%, the SPF of the blended lignin sunscreen reached 18.8. After irradiation of the CA@L-PBA-NPs sunscreen under UV for 3 h, the SPF of the blended lignin-based sunscreen increased slightly because of more conjugated structures produced in lignin. The CA@L-PBA-NPs in sunscreens have great potential as a green ingredient to substitute for the small-molecule sunscreen active ingredients in commercial sunscreen products.
- Researchpp 1616-1636Zhou, C., Wang, Q., Kaner, J., and Lv, Y. (2023). "Wooden door preferences based on lifestyle theory and consumer behaviour theory," BioResources 18(1), 1616-1636.AbstractArticlePDF
This paper analyses users with different lifestyles and consumer behaviour, and then segments wooden door users with different consumer preferences, to inspire wooden door companies in their product design and further research on wooden doors. In this paper, a wooden door user research questionnaire was created based on Lifestyle Theory and Consumer Behaviour Theory, and data collection was completed at Nanjing Forestry University. The collected data were analysed using cluster analysis, factor analysis, cross-over analysis, and other analysis methods. The Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) was used to simplify the analysis model and process the data, and finally the wooden door users were divided into four categories. The categories were trendy home users, budget-conscious sensible users, basic needs users, and impulsive enjoyable users. Male users were found to be more likely to be “trendy home users” and “impulsive enjoyable users,” while female users were more likely to be “budget-conscious sensible users” and “trendy home users.” For the number of users, the “trendy home users” were the most numerous, followed by the “budget-conscious sensible users.” The age of wooden door users in this study was mainly distributed between 21 to 30 years old, of which “freelancers” accounted for the highest percentage.
- Researchpp 1637-1652Hwang, S., Chung, H., Lee, T., Ahn, K., Pang, S., Kim, J., Bang, J., Jung, M., Oh, J., Kwak, H., and Yeo, H. (2023). "Dimensional behavior of nail-laminated timber-concrete composite caused by changes in ambient air, and correlation among temperature, relative humidity, and strain," BioResources 18(1), 1637-1652.AbstractArticlePDF
A timber-concrete composite (TCC) slab composed of nail-laminated timber (NLT) and topping concrete (TC) was developed for flooring applications. The NLT was laminated alternately with lumber and plywood. To investigate the nonstructural dimensional behavior of the TCC slab, the temperature, relative humidity (RH), and dimensional changes of the slab exposed to outdoor air were monitored for 205 days. Temperature change was transmitted directly to both components, and RH change was transmitted gradually to the NLT. Concrete pouring caused a sharp increase in NLT width, which was the laminating direction of the nails. This resulted from swelling of the wood owing to the moisture in the concrete mixture and loosening of the nail lamination. The member composition for the nail-laminating system, fastener type, and concrete volume help to secure the dimensional stability of the NLT. Cracks in the TC caused width deformation, which was recovered by drying shrinkage of the TC. Correlation analysis among temperature, RH, and strain indicated that dimensional changes in NLT correlated strongly with RH, while those in TC correlated strongly with temperature. The correlation between longitudinal strain in the TC and strain in the three directions of the NLT was attributed to the notches designed for mechanical connection.
- Researchpp 1653-1663Johnsrude, L. M., Scheffel, A. J., Allen, B. L., and Wettstein, S. G. (2023). "Composition analysis of canola and intermediate wheatgrass biomass and the effects of extraction," BioResources 18(1), 1653-1663.AbstractArticlePDF
Knowing the composition of biomass is critical for determining accurate yields of renewable chemicals and fuels; however, nonstructural components can affect the results of standard composition procedures, leading to inaccurate reactant amounts. To remove these nonstructural components, solvent extractions can be done, but the impact on composition values has not been well-reported. For this study, compositional analysis was performed on as-received canola (Brassica napus) and intermediate wheatgrass (Thinopyrum intermedium), as well as ethanol, water, and water/ethanol extracted biomasses. Water/ethanol extraction of the intermediate wheatgrass resulted in significantly lower xylose and both acid soluble and insoluble lignin amounts when compared to the as-received analysis. Since sugar was removed during the extractions, it is recommended to use the as-received composition values for glucuronoarabinoxylans; however, the extractives may interfere with the lignin analysis and therefore, the extracted lignin values are likely more reflective of the composition.
- Researchpp 1664-1683Chu, C. J., Hafid, H. S., Omar, F. N., Hairuddin, A. A., Mokhtar, M. N., Samsu Baharuddin, A., and Wakisaka, M. (2023). "Improvement of residual oil recovery from oil palm biomass using high pressure water steam system for biodiesel production," BioResources 18(1), 1664-1683.AbstractArticlePDF
Various applications of oil palm empty fruit bunches (OPEFB) would be hindered by the presence of residual oil. This study aimed to remove and recover the residual oil from OPEFB using an integrated system, high pressure water spray system (HPWSS). The performance of the HPWSS was evaluated at different temperatures and water pressures, and the residual oil collected was recovered through water shaking method and tested for biodiesel application. A maximum of 84.9% of residual oil was removed by HPWSS at 60 °C and 8960 kPa and the highest residual oil recovery of 58.8% was observed at 95 °C, using power shaking 5 and 90% of dilution. The following ranges of deterioration of bleachability index (DOBI), free fatty acid (FFA), and peroxide value (PV) for the residual oil were 1.21 to 2.67, 7.11 to 10.4%, and 4.85 to 7.56, respectively. Biodiesel with different blends of recovered residual oil (5%, 10%, and 15%) showed lower values (9.87, 9.57, and 9.56 Nm) of brake torque as compared with diesel (10.89 Nm). Overall, this study showed the potential of HPWSS to obtain an acceptable quality of residual oil from OPEFB to be used in any value-added product generation.
- Researchpp 1684-1698Bamba, M., Assanvo, E. F., Kouassi, E. K. A., Soro, D., Ouattara, L. Y., Yao, K. B., Drogui, A. P., and Tyagi, D. R. (2023). "Preparation and characterization of cellulose triacetate from cocoa pod husk," BioResources 18(1), 1684-1698.AbstractArticlePDF
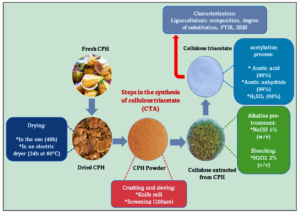
The valorisation of agricultural residues into a high value-added product is necessary to respond to the global environmental concerns caused by the pollution of agricultural waste. The objective of this study was to shed light on a new value-added usage of cocoa pod husk (CPH) for the synthesis of cellulose triacetate (CTA). Alkaline treatment with sodium hydroxide (5 wt%) followed by bleaching process with (2 wt%) hydrogen peroxide was found effective for the extraction of cellulose from CPH. The percentage of cellulose obtained was 80.5% with a yield of 54%. The CTA was synthesised by a explore new way acetylation reaction in the presence of acetic acid, acetic anhydride, and sulphuric acid. The CTA obtained had a degree of substitution of 2.87 and a percentage of acetylated group of 43.8%, as determined by titration. The result of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy showed the appearance of the stretching of the ester and the acetyl groups, indicating the formation of CTA. X-ray diffraction showed that the crystallinity index of CPH cellulose was 38.4%, while indicating the semi-crystalline nature of CTA produced. Scanning electron microscopy confirmed a change in the morphology of CTA after acetylation. X-ray energy dispersive analysis showed that the CTA was mainly composed of carbon and oxygen.
